Abstract
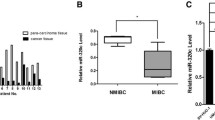
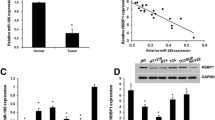
There is increasing evidence suggesting that dysregulation of certain microRNAs (miRNAs) may contribute to tumor progression and metastasis. Previous studies have shown that miR-409-3p is dysregulated in some malignancies, but its role in bladder cancer is still unknown. Here, we find that miR-409-3p is down-regulated in human bladder cancer tissues and cell lines. Enforced expression of miR-409-3p in bladder cancer cells significantly reduced their migration and invasion without affecting cell viability. Bioinformatics analysis identified the pro-metastatic gene c-Met as a potential miR-409-3p target. Further studies indicated that miR-409-3p suppressed the expression of c-Met by binding to its 3′-untranslated region. Silencing of c-Met by small interfering RNAs phenocopied the effects of miR-409-3p overexpression, whereas restoration of c-Met in bladder cancer cells bladder cancer cells overexpressing miR-409-3p, partially reversed the suppressive effects of miR-409-3p. We further showed that MMP2 and MMP9 may be downstream effector proteins of miR-409-3p. These findings indicate that miR-409-3p could be a potential tumor suppressor in bladder cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baek, J.H., Birchmeier, C., Zenke, M., and Hieronymus, T. (2012). The HGF receptor/Met tyrosine kinase is a key regulator of dendritic cell migration in skin immunity. J. Immunol. 189, 1699–1707.
Bartel, D.P. (2004). MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116, 281–297.
Bartel, D.P. (2009). MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136, 215–233.
Bartel, D.P., and Chen, C.Z. (2004). Micromanagers of gene expression: the potentially widespread influence of metazoan microRNAs. Nat. Rev. Genet. 5, 396–400.
Birchmeier, C., Birchmeier, W., Gherardi, E., and Vande Woude, G.F. (2003). Met, metastasis, motility and more. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4, 915–925.
Cheng, H.L., Trink, B., Tzai, T.S., Liu, H.S., Chan, S.H., Ho, C.L., Sidransky, D., and Chow, N.H. (2002). Overexpression of c-met as a prognostic indicator for transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder: a comparison with p53 nuclear accumulation. J. Clin. Oncol. 20, 1544–1550.
Cheng, H.L., Liu, H.S., Lin, Y.J., Chen, H.H., Hsu, P.Y., Chang, T.Y., Ho, C.L., Tzai, T.S., and Chow, N.H. (2005). Co-expression of RON and MET is a prognostic indicator for patients with transitional-cell carcinoma of the bladder. Br. J. Cancer 92, 1906–1914.
Friedman, R.C., Farh, K.K., Burge, C.B., and Bartel, D.P. (2009). Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 19, 92–105.
Gao, P., Xing, A.Y., Zhou, G.Y., Zhang, T.G., Zhang, J.P., Gao, C., Li, H., and Shi, D.B. (2012). The molecular mechanism of micro-RNA-145 to suppress invasion-metastasis cascade in gastric cancer. Oncogene 32, 491–501.
Hazan, R.B., Phillips, G.R., Qiao, R.F., Norton, L., and Aaronson, S.A. (2000). Exogenous expression of N-cadherin in breast cancer cells induces cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. J. Cell Biol. 148, 779–790.
Hirata, H., Hinoda, Y., Ueno, K., Shahryari, V., Tabatabai, Z.L., and Dahiya, R. (2012). MicroRNA-1826 targets VEGFC, beta-catenin (CTNNB1) and MEK1 (MAP2K1) in human bladder cancer. Carcinogenesis 33, 41–48.
Jemal, A., Bray, F., Center, M.M., Ferlay, J., Ward, E., and Forman, D. (2011). Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 61, 69–90.
Li, N., Fu, H., Tie, Y., Hu, Z., Kong, W., Wu, Y., and Zheng, X. (2009). miR-34a inhibits migration and invasion by down-regulation of c-Met expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 275, 44–53.
Li, C., Nie, H., Wang, M., Su, L., Li, J., Yu, B., Wei, M., Ju, J., Yu, Y., Yan, M., et al. (2012). MicroRNA-409-3p regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis by targeting PHF10 in gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 320, 189–197.
Majid, S., Dar, A.A., Saini, S., Shahryari, V., Arora, S., Zaman, M.S., Chang, I., Yamamura, S., Chiyomaru, T., Fukuhara, S., et al. (2012). MicroRNA-1280 inhibits invasion and metastasis by targeting ROCK1 in bladder cancer. PLoS One 7, e46743.
Neely, L.A., Rieger-Christ, K.M., Neto, B.S., Eroshkin, A., Garver, J., Patel, S., Phung, N.A., McLaughlin, S., Libertino, J.A., Whitney, D., et al. (2010). A microRNA expression ratio defining the invasive phenotype in bladder tumors. Urol. Oncol. 28, 39–48.
Ploeg, M., Aben, K.K., and Kiemeney, L.A. (2009). The present and future burden of urinary bladder cancer in the world. World J. Urol. 27, 289–293.
Salvi, A., Sabelli, C., Moncini, S., Venturin, M., Arici, B., Riva, P., Portolani, N., Giulini, S.M., De Petro, G., and Barlati, S. (2009). MicroRNA-23b mediates urokinase and c-met downmodulation and a decreased migration of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. FEBS J. 276, 2966–2982.
Tan, S., Li, R., Ding, K., Lobie, P.E., and Zhu, T. (2011). miR-198 inhibits migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting the HGF/c-MET pathway. FEBS Lett. 585, 2229–2234.
Uchino, K., Takeshita, F., Takahashi, R.U., Kosaka, N., Fujiwara, K., Naruoka, H., Sonoke, S., Yano, J., Sasaki, H., Nozawa, S., et al. (2013). Therapeutic effects of microRNA-582-5p and -3p on the inhibition of bladder cancer progression. Mol. Ther. 21, 610–619.
Ueno, K., Hirata, H., Majid, S., Yamamura, S., Shahryari, V., Tabatabai, Z.L., Hinoda, Y., and Dahiya, R. (2012). Tumor suppressor microRNA-493 decreases cell motility and migration ability in human bladder cancer cells by downregulating RhoC and FZD4. Mol. Cancer Ther. 11, 244–253.
Weng, C., Dong, H., Chen, G., Zhai, Y., Bai, R., Hu, H., Lu, L., and Xu, Z. (2012). miR-409-3p inhibits HT1080 cell proliferation, vascularization and metastasis by targeting angiogenin. Cancer Lett. 323, 171–179.
Wszolek, M.F., Rieger-Christ, K.M., Kenney, P.A., Gould, J.J., Silva Neto, B., Lavoie, A.K., Logvinenko, T., Libertino, J.A., and Summerhayes, I.C. (2011). A MicroRNA expression profile defining the invasive bladder tumor phenotype. Urol. Oncol. 29, 794–801 e791.
Wu, Z.S., Wu, Q., Wang, C.Q., Wang, X.N., Huang, J., Zhao, J.J., Mao, S.S., Zhang, G.H., Xu, X.C., and Zhang, N. (2011). miR-340 inhibition of breast cancer cell migration and invasion through targeting of oncoprotein c-Met. Cancer 117, 2842–2852.
Zhang, C., Yao, Z., Zhu, M., Ma, X., Shi, T., Li, H., Wang, B., Ouyang, J., and Zhang, X. (2012). Inhibitory effects of microRNA-34a on cell migration and invasion of invasive urothelial bladder carcinoma by targeting Notch1. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Med. Sci. 32, 375–382.
Zheng, B., Liang, L., Huang, S., Zha, R., Liu, L., Jia, D., Tian, Q., Wang, Q., Wang, C., Long, Z., et al. (2012). MicroRNA-409 suppresses tumour cell invasion and metastasis by directly targeting radixin in gastric cancers. Oncogene 31, 4509–4516.
Zhou, Y., Wu, D., Tao, J., Qu, P., Zhou, Z., and Hou, J. (2012). MicroRNA-133 inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting epidermal growth factor receptor and its downstream effector proteins in bladder cancer. Scand. J. Urol. [Epub ahead of print].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Chen, H., Lin, Y. et al. MicroRNA-409-3p inhibits migration and invasion of bladder cancer cells via targeting c-Met. Mol Cells 36, 62–68 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-013-0044-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-013-0044-7