Abstract
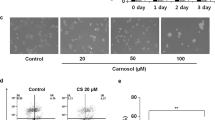
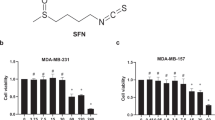
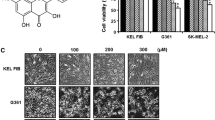
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation is linked to dynamic actin cytoskeleton reorganization, which is involved in tumor cell motility and metastasis. Thus, inhibition of ROS generation and actin polymerization in tumor cells may represent an effective anticancer strategy. However, the molecular basis of this signaling pathway is currently unknown. Here, we show that the Ecklonia cava-derived antioxidant dieckol downregulates the Rac1/ROS signaling pathway and inhibits Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP)-family verprolin-homologous protein 2 (WAVE2)-mediated invasive migration of B16 mouse melanoma cells. Steady-state intracellular ROS levels were higher in malignant B16F10 cells than in parental, nonmetastatic B16F0 cells. Elevation of ROS by H2O2 treatment increased migration and invasion ability of B16F0 cells to level similar to that of B16F10 cells, suggesting that intracellular ROS signaling mediates the prometastatic properties of B16 mouse melanoma cells. ROS levels and the cell migration and invasion ability of B16 melanoma cells correlated with Rac1 activation and WAVE2 expression. Overexpression of dominant negative Rac1 and depletion of WAVE2 by siRNA suppressed H2O2-induced cell invasion of B16F0 and B16F10 cells. Similarly, dieckol attenuates the ROS-mediated Rac1 activation and WAVE2 expression, resulting in decreased migration and invasion of B16 melanoma cells. In addition, we found that dieckol decreases association between WAVE2 and NADPH oxidase subunit p47phox. Therefore, this finding suggests that WAVE2 acts to couple intracellular Rac1/ROS signaling to the invasive migration of B16 melanoma cells, which is inhibited by dieckol.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bae, Y.A., Oh, H., Rhee, S.G., and Yoo, Y.D. (2011). Regulation of reactive oxygen species generation in cell signaling. Mol. Cells 32, 491–509.
Bedard, K., and Krause, K.H. (2007). The NOX family of ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 87, 245–313.
Binker, M.G., Binker-Cosen, A.A., Richards, D., Oliver, B., and Cosen-Binker, L.I. (2009). EGF promotes invasion by PANC-1 cells through Rac1/ROS-dependent secretion and activation of MMP-2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 379, 445–450.
Cottart, C.H., Nivet-Antoine, V., Laguillier-Morizot, C., and Beaudeux, J.L. (2010). Resveratrol bioavailability and toxicity in humans. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 54, 7–16.
Derry, J.M., Ochs, H.D., and Francke, U. (1994). Isolation of a novel gene mutated in Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Cell 78, 635–644.
Fidler, I.J., and Kripke, M.L. (1977). Metastasis results from preexisting variant cells within a malignant tumor. Science 197, 893–895.
Fidler, I.J., and Nicolson, G.L. (1976). Organ selectivity for implantation survival and growth of B16 melanoma variant tumor lines. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 57, 1199–1202.
Harfouche, R., Malak, N.A., Brandes, R.P., Karsan, A., Irani, K., and Hussain, S.N. (2005). Roles of reactive oxygen species in angiopoietin-1/tie-2 receptor signaling. FASEB J. 19, 1728–1730.
Heo, S.J., Ko, S.C., Cha, S.H., Kang, D.H., Park, H.S., Choi, Y.U., Kim, D., Jung, W.K., and Jeon, Y.J. (2009). Effect of phlorotannins isolated from Ecklonia cava on melanogenesis and their protective effect against photo-oxidative stress induced by UV-B radiation. Toxicol. In Vitro 23, 1123–1130.
Hinshaw, D.B., Sklar, L.A., Bohl, B., Schraufstatter, I.U., Hyslop, P. A., Rossi, M.W., Spragg, R.G., and Cochrane, C.G. (1986). Cytoskeletal and morphologic impact of cellular oxidant injury. Am. J. Pathol. 123, 454–464.
Hinshaw, D.B., Burger, J.M., Beals, T.F., Armstrong, B.C., and Hyslop, P.A. (1991). Actin polymerization in cellular oxidant injury. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 288, 311–316.
Ikeda, S., Yamaoka-Tojo, M., Hilenski, L., Patrushev, N.A., Anwar, G.M., Quinn, M.T., and Ushio-Fukai, M. (2005). IQGAP1 regulates reactive oxygen species-dependent endothelial cell migration through interacting with Nox2. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 25, 2295–2300.
Kandaswami, C., Lee, L.T., Lee, P.P., Hwang, J.J., Ke, F.C., Huang, Y.T., and Lee, M.T. (2005). The antitumor activities of flavonoids. In Vivo 19, 895–909.
Kurisu, S., Suetsugu, S., Yamazaki, D., Yamaguchi, H., and Takenawa, T. (2005). Rac-WAVE2 signaling is involved in the invasive and metastatic phenotypes of murine melanoma cells. Oncogene 24, 1309–1319.
Lee, S.H., Han, J.S., Heo, S.J., Hwang, J.Y., and Jeon, Y.J. (2010). Protective effects of dieckol isolated from Ecklonia cava against high glucose-induced oxidative stress in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 24, 375–381.
Meng, Q., Xia, C., Fang, J., Rojanasakul, Y., and Jiang, B.H. (2006). Role of PI3K and AKT specific isoforms in ovarian cancer cell migration, invasion and proliferation through the p70S6K1 pathway. Cell. Signal. 18, 2262–2271.
Miki, H., Miura, K., and Takenawa, T. (1996). N-WASP, a novel actin-depolymerizing protein, regulates the cortical cytoskeletal rearrangement in a PIP2-dependent manner downstream of tyrosine kinases. EMBO J. 15, 5326–5335.
Miki, H., Sasaki, T., Takai, Y., and Takenawa, T. (1998a). Induction of filopodium formation by a WASP-related actin-depolymerizing protein N-WASP. Nature 391, 93–96.
Miki, H., Yamaguchi, H., Suetsugu, S., and Takenawa, T. (2000). IRSp53 is an essential intermediate between Rac and WAVE in the regulation of membrane ruffling. Nature 408, 732–735.
Moldovan, L., Moldovan, N.I., Sohn, R.H., Parikh, S.A., and Goldschmidt-Clermont, P.J. (2000). Redox changes of cultured endothelial cells and actin dynamics. Circ. Res. 86, 549–557.
Omann, G.M., Harter, J.M., Burger, J.M., and Hinshaw, D.B. (1994). H2O2-induced increases in cellular F-actin occur without increases in actin nucleation activity. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 308, 407–412.
Pollard, T.D., and Borisy, G.G. (2003). Cellular motility driven by assembly and disassembly of actin filaments. Cell 112, 453–465.
Ryu, B., Li, Y., Qian, Z.J., Kim, M.M., and Kim, S.K. (2009). Differentiation of human osteosarcoma cells by isolated phlorotannins is subtly linked to COX-2, iNOS, MMPs, and MAPK signaling: implication for chronic articular disease. Chem. Biol. Interact. 179, 192–201.
Steinbrenner, H., Ramos, M.C., Stuhlmann, D., Mitic, D., Sies, H., and Brenneisen, P. (2005). Tumor promoter TPA stimulates MMP-9 secretion from human keratinocytes by activation of superoxide-producing NADPH oxidase. Free Radic. Res. 39, 245–253.
Suetsugu, S., Miki, H., and Takenawa, T. (1999). Identification of two human WAVE/SCAR homologues as general actin regulatory molecules which associate with the Arp2/3 complex. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 260, 296–302.
Suetsugu, S., Yamazaki, D., Kurisu, S., and Takenawa, T. (2003). Differential roles of WAVE1 and WAVE2 in dorsal and peripheral ruffle formation for fibroblast cell migration. Dev. Cell 5, 595–609.
Symons, M., Derry, J.M., Karlak, B., Jiang, S., Lemahieu, V., Mc-Cormick, F., Francke, U., and Abo, A. (1996). Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein, a novel effector for the GTPase CDC42Hs, is implicated in actin polymerization. Cell 84, 723–734.
Takenawa, T., and Miki, H. (2001). WASP and WAVE family proteins: key molecules for rapid rearrangement of cortical actin filaments and cell movement. J. Cell Sci. 114, 1801–1809.
Usatyuk, P.V., Gorshkova, I.A., He, D., Zhao, Y., Kalari, S.K., Garcia, J.G., and Natarajan, V. (2009). Phospholipase D-mediated activation of IQGAP1 through Rac1 regulates hyperoxiainduced p47phox translocation and reactive oxygen species generation in lung endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 15339–15352.
Ushio-Fukai, M., and Alexander, R.W. (2004). Reactive oxygen species as mediators of angiogenesis signaling: role of NAD(P)H oxidase. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 264, 85–97.
Wu, W.S. (2006). The signaling mechanism of ROS in tumor progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 25, 695–705.
Wu, R.F., Gu, Y., Xu, Y.C., Nwariaku, F.E., and Terada, L.S. (2003). Vascular endothelial growth factor causes translocation of p47phox to membrane ruffles through WAVE1. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 36830–36840.
Wu, R.F., Xu, Y.C., Ma, Z., Nwariaku, F.E., Sarosi, G.A., Jr., and Terada, L.S. (2005). Subcellular targeting of oxidants during endothelial cell migration. J. Cell Biol. 171, 893–904.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Park, S.J., Kim, Y.T. & Jeon, Y.J. Antioxidant dieckol downregulates the Rac1/ROS signaling pathway and inhibits Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP)-family verprolin-homologous protein 2 (WAVE2)-mediated invasive migration of B16 mouse melanoma cells. Mol Cells 33, 363–369 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-012-2285-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-012-2285-2