Abstract
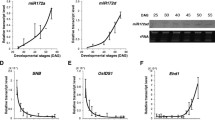
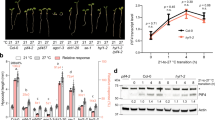
A moderate change in ambient temperature significantly affects plant physiology including flowering time. MiR399 and its target gene PHOSPHATE 2 (PHO2) are known to play a role in the maintenance of phosphate homeostasis. However, the regulation of flowering time by the miR399-PHO2 module has not been investigated. As we have previously identified miR399 as an ambient temperature-responsive miRNA, we further investigated whether a change in expression of the miR399-PHO2 module affects flowering time in response to ambient temperature changes. Here, we showed that miR399b-overexpressing plants and a loss-of-function allele of PHO2 (pho2) exhibited an early flowering phenotype only at normal temperature (23°C). Interestingly, their flowering time at lower temperature (16°C) was similar to that of wild-type plants, suggesting that alteration in flowering time by miR399 and its target PHO2 was seen only at normal temperature (23°C). Flowering time ratio (16°C/23°C) revealed that miR399b-overexpressing plants and pho2 mutants showed increased sensitivity to ambient temperature changes. Expression analysis indicated that expression of TWIN SISTER OF FT (TSF) was increased in miR399b-overexpressing plants and pho2 mutants at 23°C, suggesting that their early flowering phenotype is associated with TSF upregulation. Taken together, our results suggest that miR399, an ambient temperature-responsive miRNA, plays a role in ambient temperature-responsive flowering in Arabidopsis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aung, K., Lin, S.I., Wu, C.C., Huang, Y.T., Su, C.L., and Chiou, T.J. (2006). pho2, a phosphate overaccumulator, is caused by a nonsense mutation in a microRNA399 target gene. Plant Physiol. 141, 1000–1011.
Ausin, I., Alonso-Blanco, C., Jarillo, J.A., Ruiz-Garcia, L., and Martinez-Zapater, J.M. (2004). Regulation of flowering time by FVE, a retinoblastoma-associated protein. Nat. Genet. 36, 162–166.
Bari, R., Datt Pant, B., Stitt, M., and Scheible, W.R. (2006). PHO2, microRNA399, and PHR1 define a phosphate-signaling pathway in plants. Plant Physiol. 141, 988–999.
Chiou, T.J., Aung, K., Lin, S.I., Wu, C.C., Chiang, S.F., and Su, C.L. (2006). Regulation of phosphate homeostasis by MicroRNA in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 18, 412–421.
Devaiah, B.N., Madhuvanthi, R., Karthikeyan, A.S., and Raghothama, K.G. (2009). Phosphate starvation responses and gibberellic acid biosynthesis are regulated by the MYB62 transcription factor in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2, 43–58.
Franco-Zorrilla, J.M., Valli, A., Todesco, M., Mateos, I., Puga, M.I., Rubio-Somoza, I., Leyva, A., Weigel, D., Garcia, J.A., and Paz-Ares, J. (2007). Target mimicry provides a new mechanism for regulation of microRNA activity. Nat. Genet. 39, 1033–1037.
Hong, S.M., Bahn, S.C., Lyu, A., Jung, H.S., and Ahn, J.H. (2010). Identification and testing of superior reference genes for a starting pool of transcript normalization in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 51, 1694–1606.
Jang, S., Torti, S., and Coupland, G. (2009). Genetic and spatial interactions between FT, TSF and SVP during the early stages of floral induction in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 60, 614–625.
Jung, J.H., Seo, Y.H., Seo, P.J., Reyes, J.L., Yun, J., Chua, N.H., and Park, C.M. (2007). The GIGANTEA-regulated microRNA172 mediates photoperiodic flowering independent of CONSTANS in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 19, 2736–2748.
Kardailsky, I., Shukla, V.K., Ahn, J.H., Dagenais, N., Christensen, S.K., Nguyen, J.T., Chory, J., Harrison, M.J., and Weigel, D. (1999). Activation tagging of the floral inducer FT. Science 286, 1962–1965.
Kobayashi, Y., Kaya, H., Goto, K., Iwabuchi, M., and Araki, T. (1999). A pair of related genes with antagonistic roles in mediating flowering signals. Science 286, 1960–1962.
Kumar, S.V., and Wigge, P.A. (2010). H2A.Z-containing nucleosomes mediate the thermosensory response in Arabidopsis. Cell 140, 136–147.
Lee, J.H., Yoo, S.J., Park, S.H., Hwang, I., Lee, J.S., and Ahn, J.H. (2007). Role of SVP in the control of flowering time by ambient temperature in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev. 21, 397–402.
Lee, H., Yoo, S.J., Lee, J.H., Kim, W., Yoo, S.K., Fitzgerald, H., Carrington, J.C., and Ahn, J.H. (2010). Genetic framework for flowering-time regulation by ambient temperature-responsive miRNAs in Arabidopsis. Nucleic Acids Res. 38, 3081–3093.
Li, S., Zhou, X., Chen, L., Huang, W., and Yu, D. (2010). Functional characterization of Arabidopsis thaliana WRKY39 in heat stress. Mol. Cells 29, 475–483.
Lin, S.I., Chiang, S.F., Lin, W.Y., Chen, J.W., Tseng, C.Y., Wu, P.C., and Chiou, T.J. (2008). Regulatory network of microRNA399 and PHO2 by systemic signaling. Plant Physiol. 147, 732–746.
Macknight, R., Bancroft, I., Page, T., Lister, C., Schmidt, R., Love, K., Westphal, L., Murphy, G., Sherson, S., Cobbett, C., et al. (1997). FCA, a gene controlling flowering time in Arabidopsis, encodes a protein containing RNA-binding domains. Cell 89, 737–745.
Moon, J., Suh, S.S., Lee, H., Choi, K.R., Hong, C.B., Paek, N.C., Kim, S.G., and Lee, I. (2003). The SOC1 MADS-box gene integrates vernalization and gibberellin signals for flowering in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 35, 613–623.
Palatnik, J.F., Allen, E., Wu, X., Schommer, C., Schwab, R., Carrington, J.C., and Weigel, D. (2003). Control of leaf morphogenesis by microRNAs. Nature 425, 257–263.
Pant, B.D., Buhtz, A., Kehr, J., and Scheible, W.R. (2008). Micro-RNA399 is a long-distance signal for the regulation of plant phosphate homeostasis. Plant J. 53, 731–738.
Ramakers, C., Ruijter, J.M., Deprez, R.H., and Moorman, A.F. (2003). Assumption-free analysis of quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) data. Neurosci. Lett. 339, 62–66.
Scortecci, K., Michaels, S.D., and Amasino, R.M. (2003). Genetic interactions between FLM and other flowering-time genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol. Biol. 52, 915–922.
Sheldon, C.C., Rouse, D.T., Finnegan, E.J., Peacock, W.J., and Dennis, E.S. (2000). The molecular basis of vernalization: the central role of FLOWERING LOCUS C (FLC). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 3753–3758.
Simpson, G.G., and Dean, C. (2000). Environmental-dependent acceleration of a developmental switch: the floral transition. Sci. STKE 2000, pe1.
Sunkar, R., and Zhu, J.K. (2004). Novel and stress-regulated microRNAs and other small RNAs from Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16, 2001–2019.
Todesco, M., Rubio-Somoza, I., Paz-Ares, J., and Weigel, D. (2010). A collection of target mimics for comprehensive analysis of microRNA function in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Genet. 6, e1001031.
Udvardi, M.K., Czechowski, T., and Scheible, W.R. (2008). Eleven golden rules of quantitative RT-PCR. Plant Cell 20, 1736–1737.
Vandesompele, J., De Preter, K., Pattyn, F., Poppe, B., Van Roy, N., De Paepe, A., and Speleman, F. (2002). Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. 3, RESEARCH 0034.
Wang, J.W., Schwab, R., Czech, B., Mica, E., and Weigel, D. (2008). Dual effects of miR156-targeted SPL genes and CYP78A5/KLUH on plastochron length and organ size in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 20, 1231–1243.
Wang, J.W., Czech, B., and Weigel, D. (2009). miR156-regulated SPL transcription factors define an endogenous flowering pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana. Cell 138, 738–749.
Wu, G., Park, M.Y., Conway, S.R., Wang, J.W., Weigel, D., and Poethig, R.S. (2009). The sequential action of miR156 and miR172 regulates developmental timing in Arabidopsis. Cell 138, 750–759.
Yamaguchi, A., Kobayashi, Y., Goto, K., Abe, M., and Araki, T. (2005). TWIN SISTER OF FT (TSF) acts as a floral pathway integrator redundantly with FT. Plant Cell Physiol. 46, 1175–1189.
Yoo, S.K., Chung, K.S., Kim, J., Lee, J.H., Hong, S.M., Yoo, S.J., Yoo, S.Y., Lee, J.S., and Ahn, J.H. (2005). CONSTANS activates SUPPRESSOR OF OVEREXPRESSION OF CONSTANS 1 through FLOWERING LOCUS T to promote flowering in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 139, 770–778.
Yoo, S.K., Hong, S.M., Lee, J.S., and Ahn, J.H. (2011). A genetic screen for leaf movement mutants identifies a potential role for AGAMOUS-LIKE 6 (AGL6) in circadian-clock control. Mol. Cells 31, 281–287.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, W., Ahn, H.J., Chiou, TJ. et al. The role of the miR399-PHO2 module in the regulation of flowering time in response to different ambient temperatures in Arabidopsis thaliana . Mol Cells 32, 83–88 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-011-1043-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-011-1043-1