Abstract
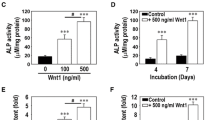
Wnt/β-catenin signaling has been known to influence bone formation and homeostasis. In this study, we investigated the canonical Wnt signaling regulation of osteogenic differentiation from periodontal ligament (PDL) fibroblasts. Stimulating PDL fibroblasts with lithium chloride (LiCl), a canonical Wnt activator, significantly increased mineralized nodule and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity in a time- and dose-dependent manner. LiCl up-regulated protein expression of osteogenic transcription factors, including the runt-related gene 2, Msx2, and Osterix 2, in the PDL fibroblasts. Treatment of these cells with LiCl also increased the mRNA levels of ALP, FosB, and Fra1 in a dose-dependent manner. Blockage of canonical Wnt signaling by treating the cells with DKK1 inhibited Wnt1-stimulated mRNA expression of these osteogenic factors. Furthermore, pretreatment with DKK1 reduced the ALP activity and matrix mineralization stimulated by Wnt1. Collectively, these results suggest that canonical Wnt signaling leads to the differentiation of PDL fibroblasts into osteogenic lineage with the attendant stimulation of osteogenic transcription factors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amantea, C.M., Kim, W.K., Meliton, V., Tetradis, S., and Parhami, F. (2008). Oxysterol-induced osteogenic differentiation of marrow stromal cells is regulated by Dkk-1 inhibitable and PI3-kinase mediated signaling. J. Cell. Biochem. 105, 424–436.
Bennett, C.N., Longo, K.A., Wright, W.S., Suva, L.J., Lane, T.F., Hankenson, K.D., and MacDougald, O.A. (2005). Regulation of osteoblastogenesis and bone mass by Wnt10b. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 3324–3329.
Bennett, C.N., Ouyang, H., Ma, Y.L., Zeng, Q., Gerin, I., Sousa, K.M., Lane, T.F., Krishnan, V., Hankenson, K.D., and MacDougald, O.A. (2007). Wnt10b increases postnatal bone formation by enhancing osteoblast differentiation. J. Bone Miner. Res. 22, 1924–1932.
Bordin, S., Page, R.C., and Narayanan, A.S. (1984). Heterogeneity of normal human diploid fibroblasts: Isolation and characterization of one phenotype. Science 223, 171–173.
Bradbury, J.M., Niemeyer, C.C., Dale, T.C., and Edwards, P.A. (1994). Alterations of the growth characteristics of the fibroblast cell line C3H 10T1/2 by members of the Wnt gene family. Oncogene 9, 2597–2603.
Bradford, M.M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–254.
Cheng, S.L., Shao, J.S., Cai, J., Sierra, O.L., and Towler, D.A. (2008). Msx2 exerts bone anabolism via canonical Wnt signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 20505–20522.
Clément-Lacroix, P., Ai, M., Morvan, F., Roman-Roman, S., Vayssière, B., Belleville, C., Estrera, K., Warman, M.L., Baron, R., and Rawadi, G. (2005). Lrp5-independent activation of Wnt signaling by lithium chloride increases bone formation and bone mass in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 17406–17411.
Day, T.F., Guo, X., Garrett-Beal, L., and Yang, Y. (2005). Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in mesenchymal progenitors controls osteoblast and chondrocyte differentiation during vertebrate skeletogenesis. Dev. Cell 8, 739–750.
Deng, Z.L., Sharff, K.A., Tang, N., Song, W.X., Luo, J., Luo, X., Chen, J., Bennett, E., Reid, R., Manning, D., et al. (2008). Regulation of osteogenic differentiation during skeletal development. Front Biosci. 13, 2001–2021.
Franceschi, R.T., Ge, C., Xiao, G., Roca, H., and Jiang, D. (2007). Transcriptional regulation of osteoblasts. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 1116, 196–207.
Gaur, T., Lengner, C.J., Hovhannisyan, H., Bhat, R.A., Bodine, P.V., Komm, B.S., Javed, A., van Wijnen, A.J., Stein, J.L., Stein, G.S., et al. (2005). Canonical WNT signaling promotes osteogenesis by directly stimulating Runx2 gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 33132–33140.
Gong, Y., Slee, R.B., Fukai, N., Rawadi, G., Roman-Roman, S., Reginato, A.M., Wang, H., Cundy, T., Glorieux, F.H., Lev, D., et al. (2001). LDL receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) affects bone accrual and eye development. Cell 107, 513–523.
Gordon, M.D., and Nusse, R. (2006). Wnt signaling: multiple pathways, multiple receptors, and multiple transcription factors. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 22429–22433.
Haasper, C., Jagodzinski, M., Drescher, M., Meller, R., Wehmeier, M., Krettek, C., and Hesse, E. (2008). Cyclic strain induces FosB and initiates osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal cells. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 59, 355–363.
Han, C., Yang, Z., Zhou, W., Jin, F., Song, Y., Wang, Y., Huo, N., Chen, L., Qian, H., Hou, R., et al. (2009). Periapical follicle stem cell: a promising candidate for cementum/periodontal ligament regeneration and bio-root engineering. Stem Cells Dev. 19, 1405–1415.
Hartmann, C. (2007). Skeletal development-Wnts are in control. Mol. Cells 24, 177–184.
He, X., Semenov, M., Tamai, K., and Zeng, X. (2004). LDL receptor-related proteins 5 and 6 in Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: arrows point the way. Development 131, 1663–1677.
Howard, P.S., Kucich, U., Taliwal, R., and Korostoff, J.M. (1998). Mechanical forces alter extracellular matrix synthesis by human periodontal ligament fibroblasts. J. Periodontal Res. 33, 500–508.
Ichida, F., Nishimura, R., Hata, K., Matsubara, T., Ikeda, F., Hisada, K., Yatani, H., Cao, X., Komori, T., Yamaguchi, A., et al. (2004). Reciprocal roles of MSX2 in regulation of osteoblast and adipocyte differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 34015–34022.
Jochum, W., David, J.P., Elliott, C., Wutz, A., Plenk Jr, H., Matsuo, K., and Wagner, E.F. (2000). Increased bone formation and osteosclerosis in mice overexpressing the transcription factor Fra-1. Nat. Med. 6, 980–984.
Komori, T. (2005). Regulation of skeletal development by the Runx family of transcription factors. J. Cell. Biochem. 95, 445–453.
Kook, S.H., Hwang, J.M., Park, J.S., Kim, E.M., Heo, J.S., Jeon, Y.M., and Lee, J.C. (2009). Mechanical force induces type I collagen expression in human periodontal ligament fibroblasts through activation of ERK/JNK and AP-1. J. Cell. Biochem. 106, 1060–1067.
Krishnan, V., Bryant, H.U., and Macdougald, O.A. (2006). Regulation of bone mass by Wnt signaling. J. Clin. Invest. 116, 1202–1209.
Liu, F., Kohlmeier, S., and Wang, C.Y. (2008) Wnt signaling and skeletal development. Cell. Signal. 20, 999–1009.
Mao, B., Wu, W., Li, Y., Hoppe, D., Stannek, P., Glinka, A., and Niehrs, C. (2001). LDL receptor-related protein 6 is a receptor for Dickkopf proteins. Nature 411, 321–325.
Mao, B., Wu, W., Davidson, G., Marhold, J., Li, M., Mechler, B.M., Delius, H., Stannek, P., Walter, C., Glinka, A., et al. (2002). Kremen proteins are Dickkopf receptors that regulate Wnt/β-catenin signalling. Nature 417, 664–647.
Maulik, N., Sato, M., Price, B.D., and Das, D.K. (1998). An essential role of NF-kappaB in tyrosine kinase signaling of p38 MAP kinase regulation of myocardial adaptation to ischemia. FEBS Lett. 429, 365–369.
McCulloch, C.A., and Bordin, S. (1991). Role of fibroblast subpopulations in periodontal physiology and pathology. J. Periodontal Res. 26, 144–154.
Morvan, F., Boulukos, K., Clément-Lacroix, P., Roman Roman, S., Suc-Royer, I., Vayssière, B., Ammann, P., Martin, P., Pinho, S., Pognonec, P., et al. (2006). Deletion of a single allele of the Dkk1 gene leads to an increase in bone formation and bone mass. J. Bone Miner. Res. 21, 934–945.
Nakashima, K., Zhou, X., Kunkel, G., Zhang, Z., Deng, J.M., Behringer, R.R., and de Crombrugghe, B. (2002). The novel zinc finger-containing transcription factor osterix is required for osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Cell 108, 17–29.
Nusse, R. (2005). Wnt signaling in disease and in development. Cell Res. 15, 28–32.
Qiang, Y.W., Barlogie, B., Rudikoff, S., and Shaughnessy, J.D. Jr. (2008). Dkk1-induced inhibition of Wnt signaling in osteoblast differentiation is an underlying mechanism of bone loss in multiple myeloma. Bone 42, 669–680.
Roberts, W.E., Mozsary, P.G., and Klingler, E. (1982). Nuclear size as a cell-kinetic marker for osteoblast differentiation. Am. J. Anat. 165, 373–384.
Rodda, S.J., and McMahon, A.P. (2006). Distinct roles for Hedgehog and canonical Wnt signaling in specification, differentiation and maintenance of osteoblast progenitors. Development 133, 3231–3244.
ten Dijke, P., Krause, C., de Gorter, D.J., Lowik, C.W., and van Bezooijen, R.L. (2008). Osteocyte-derived sclerostin inhibits bone formation: its role in bone morphogenetic protein and Wnt signaling. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 90, 31–35.
Westendorf, J.J., Kahler, R.A., and Schroeder, T.M. (2004). Wnt signaling in osteoblasts and bone diseases. Gene 341, 19–39.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Heo, J.S., Lee, SY. & Lee, JC. Wnt/β-catenin signaling enhances osteoblastogenic differentiation from human periodontal ligament fibroblasts. Mol Cells 30, 449–454 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-010-0139-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-010-0139-3