Abstract
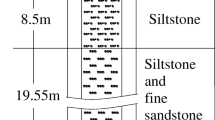
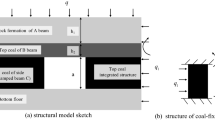
To propose a support stiffness based method for improving the stability of coal wall, static stiffness of the support and fracture development of the coal wall are monitored during retraction period of a panel in the second coal mine of Zhaogu coalfield. It is revealed that the range of support stiffness falls between 50 and 450 MN/m. In face length direction, support stiffness is characterized by three zones. It is small in the middle section while large magnitude is observed at two end areas. Fracture development of the coal wall is detected by geological radar, which reveal that fracture development is high in the middle section, and a decreasing trend is experienced from the middle to side areas. Such results imply face stability is strongly influenced by support stiffness. Based on such understanding, mechanical model for supporting system of the longwall face is established by considering the stiffness. The results demonstrate that roof pressure transferred onto the coal wall is negatively related to support stiffness. Then, in situ monitored relationship between support stiffness and fracture development of the coal wall is reasonably explained. Moreover, numerical modeling is carried out to validate the influence of support stiffness on face stability, and the results show the minimum support stiffness is proposed to be 100 MN/m for the target panel. The study provides a new method for selecting support stiffness in longwall panel with similar geological conditions.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, and further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
This research does not involve human participants and/or animals.
References
Aguado MBD, González C (2009) Influence of the stress state in a coal bump-prone deep conal bed: a case study. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 46(2):333–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2008.07.005
Azerani T, Zhao J (2014) A microstructure-based model to characterize micromechanical parameters controlling compressive and tensile failure in crystallized rock. Rock Mech Rock Eng. 47(2):435–452. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-013-0402-y
Bai QS, Tu SH, Zhang XG, Zhang C, Yuan Y (2013) Numerical modeling on brittle failure of coal wall in longwall face-a case study. Arab J Geosci 7(12):5067–5080. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-1181-1
Bai QS, Tu SH, Li ZX, Tu HS (2015) Theoretical analysis on the deformation characteristics of coal wall in a longwall top coal caving face. Int J Min Sci Technol 25(2):199–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2015.02.006
Chang JC, Xie GX, Zhang XH (2015) Analysis of coal face spalling mechanism of fully mechanized top-coal caving face with great mining height in the extra-thick coal seam. Rock Soil Mech 36(3):803–808. https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2015.03.026
Christopher M (2016) Coal bursts in the deep longwall mines of the United States. Int J Coal Sci Technol 3(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40789-016-0102-9
Fabjan T, Ivars DM, Vukadin V (2015) Numerical simulation of intact rock behaviour via the continuum and voronoi tessellation models: a sensitivity analysis. Acta Geotech Slov 12(2):4–23
Gao F, Stead D, Kang H (2014a) Simulation of roof shear failure in coal mine roadways using an innovative UDEC trigon approach. Comput Geotech 61(3):33–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2014.04.009
Gao F, Stead D, Kang H, Wu Y (2014b) Discrete element modelling of deformation and damage of a roadway driven along an unstable goaf-a case study. Int J Coal Geol 127(7):100–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2014.02.010
Gao FQ, Stead D (2014) The application of a modified Voronoi logic to brittle fracture modelling at the laboratory and field scale. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 68(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.02.003
He MC, Sousa LR, Miranda T, Zhu GL (2015) Rock burst laboratory tests database-application of data mining technique. Eng Geol 185(5):116–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.12.008
Iannacchione AT, Tadolini SC (2016) Occurrence, predication, and control of coal burst events in the U.S. Int J Min Sci Technol 26(1):39–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2015.11.008
ITASCA (2014) Consulting Group I. UDEC, Universal Distinct Element Code, 4th edn. Minneapolis, USA, pp 130–157
Kong DZ, Cheng ZB, Zheng SS (2019) Study on the failure mechanism and stability control measures in a large-cutting-height coal mining face with a deep-buried seam. Bull Eng Geol Environ 78(8):6143–6157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01523-0
Kong DZ, Wu GY, Ma ZQ, Yang L (2017a) Development and application of a physical model for longwall coal face failure simulation. Int J Min Miner Eng 8(2):131–143. https://doi.org/10.1504/ijmme.2017.084204
Kong DZ, Yang SL, Gao L, Ma ZQ (2017b) Determination of support capacity based on coal face stability control. J China Coal Soc 42(3):590–596. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2016.1296
Li XP, Kang TH, Yang YK, Li H, Li CY, Wu LL, Du MZ (2015) Analysis of coal face slip risk and caving depth based on bishop method. J China Coal Soc 40(7):1498–1504. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2014.0912
Li XH, Ju MH, Yao QL, Zhou J, Chong ZH (2016) Numerical investigation of the effect of the location of critical rock block fracture on crack evolution in a gob-side filling wall. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49(3):1041–1058. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-015-0783-1
Lisjak A, Grasselli G (2014) A review of discrete modeling techniques for fracturing processes in discontinuous rock masses. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 6(4):301–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2013.12.007
Liu CY, Qian MG, Cao SG (1998) Study on stiffness of support and surrounding rock system of mining face. Mine Pressure and Roof Management 1998(3):3–5+81. http://kns.cnki.net/kns8/defaultresult/index
Liu XJ, Luan HB (2015) A brief analysis of the circumstances of the current coal industry and its trends in China. Int J Min Miner Eng 6(1):87–96. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJMME.2015.067953
Long YQ, Bao SH, Yuan S (2018) Structural mechanics I. Higher education press, Beijing
Mazaira A, Konicek P (2015) Intense rock burst impacts in deep underground construction and their prevention. Can Geotech J 52(8):1426–1439. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2014-0359
Medhurst TP, Reed K (2005) Ground response curves for longwall support assessment. Trans Inst Min Metall A Min Tech 114(2):81–88. https://doi.org/10.1179/037178405x44575
Morissette P, Hadjigeorgiou J (2019) Ground support design for dynamic loading conditions: a quantitative data-driven approach based on rock burst case studies. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 11(5):909–919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2019.03.002
Nicksiar M, Martin CD (2014) Factors affecting crack initiation in low porosity crystalline rocks. Rock Mech Rock Eng 47(4):1165–1181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-013-0451-2
Pang YH, Wang GF (2017) Hydraulic support protecting board analysis based on coal face spalling “tensile cracking-sliding” mechanical model. J China Coal Soc 42(8):1941–1950. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2016.1696
Peng SS, Chiang HS (1984) Longwall mining. John Wiley and Sons Inc, New York
Qian MG, He FL, Wang ZT (1994) Again on the theory of stope mine pressure. J China Univ Min Technol 23(3):1–9
Ren HW, Zhang DS, Gong SX, Zhou K, Xi CY, He M, Li TJ (2021) Dynamic impact experiment and response characteristics analysis for 1:2 reduced-scale model of hydraulic support. Int J Min Sci Techno 31(3):347–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2021.03.004
Suorineni FT, Mgumbwa JJ, Kaiser PK, Thibodeau D (2014) Mining of orebodies under shear loading part 2-failure modes and mechanisms. Min Technol 123(4):240–249. https://doi.org/10.1179/1743286314Y.0000000072
Szurgacz D, Brodny J (2019) Analysis of the influence of dynamic load on the work parameters of a powered roof support’s hydraulic leg. Sustainability 11(9):1–13. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11092570
Van B, Vervoort A, Napier J, Durrheim RJ (2003) Implementation of a flaw model to the fracturing around a vertical shaft. Rock Mech Rock Eng 36:143–161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-002-0040-2
Verma AK, Deb D (2007) Analysis of chock shield pressure using finite element method and face stability index. Min Technol 116(2):67–78. https://doi.org/10.1179/174328607x191056
Wang GF, Pang YH (2015) Relationship between hydraulic support and surrounding rock coupling and its application. J China Coal Soc 40(1):30–34. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2013.1704
Wang JC (2007) Mechanism of the rib spalling and the controlling in the very soft coal seam. J China Coal Soc 32(8):785–788. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2007.08.004
Wang JC, Wang ZH, Kong DZ (2015) Failure and prevention mechanism of coal wall in hard coal seam. J China Coal Soc 40(10):2243–2250. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2015.6013
Wang JC, Yang SL, Kong DZ (2016a) Failure mechanism and control technology of Longwall coal face in large-cutting-height mining method. Int J Min Sci Technol 26(1):111–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2015.11.018
Wang JC, Liu F, Wang L (2016b) Sustainable coal mining and mining sciences. J China Coal Soc 41(11):2651–2660. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.Jccs.2016.1395
Wang ZH, Wang JC, Yang Y, Tang YS, Wang L (2019a) Analysis of stiffness effect of coal seam stability in fully mechanized Face. J China Univer Min Technol 48(2):258–267. https://doi.org/10.13247/j.cnki.jcumt.000980
Wang JC, Yang SL, Yang BG (2019b) Roof sub-regional fracturing and support resistance distribution in deep longwall face with ultra-large length. J China Coal Soc 44(1):54–63. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2018.5139
Wang ZH, Sun WC, Shui YT (2022) Mining ⁃ induced stress rotation trace and its sensitivity to face advance direction in kilometer deep longwall panel with large face length. J China Coal Soc 47(2):634–650. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.xr21.1549
Witek M, Prusek S (2016) Numerical calculations of shield support stress based on laboratory test results. Comput Geotech 72(1):74–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2015.11.00
Xu G (2015) Experimental and theoretical study on hydraulic support in working face and its relationship with roof subsidence. J China Coal Soc 40(7):1485–1490. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2015.0220
Xu G, Zhang Z, Yang JZ, Liu QJ, Fan ZZ, Li ZG (2022) Interaction between support and surrounding rock in 8.8m super mining height working face. J China Coal Soc 47(4):1462–1472. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2021.0080
Yang SL, Song GF, Kong DZ (2019a) An evaluation of longwall face stability in thick coal seams through a basic understanding of shieldstrata interaction. J Geophys Eng 16(1):125–135. https://doi.org/10.1093/jge/gxy011
Yang S, Li M, Song G, Yang Y, Xie F (2019b) Optimization of face flexible bolting and grouting technology for longwall face support under difficult geological conditions. Energy Sci Eng 1(6):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/ese3.591
Zeng XT, Meng GY, Zhou JH (2018) Analysis on the pose and dynamic response of hydraulic support under dual impact loads. Int J Simul Model 17(1):69–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2021.03.004
Zhao TB, Guo WY, Tan YL, Lu CP, Wang CW (2018) Case histories of rock bursts under complicated geological conditions. Bull Eng Geol Environ 77(4):1529–1545. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1014-7
Zhou H, Meng FZ, Zhang CQ, Hu DW, Yang FJ, Lu JJ (2015) Analysis of rock burst mechanisms induced by structural planes in deep tunnels. Bull Eng Geol Environ 74(4):1435–1451. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-014-0696-3
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the following funds for supporting this research and editors and reviewers for their comments and suggestions.
Funding
This research was fnancially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No: 51934008; 51904304).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jiachen Wang and Zhaohui Wang designed the study. Meng Li carried out the and simulation and wrote the paper. JiaLong Li, Zheng Li, and ZhiFeng Wang carried out the test. YueSong Tang commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Li, M., Wang, Z. et al. A new method for improving coal wall stability in longwall mining by considering support stiffness. Bull Eng Geol Environ 82, 163 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03179-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03179-3