Abstract
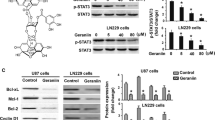
Caffeine is the most commonly ingested methylxanthine and has anti-cancer effects in several types of cancer. In this study, we examined the anti-cancer effects of caffeine on gliomas, both in vitro and in vivo. In vitro, caffeine treatment reduced glioma cell proliferation through G0/G1-phase cell cycle arrest by suppressing Rb phosphorylation. In addition, caffeine induced apoptosis through caspase-3 activation and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) cleavage. Caffeine also phosphorylated serine 9 of glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3β). Pretreatment with H89, a pharmacological inhibitor of protein kinase A (PKA), was able to antagonize caffeine-induced GSK3βser9 phosphorylation, suggesting that the mechanism might involve a cAMP-dependent PKA-dependent pathway. In vivo, caffeine-treated tumors exhibited reduced proliferation and increased apoptosis compared with vehicle-treated tumors. These results suggest that caffeine induces cell cycle arrest and caspase-dependent cell death in glioma cells, supporting its potential use in chemotherapeutic options for malignant gliomas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blomgren, K., Leist, M., and Groc, L. (2007). Pathological apoptosis in the developing brain. Apoptosis 12, 993–1010.
Bode, A.M., and Dong, Z. (2007). The enigmatic effects of caffeine in cell cycle and cancer. Cancer Lett. 247, 26–39.
Choi, B.H., Kim, C.G., Bae, Y.S., Lim, Y., Lee, Y.H., and Shin, S.Y. (2008). p21Waf1/Cip1 expression by curcumin in U-87MG human glioma cells: role of early growth response-1 expression. Cancer Res. 68, 1369–1377.
Conney, A.H., Zhou, S., Lee, M.J., Xie, J.G., Yang, C.S., Lou, Y.R., and Lu, Y. (2007). Stimulatory effect of oral administration of tea, coffee or caffeine on UVB-induced apoptosis in the epidermis of SKH-1 mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 224, 209–213.
Daly, J.W., and Fredholm, B.B. (1998). Caffeine-an atypical drug of dependence. Drug Alcohol Depend. 51, 199–206.
Doble, B.W., and Woodgett, J.R. (2003). GSK-3: tricks of the trade for a multi-tasking kinase. J. Cell Sci. 116, 1175–1186.
Fang, X., Yu, S.X., Lu, Y., Bast, R.C. Jr., Woodgett, J.R., and Mills, G.B. (2000). Phosphorylation and inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 by protein kinase A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 11960–11965.
Fredholm, B.B., Bättig, K., Holmén, J., Nehlig, A., and Zvartau, E.E. (1999). Actions of caffeine in the brain with special reference to factors that contribute to its widespread use. Pharmacol. Rev. 51, 83–133.
Gabrielli, B., Chau, Y.Q., Giles, N., Harding, A., Stevens, F., and Beamish, H. (2007). Caffeine promotes apoptosis in mitotic spindle checkpoint-arrested cells. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 6954–6964.
Hashimoto, T., He, Z., Ma, W.Y., Schmid, P.C., Bode, A.M., Yang, C.S., and Dong, Z. (2004). Caffeine inhibits cell proliferation by G0/G1 phase arrest in JB6 cells. Cancer Res. 64, 3344–3349.
He, Z., Ma, W.Y., Hashimoto, T., Bode, A.M., Yang, C.S., and Dong, Z. (2003). Induction of apoptosis by caffeine is mediated by the p53, Bax, and caspase 3 pathway. Cancer Res. 63, 4396–4401.
Hino, S., Tanji, C., Nakayama, K.I., and Kikuchi, A. (2005). Phosphorylation of beta-catenin by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase stabilizes beta-catenin through inhibition of its ubiquitination. Mol. Cell. Biol. 25, 9063–9072.
Holick, C.N., Smith, S.G., Giovannucci, E., and Michaud, D.S. (2010). Coffee, tea, caffeine intake, and risk of adult glioma in three prospective cohort studies. Cancer Epodemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 19, 39–47.
Jang, M.H., Shin, M.C., Kang, I.S., Baik, H.H., Cho, Y.H., Chu, J.P., Kim, E.H., and Kim, C.J. (2002). Caffeine induces apoptosis in human neuroblastoma cell line SK-N-MC. J. Korean Med. Sci. 17, 674–678.
Kang, J.Y., Kim, J.J., Jang, S.Y., and Bae, Y.S. (2009). The p53-p21(Cip1/WAF1) pathway is necessary for cellular senescence induced by the inhibition of protein kinase CKII in human colon cancer cells. Mol. Cells 28, 489–94.
Kang, S.S., Han, K.S., Ku, B.M., Lee, Y.K., Hong, J., Shin, H.Y., Almonte, A.G., Woo, D.H., Brat, D.F., Hwang, E.M., et al. (2010). Caffeine-mediated inhibition of calcium release channel inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor subtype 3 blocks glioblastoma invasion and extends survival. Cancer Res. 70, 1173–1183.
Lee, S.H., Pyo, C.W., Hahm, D.H., Kim, J., and Choi, S.Y. (2009). Iron-saturated lactoferrin stimulates cell cycle progression through PI3K/Akt pathway. Mol. Cells 28, 37–42.
Lu, G., Liao, J., Yang, G., Reuhl, K.R., Hao, X., and Yang, C.S. (2006). Inhibition of adenoma progression to adenocarcinoma in a 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone-induced lung tumorigenesis model in A/J mice by tea polyphenols and caffeine. Cancer Res. 66, 11494–11501.
Luo, J. (2009) Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta (GSK3beta) in tumorigenesis and cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Lett. 273, 194–200.
Maddika, S., Ande, S.R., Panigrahi, S., Paranjothy, T., Weglarczyk, K., Zuse, A., Eshraghi, M., Manda, K.D., Wiechec, E., and Los, M. (2007). Cell survival, cell death and cell cycle pathways are interconnected: implications for cancer therapy. Drug Resist. Updat. 10, 13–29.
Miyashita, K., Kawakami, K., Nakada, M., Mai, W., Shakoori, A., Fujisawa, H., Hayashi, Y., Hamada, J., and Minamoto, T. (2009). Potential therapeutic effect of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta inhibition against human glioblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 15, 887–897.
Nakada, M., Nakada, S., Demuth, T., Tran, N.L., Hoelzinger, D.B., and Berens, M.E. (2007). Molecular targets of glioma invasion. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 64, 458–478.
Nomura, M., Ichimatsu, D., Moritani, S., Koyama, I., Dong, Z., Yokogawa, K., and Miyamoto, K. (2005). Inhibition of epidermal growth factor-induced cell transformation and Akt activation by caffeine. Mol. Carcinog. 44, 67–76.
Ohtani, N., Yamakoshi, K., Takahashi, A., and Hara, E. (2004). The p16INK4a-RB pathway: molecular link between cellular senescence and tumor suppression. J. Med. Invest. 51, 146–153.
Okano, J., Nagahara, T., Matsumoto, K., and Murawaki, Y. (2008). Caffeine inhibits the proliferation of liver cancer cells and activates the MEK/ERK/EGFR signaling pathway. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 102, 543–551.
Qi, W., Qiao, D., and Martinez, J.D. (2002). Caffeine induces TP53-independent G(1)-phase arrest and apoptosis in human lung tumor cells in a dose-dependent manner. Radiat. Res. 157, 166–174.
Stupp, R., Hegi, M.E., Gilbert, M.R., and Chakravarti, A. (2007). Chemoradiotherapy in malignant glioma: standard of care and future directions. J. Clin. Oncol. 25, 4127–4136.
Tsai, N.M., Chen, Y.L., Lee, C.C., Lin, P.C., Cheng, Y.L., Chang, W.L., Lin, S.Z., and Harn, H.J. (2006). The natural compound nbutylidenephthalide derived from Angelica sinensis inhibits malignant brain tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. J. Neurochem. 99, 1251–1262.
Villano, J.L., Seery, T.E., and Bressler, L.R. (2009). Temozolomide in malignant gliomas: current use and future targets. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 64, 647–655.
Yang, H., Rouse, J., Lukes, L., Lancaster, M., Veenstra, T., Zhou, M., Shi, Y., Park, Y.G., and Hunter, K. (2004). Caffeine suppersses metastasis in a transgenic mouse model: a prototype molecule for prophylaxis of metastasis. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 21, 719–735.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Ku, B.M., Lee, Y.K., Jeong, J.Y. et al. Caffeine inhibits cell proliferation and regulates PKA/GSK3β pathways in U87MG human glioma cells. Mol Cells 31, 275–279 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-011-0027-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-011-0027-5