Abstract
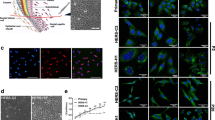
Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath/Epithelial rests of Malassez (HERS/ERM) cells are unique epithelial cells in the periodontal ligament. They remain in periodontal tissues through-out the adult life, and it is expected that their functional role is to maintain the homeostasis of the periodontium through reciprocal interactions with other periodontal cells. In this study, we investigated whether HERS/ERM cells have primitive stem cell characteristics: those of embryonic stem cells as well as of epithelial stem cells. Primary HERS/ERM cells had typical epithelial cell morphology and characteristics and they maintained for more than five passages. They expressed epithelial stem cell-related genes: ABCG2, ANp63, p75, EpCAM, and Bmi-1. Moreover, the expression of embryonic stem cell markers such as Oct-4, Nanog, and SSEA-4 were detected. Next, we investigated whether the expression of these stem cell markers was maintained during the sub-culture process. HERS/ERM cells showed different expression levels of these stemness genes at each passage, but their expression was maintained throughout the passages. Taken together, our data suggest that a primary culture of HERS/ERM cells contains a population of primitive stem cells that express epithelial stem cell markers and embryonic stem cell markers. Furthermore, these cell populations were maintained during the sub-culturing process in our culture conditions. Therefore, our findings suggest that there is a strong possibility of accomplishing cementum tissue engineering with HERS/ERM cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balzar, M., Winter, M.J., de Boer, C.J., and Litvinov, S.V. (1999). The biology of the 17-1A antigen (Ep-CAM). J. Mol. Med. 77, 699–712.
Barbareschi, M., Pecciarini, L., Cangi, M.G., Macri, E., Rizzo, A., Viale, G., and Doglioni, C. (2001). p63, a p53 homologue, is a selective nuclear marker of myoepithelial cells of the human breast. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 25, 1054–1060.
Chambers, I., Colby, D., Robertson, M., Nichols, J., Lee, S., Tweedie, S., and Smith, A. (2003). Functional expression cloning of Nanog, a pluripotency sustaining factor in embryonic stem cells. Cell 113, 643–655.
Cho, M., Lee, E.J., Nam, H., Yang, J.H., Cho, J., Lim, J.M., and Lee, G. (2010). Human feeder layer system derived from umbilical cord stromal cells for human embryonic stem cells. Fertil. Steril. 93, 2525–2531.
de Paiva, C.S., Chen, Z., Corrales, R.M., Pflugfelder, S.C., and Li, D.Q. (2005). ABCG2 transporter identifies a population of clonogenic human limbal epithelial cells. Stem Cells 23, 63–73.
De Paiva, C.S., Pflugfelder, S.C., and Li, D.Q. (2006). Cell size correlates with phenotype and proliferative capacity in human corneal epithelial cells. Stem Cells 24, 368–375.
Ding, X.W., Wu, J.H., and Jiang, C.P. (2010). ABCG2: a potential marker of stem cells and novel target in stem cell and cancer therapy. Life Sci. 86, 631–637.
Foster, B.L., Popowics, T.E., Fong, H.K., and Somerman, M.J. (2007). Advances in defining regulators of cementum development and periodontal regeneration. Curr. Top Dev. Biol. 78, 47–126.
Gang, E.J., Bosnakovski, D., Figueiredo, C.A., Visser, J.W., and Perlingeiro, R.C. (2007). SSEA-4 identifies mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow. Blood 109, 1743–1751.
Gronthos, S., Mankani, M., Brahim, J., Robey, P.G., and Shi, S. (2000). Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 13625–13630.
Izumi, K., Tobita, T., and Feinberg, S.E. (2007). Isolation of human oral keratinocyte progenitor/stem cells. J. Dent. Res. 86, 341–346.
Jacobs, J.J., and van Lohuizen, M. (1999). Cellular memory of transcriptional states by Polycomb-group proteins. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 10, 227–235.
Kaneko, H., Hashimoto, S., Enokiya, Y., Ogiuchi, H., and Shimono, M. (1999). Cell proliferation and death of Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath in the rat. Cell Tissue Res. 298, 95–103.
Kawanabe, N., Murata, S., Murakami, K., Ishihara, Y., Hayano, S., Kurosaka, H., Kamioka, H., Takano-Yamamoto, T., and Yamashiro, T. (2010). Isolation of multipotent stem cells in human periodontal ligament using stage-specific embryonic antigen-4. Differentiation 79, 74–83.
Milyavsky, M., Shats, I., Erez, N., Tang, X., Senderovich, S., Meerson, A., Tabach, Y., Goldfinger, N., Ginsberg, D., Harris, C. C., et al. (2003). Prolonged culture of telomerase-im-mortalized human fibroblasts leads to a premalignant phenotype. Cancer Res. 63, 7147–7157.
Mitsui, K., Tokuzawa, Y., Itoh, H., Segawa, K., Murakami, M., Takahashi, K., Maruyama, M., Maeda, M., and Yamanaka, S. (2003). The homeoprotein Nanog is required for maintenance of pluripotency in mouse epiblast and ES cells. Cell 113, 631–642.
Miura, M., Gronthos, S., Zhao, M., Lu, B., Fisher, L.W., Robey, P.G., and Shi, S. (2003). SHED: stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 5807–5812.
Molofsky, A.V., Pardal, R., Iwashita, T., Park, I.K., Clarke, M.F., and Morrison, S.J. (2003). Bmi-1 dependence distinguishes neural stem cell self-renewal from progenitor proliferation. Nature 425, 962–967.
Morsczeck, C., Gotz, W., Schierholz, J., Zeilhofer, F., Kuhn, U., Mohl, C., Sippel, C., and Hoffmann, K.H. (2005). Isolation of precursor cells (PCs) from human dental follicle of wisdom teeth. Matrix Biol. 24, 155–165.
Nakamura, T., Endo, K., and Kinoshita, S. (2007). Identification of human oral keratinocyte stem/progenitor cells by neurotrophin receptor p75 and the role of neurotrophin/p75 signaling. Stem Cells 25, 628–638.
Nam, H., and Lee, G. (2009). Identification of novel epithelial stem cell-like cells in human deciduous dental pulp. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 386, 135–139.
Okumura, T., Shimada, Y., Imamura, M., and Yasumoto, S. (2003). Neurotrophin receptor p75(NTR) characterizes human esophageal keratinocyte stem cells in vitro. Oncogene 22, 4017–4026.
Park, I.K., Qian, D., Kiel, M., Becker, M.W., Pihalja, M., Weissman, I.L., Morrison, S.J., and Clarke, M.F. (2003). Bmi-1 is required for maintenance of adult self-renewing haematopoietic stem cells. Nature 423, 302–305.
Parsa, R., Yang, A., McKeon, F., and Green, H. (1999). Association of p63 with proliferative potential in normal and neoplastic human keratinocytes. J. Invest. Dermatol. 113, 1099–1105.
Pellegrini, G., Dellambra, E., Golisano, O., Martinelli, E., Fantozzi, I., Bondanza, S., Ponzin, D., McKeon, F., and De Luca, M. (2001). p63 identifies keratinocyte stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 3156–3161.
Pyle, A.D., Lock, L.F., and Donovan, P.J. (2006). Neurotrophins mediate human embryonic stem cell survival. Nat. Biotechnol. 24, 344–350.
Raaphorst, F.M., Otte, A.P., and Meijer, C.J. (2001). Polycombgroup genes as regulators of mammalian lymphopoiesis. Trends Immunol. 22, 682–690.
Romano, A.C., Espana, E.M., Yoo, S.H., Budak, M.T., Wolosin, J.M., and Tseng, S.C. (2003). Different cell sizes in human limbal and central corneal basal epithelia measured by confocal microscopy and flow cytometry. Invest Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 44, 5125–5129.
Rosner, M.H., Vigano, M.A., Ozato, K., Timmons, P.M., Poirier, F., Rigby, P.W., and Staudt, L.M. (1990). A POU-domain transcription factor in early stem cells and germ cells of the mammalian embryo. Nature 345, 686–692.
Scholer, H.R., Ruppert, S., Suzuki, N., Chowdhury, K., and Gruss, P. (1990). New type of POU domain in germ line-specific protein Oct-4. Nature 344, 435–439.
Seo, B.M., Miura, M., Gronthos, S., Bartold, P.M., Batouli, S., Brahim, J., Young, M., Robey, P.G., Wang, C.Y., and Shi, S. (2004). Investigation of multipotent postnatal stem cells from human periodontal ligament. Lancet 364, 149–155.
Shin, D.M., Liu, R., Klich, I., and Ratajczak, M.Z. (2010). Molecular characterization of isolated from murine adult tissues very small embryonic/epiblast like stem cell (VSELs). Mol. Cells 29, 533–538.
Sonoyama, W., Liu, Y., Fang, D., Yamaza, T., Seo, B.M., Zhang, C., Liu, H., Gronthos, S., Wang, C.Y., Wang, S., et al. (2006). Mesenchymal stem cell-mediated functional tooth regeneration in swine. PLoS One 1, e79.
Sonoyama, W., Seo, B.M., Yamaza, T., and Shi, S. (2007). Human Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath cells play crucial roles in cementum formation. J. Dent. Res. 86, 594–599.
Sonoyama, W., Liu, Y., Yamaza, T., Tuan, R.S., Wang, S., Shi, S., and Huang, G.T. (2008). Characterization of the apical papilla and its residing stem cells from human immature permanent teeth: a pilot study. J. Endod. 34, 166–171.
Spouge, J.D. (1980). A new look at the rests of Malassez. A review of their embryological origin, anatomy, and possible role in periodontal health and disease. J. Periodontol. 51, 437–444.
Stripp, B.R. (2008). Hierarchical organization of lung progenitor cells: is there an adult lung tissue stem cell? Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 5, 695–698.
Sundberg, M., Jansson, L., Ketolainen, J., Pihlajamaki, H., Suuronen, R., Skottman, H., Inzunza, J., Hovatta, O., and Narkilahti, S. (2009). CD marker expression profiles of human embryonic stem cells and their neural derivatives, determined using flowcytometric analysis, reveal a novel CD marker for exclusion of pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Res. 2, 113–124.
Thomson, J.A., Kalishman, J., Golos, T.G., Durning, M., Harris, C.P., Becker, R.A., and Hearn, J.P. (1995). Isolation of a primate embryonic stem cell line. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 7844–7848.
Thomson, J.A., Itskovitz-Eldor, J., Shapiro, S.S., Waknitz, M.A., Swiergiel, J.J., Marshall, V.S., and Jones, J.M. (1998). Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science 282, 1145–1147.
Verstappen, J., Katsaros, C., Torensma, R., and Von den Hoff, J.W. (2009). A functional model for adult stem cells in epithelial tissues. Wound Repair Regen. 17, 296–305.
Volponi, A.A., Pang, Y., and Sharpe, P.T. (2010). Stem cell-based biological tooth repair and regeneration. Trends Cell Biol. 20, 715–722.
Wentz, F.M., Weinmann, J.P., and Schour, I. (1950). The prevalence, distribution, and morphologic changes of the epithelial remnants in the molar region of the rat. J. Dent. Res. 29, 637–646.
Yang, A., Kaghad, M., Wang, Y., Gillett, E., Fleming, M.D., Dotsch, V., Andrews, N.C., Caput, D., and McKeon, F. (1998). p63, a p53 homolog at 3q27–29, encodes multiple products with transactivating, death-inducing, and dominant-negative activities. Mol. Cell 2, 305–316.
Yang, A., Schweitzer, R., Sun, D., Kaghad, M., Walker, N., Bronson, R.T., Tabin, C., Sharpe, A., Caput, D., Crum, C., et al. (1999). p63 is essential for regenerative proliferation in limb, craniofacial and epithelial development. Nature 398, 714–718.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Nam, H., Kim, J., Park, J. et al. Expression profile of the stem cell markers in human Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath/Epithelial rests of Malassez cells. Mol Cells 31, 355–360 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-011-0045-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-011-0045-3