Abstract
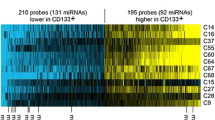
Increasing evidence demonstrates that miRNAs are involved in the dysregulation of tumor initiating cells (TICs) in various tumors. Due to a lack of definitive markers, cell sorting is not an ideal separation method for lung adenocarcinoma initiating cells. In this study, we combined paclitaxel with serum-free medium cultivation (inverse-induction) to enrich TICs from A549 cells, marked by CD133/CD326, defined features of stemness. We next investigated aberrant microRNAs in this subpopulation compared to normal cells with miRNA microarray and found that 50 miRNAs exhibited a greater than 2-fold change in expression. As further validation, 10 miRNAs were chosen to perform quantitative RT-PCR on the A549 cell line and primary samples. The results suggest that aberrant expression of miRNAs such as miR-29ab, miR-183, miR-17-5p and miR-127-3P may play an important role in regulating the bio-behavior of TICs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Hajj, M., Wicha, M.S., Hernandez, A.B., Morrison, S.J., and Clarke, M.F. (2003). Prospective identification of tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 3983–3988.
Bonnet, D., and Dick, J.E. (1997). Human acute myeloid leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates form a primitive hematopoietic cell. Nat. Med. 3, 730–737.
Bertolinia, G., Roza, L., Peregob, P., Tortoretob, M., Fontanellac, E., Gattib, L., Pratesib, G., Fabbrid, A., Andriania, F., Tinellib, S., et al. (2009). Highly tumorigenic lung cancer CD133+ cells display stem-like features and are spared by cisplatin treatment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 16281–16286.
Chiou, S.H., Yu, C.C., Huang, C.Y., Lin, S.C., Liu, C.J., Tsai, T.H., Chou, S.H., Chien, C.S., Ku, H.H., and Lo, J.F. (2008). Positive correlations of Oct-4 and Nanog in oral cancer stem-like cells and high-grade oral squamous cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 14, 4085–4095.
Cloonan, N., Brown, M.K., Steptoe, A.L., Wani, S., Chan, W.L., Forrest, A.R.R., Kolle, G., Gabrielli, B., and Grimmond, S.M. (2008). The miR-17-5p microRNA is a key regulator of the G1/S phase cell cycle transition. Genome Biol. 9, R127.
Collins, A.T., and Maitland, N.J. (2006). Prostate cancer stem cells. Eur. J. Cancer 42 1213–1218.
DeSano, J.T., and Xu, L. (2009). MicroRNA regulation of cancer stem cells and therapeutic implications. AAPS J. 11, 682–692.
Eramo, A., Lotti, F., Sette, G., Pilozzi, E., Biffoni, M., Virgilio, A.D., Conticello, C., Ruco, L., Peschle, C., and Maria, R.D. (2008). Identification and expansion of the tumorigenic lung cancer stem cell population. Cell Death Differ.15, 504–514.
Garzia, L., Andolfo, I., Cusanelli, E., Marino, N., Petrosino, G., Martino, D.D., Esposito, V., Galeone, A., Navas, L., Esposito, S., et al. (2009). MicroRNA-199b-5p impairs cancer stem cells through negative regulation of HES1 in medulloblastoma. PLOS One 4, e–4998.
Godlewskil, J., Nowicki, M.O., Bronisz, A., Williams, S., Otsuki, A., Nuovo, G., Chaudhury, A.R., Newton, H.B., Chiocca, E.A., and Lawler, S. (2008). Targeting of the Bmi-1 oncogene/stem cell renewal factor by microRNA-128 inhibits glioma proliferation and self-renewal. Cancer Res. 68, 9125–9130.
Hatfield, S., and Ruohola-Baker, H. (2008).microRNA and stem cell function. Cell Tissue Res. 331, 57–66.
Hermann, P.C., Huber, S.L., Herrler, T., Aicher, A., Ellwart, J.W., Guba, M., Bruns, C.J., and Heeschen, C. (2007). Distinct populations of cancer stem cells determine tumor growth and metastatic activity in human pancreatic cancer. Cell Stem Cell 1, 313–323.
Hossain, A., Kuo, M.T., and Saunders, G.F. (2006). Mir-17-5p regulates breast cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting translation of AIB1 mRNA. Mol. Cell. Biol. 26, 8191–8201.
Ji, J., Yamashita, T., Budhu, A., Forgues, M., Jia, H.L., Li, C., Deng, C., Wauthier, E., Reid, L.M., Ye, Q.H., et al. (2009). Identification of microRNA-181 by genome-wide screening as a critical player in EpCAM-positive hepatic cancer stem cells. Hepatology 50, 472–480.
Ji, Q., Hao, X., Zhang, M., Tang, W., Meng, Y., Li, L., Xiang, D., Jeffrey, T., Sano, D., Bommer, G.T., et al. (2009). MicroRNA miR-34 inhibits human pancreatic cancer tumor-initiating cells. PLOS One 4, e6816.
Jiang, J., Gusev, Y., Aderca, I., Mettler, T.A., Nagorney, D.M., Brackett, D.J., Roberts, L.R., and Schmittgen, T.D. (2008). Association of MicroRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinomas with hepatitis infection, cirrhosis, and patient survival. Clin. Cancer Res. 14, 419–427.
Levina, V., Marrangoni, A.M., DeMarco, R., Gorelik, E., and Lokshin, A.E. (2008). Drug-elected human lung cancer stem cells: cytokine network, tumorigenic and metastatic properties. PLOS One 3, e3077.
Li, G., Luna, C., Qiu, J., Epstein, D.L., and Gonzaenz, P. (2010). Targeting of integrinβ1 and kinesin 2A by microRNA 183. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 5461–5471.
Li, H., Bian, C., Liao, L., Li, J., and Zhao, R.C. (2011). miR-17-5p promotes human breast cancer cell migration and invasion through suppression HBP1. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 126. 565–575.
Li, J., Fu, H., Xu, C., Tie, Y., Xing, R., Zhu, J., Qin, Y., Sun, Z., and Zheng, X. (2011). MiR-183 inhibits TGFβ1-induced apoptosis by downregulation of PDCD4 expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. BMC Cancer 10, 354.
Lu, W., Thomson, J.M., Wong, H.Y.F., Hammond, S.M., and Hogan, B.L.M. (2007). Transgenic over-expression of the microRAN miR-17-92 cluster promotes proliferation and inhibits differenttiation of lung epithelial progenitor cells. Dev. Biol. 310, 442–453.
Ma, S., Tang, K., Chan, Y., Lee, T., Kwan, P., Castilho, A., Ng, I., Man, K., Wong, N., To, K.F., et al. (2010). miR-130b promotes CD133+ liver tumor-initiating cell growth and self-renewal via tumor protein 53-induced nuclear protein 1. Cell Stem Cell 7, 694–707.
Meng, X., Li, M., Wang, X., Wang, Y., and Ma, D. (2009). Both CD133+ and CD133− sub populations of A549 and H446 cells contain cancer-initiating cells. Cancer Sci. 100, 1040–1046.
Peacock, D.C., and Watkins, D.N. (2008). Cancer stem cells and the ontogeny of lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 26, 2883–2889.
Ricci-Vitiani, L., Lombardi, D.G., Pilozzi, E., Biffoni, M., Todaro, M., Peschle, C., and Maria, R.D. (2007). Identification and expansion of human colon-cancer-initiating cells. Nature 445, 111–115.
Saito, Y., Liang, G., Egger, G., Friedman, J.M., Chuang, J., Coetzee, G.A., and Jones, P.A. (2006). Specific activation of microRNA-127 with down-regulation of the proto-oncogene BCL6 by chromatin-modifying drugs in human cancer cells. Cancer Cell 9. 435–443.
Saver, A.L., Li, L.H., and Subramanian, S. (2010). MicroRNA miR-183 functions as an oncogene by targeting the transcription factor EGR1 and promoting tumor cell migration. Cancer Res. 70, 9570–9580.
Singh, S.K., Hawkins, C., Clarke, I.D., Squire, J.A., Bayani, J., Hide, T., Henkelman, R.M., Cusimano, M.D., and Dirks, P.B. (2004). Identification of a cancer stem cell in human brain tumors. Nature 432, 396–401.
Shan, S.W., Lee, D.Y., Deng, Z., Shatseva, T., Jeyapalan, Z., Du, W.W., Zhang, Y., Xuan, J.W., Yee, S.P., Siragam, V., et al. (2009). MicroRNA miR-17 retards tissue growth and represses fibronectin expression. Nat. Cell Biol. 11, 1031–1038.
Shi, L., Zhang, J.X., Pan, T.H., Zhou, J.F., Gong, W.Y., Liu, N., Fu, Z., and You, Y.P. (2010). MiR-125b is critical for the suppression of human U251 glioma stem cell proliferation. Brain Res. 1312, 120–126.
Shimono, Y., Zabala, M., Cho, R.W., Lobo, N., Dalerba, P., Qian, D., Diehn, M., Liu, H., Panula, S.P., Chiao, E., et al. (2009). Down-regulation of miRNA-200c links breast cancer stem cells with normal stem cells. Cell 138, 592–603.
Tagawa, H., Karube, K., Tsuzuki, S., Ohshima, K., Seto, M., and Tagawa, H. (2007). Synergistic action of the microRNA-17 polycistron and myc in aggressive cancer development. Cancer Sci. 98, 1482–1490.
Teng, Y., Wang, X.W., Wang, Y.W., and Ma, D.X. (2010). Wnt/beta-catenin signaling regulates cancer stem cells in lung cancer A549 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 392, 373–379.
Tirino, V., Camerlingo, R., Franco, R., Malanga, D., Rocca, A.L., Viglietto, G., Rocco, G., and Pirozzi, G. (2009). The role of CD133 in the identification and characterisation of tumour-initiating cells in non-small-cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 36, 446–453.
Tryndyak, V.P., Ross, S.A., Beland, F.A., and Pogribny, I.P. (2009). Down-regulation of the microRNAs miR-34a, miR-127, and miR-200b in rat liver during hepatocarcinogenesis induced by a methy1-deficient diet. Mol. Carcinog. 48, 479–487.
Ura, S., Honda, M., Yamashita, T., Ueda, T., Takatori, H., Nishino, R., Sunakozaka, H., Sakai, Y., Horimoto, K., and Kaneko, S. (2009). Differential microRNA expression between hepatitis B and hepatitis C leading disease progression to hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 49, 1098–1112.
Yu, F., Deng, H., Yao, H., Liu, Q., Su, F., and Song, E. (2010). Mir-30 reduction maintainsself-renewal and inhibits apoptosis in breast tumor-initiating cells. Oncogene 29, 4194–4204.
Wang, G. F., Mao, W.M., and Zheng, S. (2008). MicroRNA-183 regulates Ezrin expression in lung cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 582, 3663–3668.
Wang, Z.W., Li, Y.W., Ahmad, A., Azmi, A.S., Kong, D.J., Banerjee, S., and Sarkar, F.H. (2010). Targeting miRNAs involved in cancer stem cell and EMT regulation: an emerging concept in overcoming drug resistance. Drug Resist. Updat. 13 109–118.
Wiemer, E.A. (2007). The role of microRNAs in cancer: no small matter. Eur. J. Cancer 43, 1529–1544.
Wong, P., Iwasaki, M., Somervaille, T.C.P, Ficara, F., Carico, C., Arenold, C., Chen, C.Z., and Cleary, M. (2010). The miR-17-92 microrna polycistron regulates MLL leukemia stem cell potential by modulating p21 expression. Cancer Res. 70, 3383–3342.
Wellner, U., Schubert, J., Burk, U.C., Schmalhofer, O., Zhu, F., Sonntag, A., Waldvogel, B., Vannier, C., Darling, D., Hausen, A., et al. (2009).The EMT-activator ZEB1 promotes tumorigenicity by repressing stemness-inhibiting microRNAs. Nat. Cell Biol. 11, 1487–1495.
Zabierowski, S.E., and Herlyn, M. (2008). Melanoma stem cells: the dark seed of melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 26, 2890–2894.
Zhang, S., Balch, C., Chan, M.W., Lai, H.C., Matei, D., Schilder, J.M., Yan, P.S., Huang, T.H.M., and Nephew, K.P. (2008). Identification and characterization of ovarian cancer-initiating cells from primary human tumors, Cancer Res. 68, 4311–4320.
Zhang, M., Liu, Q., Mi, S., Liang, X., Zhang, Z., Su, X., Liu, J., Chen, Y., Wang, M., Zhang, Y., et al. (2011). Both miR-17-5p and miR-20a alleviate suppressive potential of myeloid-derived suppressor cells by modulating STAT3 expression. J. Immunol. 186, 4716–4724.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, S., Sun, Jg., Wu, Jb. et al. Aberrant microRNAs expression in CD133+/CD326+ human lung adenocarcinoma initiating cells from A549. Mol Cells 33, 277–283 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-012-2252-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-012-2252-y