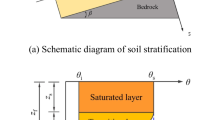
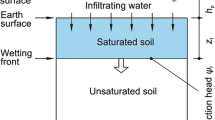
Abstract
Rainfall-induced landslides are a major cause of slope failure in mountainous areas. As rainfall begins to infiltrate a slope the wetting front advances into the soil and reduces its shear strength. Slope failures occur when the reduced shear strength becomes less than the resisting shear strength needed for equilibrium. These areas of instability are usually located near the ground surface where pore-water pressure changes rapidly during infiltration. The wetting front depth in a slope plays an important role in slope stability. In this study a well-known infiltration model, the Green and Ampt model, is integrated into three GIS-based three-dimensional limit equilibrium methods to assess the impact of rainfall on slope stability. This infiltration model can predict the depth of the wetting front during steady and unsteady rainfall. The applied three-dimensional methods are modified according to different positions of the wetting front to reflect the influence of rainfall on slope stability. This approach is capable of calculating safety factors corresponding to individual rainfall events and is also capable of predicting the corresponding failure time. The accuracy of the presented study has been verified by simulating the failure process of a real landslide triggered by a rainstorm.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander DE (2008) A brief survey of GIS in mass-movement studies, with reflections on theory and methods. Geomorphology 94(3–4):261–267. doi:10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.09.022
Burrough PA, McDonnell RA (1998) Principles of geographical information systems. Oxford University Press.
Casagli N, Dapporto S, Ibsen ML, Tofani V, Vannocci P (2006) Analysis of the landslide triggering mechanism during the storm of 20th–21st November 2000, Northern Tuscany. Landslides 3(1):13–21. doi:10.1007/s10346-005-0007-y
Chang MS (2002) A 3D slope stability analysis method assuming parallel lines of intersection and differential straining of block contacts. Can Geotech J 39(4):799–811. doi:10.1139/T02-020
Cho SE, Lee SR (2002) Evaluation of surficial stability for homogeneous slopes considering rainfall characteristics. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 128(9):756–763. doi:10.1061/(Asce)1090-0241(2002)128:9(756)
Chu ST (1978) Infiltration during an unsteady rain. Water Resour Res 14(3):461–466
Crosta GB, Frattini P (2003) Distributed modelling of shallow landslides triggered by intense rainfall. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 3(1–2):81–93
Duncan JM (1996) State of art: limit equilibrium and finite-element analysis of slopes. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng, ASCE 122(7):577–596
Duncan JM, Wright SG (2005) Soil strength and slope stability. Wiley, Inc. Hoboken, New Jersey
Gasmo JM, Rahardjo H, Leong EC (2000) Infiltration effects on stability of a residual soil slope. Comput Geotech 26(2):145–165
Govindaraju RS, Kavvas ML, Jones SE, Rolston DE (1996) Use of Green-Ampt model for analyzing one-dimensional convective transport in unsaturated soils. J Hydrol 178(1–4):337–350
Green WH, Ampt GA (1911) Studies on soil physics part I—the flow of air and water through soils. J Agric Sci 4:1–24
Hovland HJ (1977) Three-dimensional slope stability analysis method. ASCE J Geotech Eng Div 103(9):971–986
Hungr O, Salgado FM, Byrne PM (1989) Evaluation of a three-dimensional method of slope stability analysis. Can Geotech J 26:679–686
Jia GW, Zhan TLT, Chen YM, Fredlund DG (2009) Performance of a large-scale slope model subjected to rising and lowering water levels. Eng Geol 106(1–2):92–103. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2009.03.003
Kim YK, Lee SR (2010) Field infiltration characteristics of natural rainfall in compacted roadside slopes. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 136(1):248–252. doi:10.1061/(Asce)Gt.1943-5606.0000160
Kim J, Jeong S, Park S, Sharma J (2004) Influence of rainfall-induced wetting on the stability of slopes in weathered soils. Eng Geol 75(3–4):251–262. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2004.06.017
Lysandros P, Griffiths DV (2012) Stability assessment of slopes using different factoring strategies. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 138(9):1158–1160
Muntohar AS, Liao HJ (2010) Rainfall infiltration: infinite slope model for landslides triggering by rainstorm. Nat Hazards 54(3):967–984. doi:10.1007/s11069-010-9518-5
Ng CWW, Shi Q (1998) A numerical investigation of the stability of unsaturated soil slopes subjected to transient seepage. Comput Geotech 22(1):1–28
Ng CWW, Wang B, Tung YK (2001) Three-dimensional numerical investigations of groundwater responses in an unsaturated slope subjected to various rainfall patterns. Can Geotech J 38(5):1049–1062
Ogden FL, Saghafian B (1997) Green and Ampt infiltration with redistribution. J Irrig Drain Eng-ASCE 123(5):386–393
Ormsby T, Napoleon E, Burke R, Groessl C, Feaster L (2001) Getting to know ArcGIS desktop. Environmental Systems Research Institute Press, Redlands
Philip JR (1957) The theory of infiltration: 1. The infiltration equation and its solution. Soil Sci 83:345–357
Qi Z (2006) Comparison of finite difference method, Philip’s method and Green-Ampt model in infiltration simulation. http://www.public.iastate.edu/~qzhiming/coursework/agron677/Agron677_final_project.doc.2012
Qiu C, Esaki T, Xie M, Mitani Y, Wang C (2007) Spatio-temporal estimation of shallow landslide hazard triggered by rainfall using a three-dimensional model. Environ Geol 52(8):1569–1579
Rawls WJ, Brakensiek DL, Miller N (1983) Green-Ampt infiltration parameters from soils data. J Hydraul Eng-ASCE 109(1):62–70
Richards RA (1931) Capillary conduction of liquid through porous media. Physics 1:318–333
Serrano SE (2003) Improved decomposition solution to green and ampt equation. J Hydrol Eng 8(3):158–160. doi:10.1061/(Asce)1084-0699(2003)8:3(158)
Smith RE, Corradini C, Melone F (1993) Modeling infiltration for multistorm runoff events. Water Resour Res 29(1):133–144
Trigila A, Iadanza C, Spizzichino D (2010) Quality assessment of the Italian landslide inventory using GIS processing. Landslides 7(4):455–470. doi:10.1007/s10346-010-0213-0
Van Westen CJ, Van Asch TWJ, Soeters R (2006) Landslide hazard and risk zonation–Why is it still so difficult? Bull Eng Geol Environ 65(2):167–184
West Nippon Expressway Company Limited (2010) Geological hazard investigation report for the landslides along Kyushu highway (in Japanese) report of NEXCO
Xie MW, Esaki T, Cai M (2004) A GIS-based method for locating the critical 3D slip surface in a slope. Comput Geotech 31:267–277
Xie MW, Esaki T, Qiu C, Wang CX (2006) Geographical information system-based computational implementation and application of spatial three-dimensional slope stability analysis. Comput Geotech 33(4–5):260–274. doi:10.1016/j.compgeo.2006.07.003
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, N., Yang, Z., Xie, M. et al. GIS-based three-dimensional slope stability analysis considering rainfall infiltration. Bull Eng Geol Environ 74, 919–931 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-014-0661-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-014-0661-1