Abstract
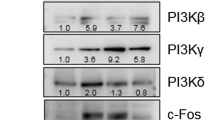
Drug repositioning can identify new therapeutic applications for existing drugs, thus mitigating high R&D costs. The Protein kinase 2 (CK2) inhibitor CX-4945 regulates human cancer cell survival and angiogenesis. Here we found that CX-4945 significantly inhibited the RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation, but enhanced the BMP2-induced osteoblast differentiation in a cell culture model. CX-4945 inhibited the RANKL-induced activation of TRAP and NFATc1 expression accompanied with suppression of Akt phosphorylation, but in contrast, it enhanced the BMP2-mediated ALP induction and MAPK ERK1/2 phosphorylation. CX-4945 is thus a novel drug candidate for bone-related disorders such as osteoporosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, K. (1999). Nuclear matrix and protein kinase CK2 signaling. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 9, 329–336.
Ahmed, K., Gerber, D.A., and Cochet, C. (2002). Joining the cell survival squad: An emerging role for protein kinase CK2. Trends Cell Biol. 12, 226–230.
Allende, J.E., and Allende, C.C. (1995). Protein kinase CK2-an enzyme with multiple substrates and a puzzling regulation. FASEB J. 9, 313–323.
Asagiri, M., and Takayanagi, H. (2007). The molecular understanding of osteoclast differentiation. Bone 40, 251–264.
Ashburn, T.T., and Thor, K.B. (2004). Drug repositioning: identifying and developing new uses or existing drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 3, 673–683.
Bessa, P.C., Cerqueira, M.T., Rada, T., Gomes, M.E., Neves, N.M., Nobre, A., Reis, R.L., and Casal, M. (2009). Expression, purification and osteogenic bioactivity of recombinant human BMP-4, -9, -10, -11 and -14. Protein Expr. Purif. 63, 89–94.
Booth, B., and Zemmel, R. (2004). Prospects for productivity. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 3, 451–456.
Bragdon, B., Thinakaran, S., Moseychuk, O., King, D., Young, K., Litchfield, D.W., Petersen, N.O., and Nohe, A. (2010). Casein kinase 2 beta-subunit is a regulator of bone morphogenetic protein 2 signaling. Biophys. J. 99, 897–904.
Chen, D., Harris, M.A., Rossini, G., Dunstan, C.R., Dallas, S.L., Feng, J.Q., Mundy, G.R., and Harris, S.E. (1997). Bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP-2) enhances BMP-3, BMP-4, and bone cell differentiation marker gene expression during the induction of mineralized bone matrix formation in cultures of fetal rat calvarial osteoblasts. Calcif. Tissue Int. 60, 283–290.
Choi, S.W., Son, Y.J., Yun, J.M., and Kim, S.H. (2012). Fisetin inhibits osteoclast differentiation via downregulation of p38 and c-Fos-NFATc1 signaling pathways. Evid. Based Complement Alternat. Med. 2012, 810563.
Cozza, G., Pinna, L.A., and Moro, S. (2012). Protein kinase CK2 inhibitors: a patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 22, 1081–1097.
Di Maira, G., Salvi, M., Arrigoni, G., Marin, O., Sarno, S., Brustolon, F., Pinna, L.A., and Ruzzene, M. (2005). Protein kinase CK2 phosphorylates and upregulates Akt/PKB. Cell Death Differ. 12, 668–677.
Franceschi, R.T., and Iyer, B.S. (1992). Relationship between collagen synthesis and expression of the osteoblast phenotype in MC3T3-E1 cells. J. Bone Miner. Res. 7, 235–246.
Grigoriadis, A.E., Wang, Z.Q., Cecchini, M.G., Hofstetter, W., Felix, R., Fleisch, H.A., and Wagner, E.F. (1994). c-Fos: a key regulator of osteoclast-macrophage lineage determination and bone remodeling. Science 266, 443–448.
Guerra, B., and Issinger, O.G. (1999). Protein kinase CK2 and its role in cellular proliferation, development and pathology. Electrophoresis 20, 391–408.
Gyenis, L., Turowec, J.P., Bretner, M., and Litchfield, D.W. (2013). Chemical proteomics and functional proteomics strategies for protein kinase inhibitor validation and protein kinase substrate identification: applications to protein kinase CK2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1834,1352–1358.
Haltmaier, H.K. (1998). A Potenz aus dem Labor: Die Erektionspille VIAGRA (‘Potency from the Lab: The Erection Pill Viagra’) (Reinbek bei Hamburg, Germany: Rowohlt Taschenbuch Verlag GmbH.).
Kawai, M., Bessho, K., Maruyama, H., Miyazaki, J., and Yamamoto, T. (2006). Simultaneous gene transfer of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-2 and BMP-7 by in vivo electroporation induces rapid bone formation and BMP-4 expression. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 7, 62.
Kim, H.J., and Kim, S.H. (2010). Tanshinone IIA enhances BMP-2-stimulated commitment of C2C12 cells into osteoblasts via p38 activation. Amino Acids 39, 1217–1226.
Kim, J., and Kim, S.H. (2012). Druggability of the CK2 inhibitor CX-4945 as an anticancer drug and beyond. Arch. Pharm. Res. 35, 1293–1296.
Kim, K., Kim, J.H., Moon, J.B., Lee, J., Kwak, H.B., Park, Y.W., and Kim, N. (2012). The transmembrane adaptor protein, linker for activation of T cells (LAT), regulates RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation. Mol. Cells 33, 401–406.
Livak, K.J., and Schmittgen, T.D. (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25, 402–408.
Longman, R. (2004). Pharmaceutical strategies: jumpstart to products. In Vivo 22, 17.
Matsuo, K., Galson, D.L., Zhao, C., Peng, L., Laplace, C., Wang, K.Z., Bachler, M.A., Amano, H., Aburatani, H., Ishikawa, H., et al. (2004). Nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) rescues osteoclastogenesis in precursors lacking c-Fos. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 26475–26480.
Moon, J.B., Kim, J.H., Kim, K., Youn, B.U., Ko, A., Lee, S.Y., and Kim, N. (2012). Akt induces osteoclast differentiation through regulating the GSK3β/NFATc1 signaling cascade. J. Immunol. 188, 163–169.
Moseychuk, O., Akkiraju, H., Dutta, J., D’Angelo, A., Bragdon, B., Duncan, R.L., and Nohe, A. (2013). Inhibition of CK2 binding to BMPRIa induces C2C12 differentiation into osteoblasts and adipocytes. J. Cell Commun. Signal. [Epub ahead of print]
Pagano, M.A., Meggio, F., Ruzzene, M., Andrzejewska, M., Kazimierczuk, Z., and Pinna, L.A. (2004). 2-Dimethylamino-4,5,6,7-tetrabromo-1H-benzimidazole: a novel powerful and selective inhibitor of protein kinase CK2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 321, 1040–1044.
Pagano, M.A., Bain, J., Kazimierczuk, Z., Sarno, S., Ruzzene, M., Maira Di, G., Elliott, M., Orzeszko., A., Cozza, G., Meggiom F., et al. (2008). The selectivity of inhibitors of protein kinase CK2: an update. Biochem. J. 415, 353–365.
Parvanta, C., Roth, Y., and Keller, H. (2013). Crowdsourcing 101: a few basics to make you the leader of the pack. Health Promot. Pract. 14, 163–167.
Pierre, F., Chua, P.C., O’Brien, S.E., Siddiqui-Jain, A., Bourbon, P., Haddach, M., Michaux, J., Nagasawa, J., Schwaebe, M.K., Stefan, E., et al. (2011a). Pre-clinical characterization of CX-4945, a potent and selective small molecule inhibitor of CK2 for the treatment of cancer. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 356, 37–43.
Pierre, F., Chua, P.C., O’Brien, S.E., Siddiqui-Jain, A., Bourbon, P., Haddach, M., Michaux, J., Nagasawa, J., Schwaebe, M.K., Stefan, E., et al. (2011b). Discovery and SAR of 5-(3-chlorophenylamino) benzo[c][2,6]naphthyridine-8-carboxylic acid (CX-4945), the first clinical stage inhibitor of protein kinase CK2 for the treatment of cancer. J. Med. Chem. 54, 635–654.
Prudent, R., and Cochet, C. (2009). New protein kinase CK2 inhibitors: jumping out of the catalytic box. Chem. Biol. 16, 112–120.
Ritt, D.A., Zhou, M., Conrads, T.P., Veenstra, T.D., Copeland, T.D., and Morrison, D.K. (2007). CK2 Is a component of the KSR1 scaffold complex that contributes to Raf kinase activation. Curr. Biol. 17, 179–184.
Sarno, S., Reddy, H., Meggio, F., Ruzzene, M., Davies, S.P., Donella-Deana, A., Shugar, D., and Pinna, L.A. (2001). Selectivity of 4,5,6,7-tetrabromobenzotriazole, an ATP site-directed inhibitor of protein kinase CK2 (‘casein kinase-2’). FEBS Lett. 296, 44–48.
Sarno, S., Papinutto, E., Franchin, C., Bain, J., Elliott, M., Meggio, F., Kazimierczuk, Z., Orzeszko, A., Zanotti, G., Battistutta, R., et al. (2011). ATP site-directed inhibitors of protein kinase CK2: an update. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 11, 1340–1351.
Siddiqui-Jain, A., Drygin, D., Streiner, N., Chua, P., Pierre, F., O’Brien, S.E., Bliesath, J., Omori, M., Huser, N., Ho, C., et al. (2010). CX-4945, an orally bioavailable selective inhibitor of protein kinase CK2, inhibits prosurvival and angiogenic signaling and exhibits antitumor efficacy. Cancer Res. 70, 10288–10298.
Son, Y.H., Song, J.S., Kim, S.H., and Kim, J. (2013). Pharmacokinetic characterization of CK2 inhibitor CX-4945. Arch. Pharm. Res. 36, 840–845.
Stuart, M. (2004). Rediscovering existing drugs. Start-Up 9, 23–30.
Takayanagi, H., Kim, S., Matsuo, K., Suzuki, H., Suzuki, T., Sato, K., Yokochi, T., Oda, H., Nakamura, K., Ida, N., et al. (2002). RANKL maintains bone homeostasis through c-Fos-dependent induction of interferon-beta. Nature 416, 744–749.
Zien, P., Duncan, J.S., Skierski, J., Bretner, M., Litchfield, D.W., and Shugar, D. (2005). Tetrabromobenzotriazole (TBBt) and tetrabromobenzimidazole (TBBz) as selective inhibitors of protein kinase CK2: evaluation of their effects on cells and different molecular forms of human CK2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1754, 271–280.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
About this article
Cite this article
Son, Y.H., Moon, S.H. & Kim, J. The protein kinase 2 inhibitor CX-4945 regulates osteoclast and osteoblast differentiation In vitro . Mol Cells 36, 417–423 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-013-0184-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-013-0184-9