Abstract
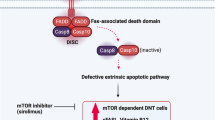
The autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome (ALPS) or Canale–Smith syndrome is a recently described clinical entity consisting of chronic, non-malignant lymphadenopathy and hepatosplenomegaly together with hypergammaglobulinemia, positive autoantibodies and/or overt autoimmune diseases. It is caused by a genetic defect in the mechanism of programmed cell death (apoptosis) and is characterized by the presence of double-negative (TCR α/β CD4− CD8−) T lymphocytes (DNT). Although well known in pediatric patients, ALPS is an unusual diagnosis in adults. The oldest reported patient was aged 54. We describe another two adult patients in whom a presenting autoimmune disease led to the diagnosis of ALPS.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALPS:
-
Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome
- DNT:
-
Double-negative lymphocytes
References
Straus SE, Sneller M, Lenardo MJ, Puck J, Strober W (1999) An inherited disorder of lymphocyte apoptosis: The autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome. Ann Intern Med 130:591–601
Drappa J, Vaishaw AK, Sullivan KE, Chu JL, Elkon KB (1996) Fas gene mutations in the Canale–Smith syndrome an inherited lymphoproliferative disorder associated with autoimmunity. N Engl J Med 335:1643–1649
Sneller MC, Straus SE, Jaffe ES et al. (1992) A novel lymphoproliferative/autoimmune syndrome resembling murine lpr/gld disease. J Clin Invest 90:334–341
Straus SE, Jaffe ES, Puck JM et al. (2001) The development of lymphomas in families with autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome with germline Fas mutations and defective lymphocyte apoptosis. Blood 98:194–200
Jackson CE, Puck JM (1999) Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome, a disorder of apoptosis. Curr Opin Pediatr 11:521–527
Rieux Laucat F, Blachere S, Danielan S et al. (1999) Lymphoproliferative syndrome with autoimmunity: a possible genetic basis for dominant expression of the clinical manifestations. Blood 94:2575–2582
Infante AJ, Britton HA, DeNapoliu T et al. (1998) The clinical spectrum in large kindred with autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome caused by a Fas mutation that impairs lymphocyte apoptosis. J Pediatr 133:629–633
Straus SE, Jaffe ES, Puck JM et al. (2001) The development of lymphomas in families with autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome with germline Fas mutations and defective lymphocyte apoptosis. Blood 98:194–200
Gronbaek K, Straten PT, Ralfkiaer E et al. (1998) Somatic Fas mutations in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: association with extranodal disease and autoimmuníty. Blood 92:3018–3024
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deutsch, M., Tsopanou, E. & Dourakis, S.P. The autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome (Canale–Smith) in adulthood. Clin Rheumatol 23, 43–44 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-003-0830-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-003-0830-2