Abstract
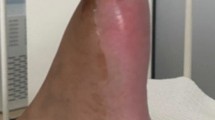
Arthritis is reported in one-third of cases with Kawasaki syndrome. It may have an early or a late onset form. We present a 15-month-old-girl who had been referred with complaints of pain and swelling in her left shoulder. Physical examination revealed bulbar conjunctival injection, erythematous lips and pharynx, strawberry tongue, erythematous rash, edema and erythema of the left shoulder, left knee, right elbow and right wrist, and moderate distress in the left shoulder and left hip. She was diagnosed with Kawasaki syndrome, and intravenous immunoglobulin infusion (IVIG) 2 g/kg and aspirin (100 mg/kg/day) were instituted. The patient had two additional episodes of arthritis involving the hip joint on the 8th day, and the shoulder and metacarpophalangeal (MCP) and interphalangeal (IP) joints of her right hand on the 15th day. Turbid material was aspirated in both instances; Gram and Wright’s staining of this material showed many leukocytes but no bacteria. A second dose of IVIG (1 g/kg) was given. At the end of the third week all extremities were painless, with a normal range of motion. Arthritis in our patient was the presenting sign, having a ‘septic arthritis mimicking’ and ‘biphasic’ pattern. Although the patient presented with severe and recurrent arthritis, which is significantly correlated with severe multisystem disease and the presence or development of coronary artery aneurysm, the response to IVIG was excellent.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- KS:
-
Kawasaki syndrome
- MCP:
-
Metacarpophalangeal
- PIP:
-
Proximal interphalangeal
References
Leung DY, Schlievert P, Meissner HC (1998) The immunopathogenesis and management of Kawasaki syndrome. Arthritis Rheum 41:1538–1547
Melish ME, Hotez P (1998) Kawasaki syndrome. In: Katz SL, Gershon AA, Hotez PJ (eds) Krugman’s infectious diseases of children, 10th edn. Mosby-Year Book, St. Louis,pp 236–245
Calvo Rey C, Cron RQ, Sherry DD (1993) Kawasaki disease; complications and clinical course. A propos of 38 cases. Ann Esp Pediatr 39:423–427
Yanagawa H, Nakamura Y, Yashiro M et al. (1988) A nation-wide incidence of Kawasaki disease in 1985–1986 in Japan. J Infect Dis 158:1296–1301
Dajani AS, Taubert KA, Gerber MA et al. (1993) Diagnosis and therapy of Kawasaki disease in children. Circulation 87:1776–1780
Marchette NJ, Melish ME, Hicks R, Kihara S, Sam E, Ching D (1990) Epstein–Barr virus and herpes virus infections in Kawasaki syndrome. J Infect Dis 161:680–684
Melish ME, Hicks RV (1986) Kawasaki syndrome. Pediatr Clin North Am 33:1151–1175
Bowler J, Drvaric D, Roberts J, Burke SW (1986) Kawasaki syndrome presenting as pyarthrosis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg 68:467–468
Koren G, Lavi S, Rose V, Rowe R (1986) Kawasaki disease: review of risk factors for coronary aneurysms. J Pediatr 108:388–392
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duzova, A., Topaloglu, R., Keskin, M. et al. An unusual pattern of arthritis in a child with Kawasaki syndrome. Clin Rheumatol 23, 73–75 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-003-0828-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-003-0828-9