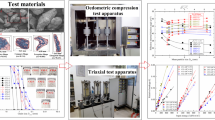
Abstract
Particle size and confining pressure are important factors that influence the shear characteristics of coral sand. In this study, multiple consolidated-drained triaxial shear tests were conducted under varying conditions, to explore the effect of particle size and confining pressure on the shear characteristics of coral sand, in terms of critical confining pressure and shear strength, respectively. Particle survival rates of coral sand under different conditions were compared. It was found that (i) the stress-softening coefficient and dilatancy coefficient had a semilogarithmic linear relationship with effective confining pressure. With an increase in effective confining pressure, the strain-softening and dilatancy of the coral sand weakened gradually. Compared with small-particle coral sand, the strain-softening and dilatancy of large-particle coral sand attenuated at a greater rate, and the mode conversion for deformation curves occurred prior to that for the strength curves. (ii) Under the same relative density, because of differences in the void ratio of coral sand with different particle sizes, the shear strength deviations increased gradually with an increase in effective confining pressure. For this reason, the internal friction angle of coral sand decreased with an increase in particle size, whereas its apparent cohesion presented an opposite trend. (iii) Under the combined action of single-particle crushing strength and particle coordination number, coarse coral sand (D = 1.0–2.0 mm) showed the largest amount of particle breakage.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altuhafi FN, Coop MR (2011) Changes to particle characteristics associated with the compression of sands. Géotechnique 61:459–471. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.9.P.114
Ben-Nun O, Einav I, Tordesillas A (2010) Force attractor in confined comminution of granular materials. Phys Rev Lett 104:108001. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.104.108001
Cao P, Jiang MJ, Ding ZJ (2020) Effects of particle size on mechanical behaviors of calcareous sand under triaxial conditions. Jap Geotech Soc Spec Pub 8:182–187. https://doi.org/10.3208/jgssp.v08.c54
Chinese Ministry of Water Resources (2019) Standard for soil test method (GB/T50123-2019) (in Chinese). China Planning Press, Beijing
Coop MR, Sorensen KK, Bodas-Freitas T, Georgoutsos G (2004) Particle breakage during shearing of a carbonate sand. Géotechnique 54:157–163. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.2004.54.3.157
Ding Z, He SH, Sun YF, Xia TD, Zhang QF (2021) Comparative study on cyclic behavior of marine calcareous sand and terrigenous siliceous sand for transportation infrastructure applications. Constr Build Mater 283:122740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.122740
Fan ZH, Hu C, Zhu QL, Jia YG, Zuo DJ, Duan ZB (2021) Three-dimensional pore characteristics and permeability properties of calcareous sand with different particle sizes. Bull Eng Geol Environ 80:2659–2670. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-020-02078-1
Ferreira C, Cardona J, Agimelen O, Tachtatzis C, Andonovic I, Sefcik J, Chen YC (2020) Quantification of particle size and concentration using in-line techniques and multivariate analysis. Powder Technol 376:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2020.08.015
He KP, Ye JH (2021) Physical modeling of the dynamics of a revetment breakwater built on reclaimed coral calcareous sand foundation in the South China Sea-tsunami wave. Bull Eng Geol Environ 80:3315–3330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02122-8
Hagerty MM, Hite DR, Ullrich CR, Hagerty DJ (1993) One-dimensional high-pressure compression of granular media. J Geotech Eng 119:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1993)119:1(1)
He SH, Shan HF, Xia TD, Liu ZJ, Ding Z, Xia F (2021) The effect of temperature on the drained shear behavior of calcareous sand. Acta Geotech 16:613–633. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-020-01030-7
Hyodo M, Wu Y, Aramaki N, Nakata Y (2016) Undrained monotonic and cyclic shear response and particle crushing of silica sand at low and high pressures. Can Geotech J 54:207–218. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2016-0212
Kuang DM, Long ZL, Wang J, Zhou XT, Yu PY (2020) Experimental study on particle size effect on mechanical behaviour of dense calcareous sand. Soils Rocks 43:567–574. https://doi.org/10.28927/SR.434567
Lim WL, Mcdowell GR, Collop AC (2004) The application of Weibull statistics to the strength of railway ballast. Granul Matter 6:229–237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-004-0180-z
Liu L, Liu HL, Xiao Y, Chu J, Xiao P, Wang Y (2018) Biocementation of calcareous sand using soluble calcium derived from calcareous sand. Bull Eng Geol Environ 77:1781–1791. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1106-4
Liu L, Yao XF, Ji ZP, Gao HM, Wang ZH, Shen ZF (2021) Cyclic behavior of calcareous sand from the South China Sea. J Mar Sci Eng 9:1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9091014
Li X, Liu JK (2021) One-dimensional compression feature and particle crushability behavior of dry calcareous sand considering fine-grained soil content and relative compaction. Bull Eng Geol Environ 80:4049–4065. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02160-2
Li YB, Lin ZH, Li B, He L, Gong J (2021) Effects of gradation and grain crushing on the liquefaction resistance of calcareous sand. Geomech Geophys Geo 7:12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-020-00208-3
Lv YR, Li X, Fan CF, Su YC (2021) Effects of internal pores on the mechanical properties of marine calcareous sand particles. Acta Geotech 16:3209–3228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-021-01223-8
Lv YR, Wang Y, Zuo DJ (2019) Effects of particle size on dynamic constitutive relation and energy absorption of calcareous sand. Powder Technol 356:21–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2019.07.088
Marschi ND, Chan CK, Seed HB (1972) Evaluation of properties of rockfill materials. J Soil Mech Found Div 98:95–114. https://doi.org/10.1061/JSFEAQ.0001735
McDowell GR, Amon A (2000) The application of Weibull statistics to the fracture of soil particles. Soils Found 40:133–141. https://doi.org/10.3208/sandf.40.5_133
McDowell GR, Bolton MD (1998) On the micromechanics of crushable aggregates. Géotechnique 48:667–679. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1998.48.5.667
McDowell GR, Bolton MD, Robertson D (1996) The fractal crushing of granular materials. J Mech Phys Solids 44:2079–2101. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5096(96)00058-0
Meng MQ, Wang L, Jiang X, Wang CG, Liu HL, Xiao Y (2020) Single-particle crushing test and numerical simulation of coarse grains based on size effect. Rock Soil Mech 41:1–11. https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2019.2000
Minh NH, Cheng YP (2013) A DEM investigation of the effect of particle-sized distribution on one-dimensional compression. Géotechnique 63:44–53. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.10.P.058
Nakata Y, Hyde FL, Hyodo M, Murata H (1999) A probabilistic approach to sand particle crushing in the triaxial test. Géotechnique 49:567–583. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1999.49.5.567
Palmer AC, Sanderson TJO (1991) Fractal crushing of ice andbrittle solids. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser A 433:469–477. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1991.0060
Rezvani R, Nabizadeh A, Tutunchian MA (2021) The effect of particle size distribution on shearing response and particle breakage of two different calcareous soils. Eur Phys J plus 136:1008. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01871-5
Saeidaskari J, Alibolandi M, Azizkandi AS (2021) Undrained monotonic and cyclic behavior of Qeshm calcareous sand. Mar Georesources Geotechnol 39:798–811. https://doi.org/10.1080/1064119X.2020.1764678
Shahnazari H, Rezvani R, Tutunchian MA (2017) Experimental study on the phase transformation point of crushable and noncrushable soils. Mar Georesources Geotechnol 35:176–185. https://doi.org/10.1080/1064119X.2015.1126773
Shang GW, Sun LQ, Li S, Liu XL, Chen WW (2020) Experimental study of the shear strength of carbonate gravel. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79:2381–2394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01704-x
Shen CM, Liu SH, Wang LJ, Wang YS (2019) Micromechanical modeling of particle breakage of granular materials in the framework of thermomechanics. Acta Geotech 14:939–954. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-018-0692-z
Shen CM, Liu SH, Wang YS (2017) Microscopic interpretation of one-dimensional compressibility of granular materials. Comput Geotech 91:161–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2017.07.010
Shen JH, Wang XZ, Wang X, Yao T, Wei HZ, Zhu CQ (2021) Effect and mechanism of fines content on the shear strength of calcareous sand. Bull Eng Geol Environ 80:7899–7919. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02398-w
Shen Y, Shen X, Liu HL, Ge HY, Rui XX (2020) Gradation affects basic mechanical characteristics of Chinese calcareous sand as airport subgrade of reefs. Mar Georesources Geotechnol 38:706–715. https://doi.org/10.1080/1064119X.2019.1614122
Sitharam TG, Nimbkar MS (2000) Micromechanical modelling of granular materials: effect of particle size and gradation. Geotech Geol Eng 18:91–117. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008982027109
Wang XZ, Wang X, Jin ZC, Meng QS, Zhu CQ, Wang R (2017) Shear characteristics of calcareous gravelly soil. Bull Eng Geol Environ 76:561–573. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-016-0978-z
Wang XZ, Wang X, Chen JW, Wang R, Hu MJ, Meng QS (2018a) Experimental study on permeability characteristics of calcareous soil. Bull Eng Geol Environ 77:1753–1762. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1104-6
Wang XZ XZ, Weng YL, Wang X, Chen WJ (2018b) Interlocking mechanism of calcareous soil. Rock Soil Mech 39:3113–3120. https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2017.2426
Wang XZ, Weng YL, Wei HZ, Meng QS, Hu MJ (2019a) Particle obstruction and crushing of dredged calcareous soil in the Nansha Islands, South China Sea. Eng Geol 261:105274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019a105274
Wang X, Wang XZ, Zhu CQ, Meng QS (2019b) Shear tests of interfaces between calcareous sand and steel. Mar Georesources Geotechnol 37:1095–1104. https://doi.org/10.1080/1064119X.2018.1529845
Wang X, Zhu CQ, Wang XZ, Qin Y (2019c) Study of dilatancy behaviors of calcareous soils in a triaxial test. Mar Georesources Geotechnol 37:1057–1070. https://doi.org/10.1080/1064119X.2018.1526236
Wang X, Wu Y, Cui J, Zhu CQ, Wang XZ (2020) Shape characteristics of coral sand from the South China Sea. J Mar Sci Eng 8:803. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8100803
Wang X, Cui J, Zhu CQ, Wu Y, Wang XZ (2021a) Experimental study of the mechanical behavior of calcareous sand under repeated loading-unloading. Bull Eng Geol Environ 80:3097–3113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02119-3
Wang X, Wu YX, Lu Y, Cui J, Wang XZ, Zhu CQ (2021b) Strength and dilatancy of coral sand in the South China Sea. Bull Eng Geol Environ 80:8279–8299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02348-6
Wang YQ (2016) Micro- and macro-mechanical behavior of calcareous sand and discrete element method analysis (in Chinese). Dissertation, Zhejiang University
Wei HZ, Li XX, Zhang SD, Zhao T, Yin M, Meng QS (2021) Influence of particle breakage on drained shear strength of calcareous sands. Int J Geomech 21:04021118. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0002078
Wei HZ, Zhao T, Meng QS, Wang XZ, Zhang B (2020) Quantifying the morphology of calcareous sands by dynamic image analysis. Int J Geomech 20:4020020. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0001640
Wu Y, Cui J, Li N, Wang X, Wu YH, Guo SY (2020a) Experimental study on the mechanical behavior and particle breakage characteristics of hydraulic filled coral sand on a coral reef island in the South China Sea. Rock Soil Mech 41:3181–3191. https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2020a.0596
Wu Y, Hyodo M, Aramaki N (2018) Undrained cyclic shear characteristics and crushing behaviour of silica sand. Geomech Eng 14:1–8. https://doi.org/10.12989/gae.2018.14.1.001
Wu Y, Li N, Wang XZ, Cui J, Chen YL, Wu YH, Yamamoto H (2021) Experimental investigation on mechanical behavior and particle crushing of calcareous sand retrieved from South China Sea. Eng Geol 280:105932. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105932
Wu Y, Wang X, Shen JH, Cui J, Zhu CQ, Wang XZ (2020b) Experimental study on the impact of water content on the strength parameters of coral gravelly sand. J Mar Sci Eng 8:634. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8090634
Xiao P, Liu HL, Xiao Y, Stuedlein AW, Evans TM (2018) Liquefaction resistance of bio-cemented calcareous sand. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 107:9–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2018.01.008
Xiao Y, Liu HL, Chen QS, Ma QF, Xiang YZ, Zheng YR (2017) Particle breakage and deformation of carbonate sands with wide range of densities during compression loading process. Acta Geotech 12:1177–1184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-017-0580-y
Xiao Y, Liu HL, Chen YM, Chu J (2014) Influence of intermediate principal stress on the strength and dilatancy behavior of rockfill material. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 140:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001178
Xiao Y, Liu HL, Ding XM, Chen YM, Jiang JS, Zhang WJ (2016) Influence of particle breakage on critical state line of rockfill material. Int J Geomech 16:04015031. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0000538
Yan CP, Long ZL, Zhou YC, Kuang DM, Chen JM (2020) Investigation on the effects of confining pressure and particle size of shear characteristics of calcareous sand. Rock Soil Mech 41:581–634. https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2019.0346
Ye JH, Zhang ZH, Shan JP (2019) Statistics-based method for determination of drag coefficient for nonlinear porous flow in calcareous sand soil. Bull Eng Geol Environ 78:3663–3670. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-018-1330-6
Yu JD, Shen CM, Liu SH, Cheng YP (2020) Exploration of the survival probability and shape evolution of crushable particles during one-dimensional compression using dyed gypsum particles. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 146:04020121. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0002371
Zhang CY, Chen M, Hu MJ, Wang XZ, Tang JJ (2019) Effect of fine particles content on shear strength of calcareous sand. Rock Soil Mech 40:195–202. https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2018.1706
Zhang JM, Wang R, Shi XF, Li JG, Chen HY (2005) Compression and crushing behavior of calcareous sand under confined compression (in Chinese). Chin J Rock Mech Eng 24:3327–3331
Zhang JM, Zhang L, Jiang GS, Wang R (2008) Research on particle crushing of calcareous sands under triaxial shear. Rock Soil Mech 29:2789–2793. https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2008.10.047
Zhang SL, Wu GJ, Yang XG, Jiang WH, Zhou JW (2018) Digital image-based identification method for the determination of the particle size distribution of dam granular material. KSCE J Civ Eng 22:2820–2833. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-017-0304-8
Acknowledgements
We thank Laura Kuhar, PhD, from Liwen Bianji (Edanz) (www.liwenbianji.cn), for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41877271 & 41572297) and the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Nos. XDA13010301 & XDA13010203).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Highlights
• Shear characteristics of coral sand were investigated.
• Effects of particle size and confining pressure on coral sand deformation were analyzed.
• Effects of particle size and confining pressure on coral sand shear strength were discussed.
• Changes in coral sand particle breakage with particle size and confining pressure were revealed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Wang, X., Shen, J. et al. Particle size and confining-pressure effects of shear characteristics of coral sand: an experimental study. Bull Eng Geol Environ 81, 97 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02599-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02599-x