Abstract
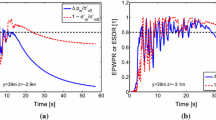
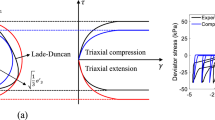
This study presents a numerical assessment of the seismic behaviour of an earth embankment founded on liquefiable foundation soils during earthquake loading. Analysis was carried out using an effective stress-based, fully coupled, finite element method. The behaviour of the sandy soil is described by means of a cyclic elastoplastic constitutive model which was developed within the framework of the Armstrong–Frederick type non-linear kinematic hardening concept. The numerical method and the analysis procedure are briefly outlined and as an example, the seismic response of an earth embankment on a saturated sand foundation is assessed. Based on the numerical results, the distinctive patterns of seismic response of the embankment are discussed. Special emphasis is given to the computed results of excess pore water pressures, co-seismic and post-seismic deformations, and accelerations during the seismic excitation. It has been found that the numerical model can capture fundamental liquefaction aspects of the embankment foundation system and produce preliminary results for its seismic assessment.
Résumé
L’étude présente la caractérisation numérique du comportement d’un barrage en terre fondé sur des sols liquéfiables et soumis à une sollicitation sismique. L’analyse a été réalisée en utilisant une méthode de calcul en éléments finis, avec une approche en contraintes effectives et une analyse couplée. Le comportement du sol sableux est décrit par un modèle rhéologique élasto-plastique développé à partir d’un concept d’écrouissage positif non linéaire de type Armstrong–Frederik. La méthode numérique et la procédure d’analyse sont brièvement présentées et, à titre d’exemple, la réponse sismique d’un barrage en terre sur un sol sableux saturé est évaluée. Sur la base des résultats numériques, les différents schémas de réponse sismique du barrage sont discutés. Un accent particulier est mis sur le calcul des sur-pressions interstitielles, des déformations co-sismiques et post-sismiques et sur les accélérations enregistrées durant la sollicitation sismique. Il a été montré que la simulation numérique est en mesure de mettre en évidence les aspects fondamentaux du processus de liquéfaction du système barrage-fondation et de produire des résultats préliminaires pour l’évaluation du comportement sismique de l’ouvrage.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adalier K, Elgamal AW, Martin GR (1998) Foundation liquefaction countermeasures for earth embankments. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng ASCE 123(6):500–517
Akai K, Tamura T (1978) Numerical analysis of multi-dimensional consolidation accompanied with elasto-plastic constitutive equation. In: Proceedings of the Japan Society of Civil Engineers, No. 269, pp 98–104 (in Japanese)
Arulanandan K, Scott RF (eds) (1993) In: Proceedings of the international conference on the verification of numerical procedures for the analysis of soil liquefaction problems, vol 1. Balkema, Rotterdam
Arulanandan K, Scott RF (eds) (1994) In: Proceedings of the international conference on the verification of numerical procedures for the analysis of soil liquefaction problems, vol 2. Balkema, Rotterdam
Aydingun O, Adalier K (2003) Numerical analysis of seismically induced liquefaction in earth embankment foundations. Part I. Benchmark model. Can Geotech J 40(4):753–765
Biot MA (1956) Theory of propagation of waves in a fluid saturated porous solid. J Acoust Soc Am 28:168–691
Elgamal A, Parra E, Yang Z, Adalier K (2002) Numerical analysis of embankment foundation liquefaction countermeasures. J Earthq Eng 6(4):447–471
Huang Y, Zhang F, Yashima A, Sawada K, Ye GL, Kubota N (2004) Three-dimensional numerical simulation of pile-soil seismic interaction in saturated deposits with liquefiable sand and soft clay. In: Proceedings of the sixth world congress on computational mechanics in conjunction with the second Asian-Pacific congress on computational mechanics. Tsinghua University Press and Springer-Verlag, Beijing, Paper No. 274
Huang Y, Yashima A, Zhang F, Uzuoka R (2005) Numerical simulation of mitigation for liquefaction by ground improvement and structural enhancement. In: Proceedings of the second China–Japan geotechnical symposium. Tongji University Press, Shanghai, China, pp 196–203
Huang Y, Yashima A, Zhang F, Sawada K (2006) Numerical simulation for earthquake liquefaction of soil embankments. In: Proceedings of the 1st international conference on computational methods—computational methods. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 269–73
Kimura M, Zhang F (2000) Seismic evaluation of pile foundations with three different methods based on three-dimensional elasto-plastic finite element analysis. Soils Found 40(5):113–132
Koga Y, Matsuo O (1990) Shaking table tests of embankments resting on liquefiable sandy ground. Soils Found 30(4):162–174
Koseki J, Koga Y, Takahashi A (1994) Liquefaction of sandy ground and settlement of embankments. In: Proceedings of the international conference centrifuge 94. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 215–220
Krinitzsky EL, Hynes ME (2002) The Bhuj, India, earthquake: lessons learned for earthquake safety of dams on alluvium. Eng Geol 66(3–4):163–196
Lemaitre J, Chaboche JL (1990) Mechanics of solid materials. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
LIQCA Development Group (2002) Reference manual for LIQCA2D01 (2001 Version). Japan (in Japanese) http://www.nakisuna2.kuciv.kyoto-u.ac.jp/liqca/
Matsuo O (1996) Damage to river dikes. Soils Found 36(1):235–240
Matsuo O, Shimazu T, Uzuoka R, Mihara M, Nishi K (2000) Numerical analysis of seismic behavior of embankments founded on liquefiable soils. Soils Found 40(2):21–39
Oka F, Yashima A, Shibata T, Kato M, Uzuoka R (1994) FEM-FDM coupled liquefaction analysis of a porous soil using an elasto-plastic model. Appl Sci Res 52:209–245
Oka F, Yashima A, Tateishi A, Taguchi Y, Yamashita S (1999) A cyclic elasto-plastic constitutive model for sand considering a plain-strain dependence of the shear modulus. Geotechnique 49(5):661–680
Park YH, Kim SR, Kim SH, Kim MM (2000) Liquefaction of embankments on sandy soils and the optimum countermeasure against the liquefaction. In: Proceedings of 12th world conference on earthquake engineering. Auckland, Paper No. 1170
Shibata T, Sato T, Uzuoka R, Oka F, Yashima A, Kato M (1991) FEM–FDM coupled liquefaction analysis of a fluid-saturated ground. In: Proceedings of 7th international conference on computer methods and advances in geomechanics. Balkema, Rotterdam, vol. 2, pp 869–874
Tateishi A, Taguchi Y, Oka F, Yashima A (1995) A cyclic elasto-plastic model for sand and its application under various stress conditions. In: Proceedings of first international symposium on earthquake geotechnical engineering, IS-TOKYO’95. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 399–404
Uzuoka R, Kubo T, Yashima A, Zhang F (2001) Numerical study on 3-dimensional behavior of a damaged pile foundation during the 1995 Hyogo-ken Nanbu earthquake. In: Proceedings of 4th international conference on recent advances in geotechnical earthquake engineering and soil dynamics. San Diego, Paper No. 6.22
Yang Z, Elgamal A, Adalier K, Sharp MK (2004) Earth dam on liquefiable foundation and remediation: numerical simulation of centrifuge experiments. J Eng Mech ASCE 130(10):1168–1176
Zhang F, Kimura M (2002) Numerical prediction of the dynamic behaviors of RC group-pile foundation. Soils Found 42(3):77–92
Zienkiewicz OC, Bettess P (1982) Soils and other saturated media under transient, dynamic conditions. General formulation and the validity of various simplifying assumptions. In: Soil mechanics-transient and cyclic loads. Wiley, New York, pp 1–16
Zienkiewicz OC, Chan AHC, Pastor M, Schrefler B, Shiomi T (1999) Computational geomechanics. Wiley, Chichester
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Yashima, A., Sawada, K. et al. Numerical assessment of the seismic response of an earth embankment on liquefiable soils. Bull Eng Geol Environ 67, 31–39 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-007-0097-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-007-0097-y
Keywords
- Liquefaction
- Embankments
- Seismic response
- Coupled analysis
- Cyclic elastoplastic constitutive models
- Finite element methods