Abstract
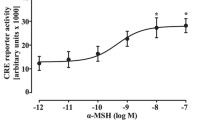
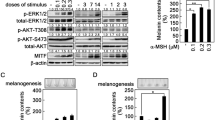
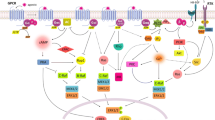
CRE-driven luciferase reporter is commonly used in drug screening systems involving G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). In a screen campaign designed to search for melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) agonists, podophyllotoxin, a microtubules disruptor, was found to induce cAMPresponsive element (CRE)-driven reporter expression. MC4R was not involved because podophyllotoxin induced CREB activation and CRE-driven transcription in cells not expressing MC4R. Previous studies indicated that intracellular calcium, PKA, and MAPKs are involved in CREB phosphorylation and activation. Our studies revealed that podophyllotoxin did not affect intracellular calcium level and the phosphorylation state of p38. Podophyllotoxin induced JNK and ERK activation, but blockade of JNK and ERK activation with specific inhibitors had no effect on podophyllotoxininduced CREB activation and CRE-regulated gene expression. Further experiments revealed that H89, a specific inhibitor of PKA, significantly inhibited podophyllotoxin-induced CREB activation. Podophyllotoxin itself did not alter intracellular cAMP level. Taken together, podophyllotoxin induces CREB activation and CRE-driven gene expression via PKA activation by a cAMP-independent mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreu, J.M., and Timasheff, S.N. (1982). Conformational states of tubulin liganded to colchicine, tropolone methyl ether, and podophyllotoxin. Biochemistry 21, 6465–6476.
Berridge, M.J. (1993). Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature 361, 315–325.
Beutner, K.R., and von Krogh, G. (1990). Current status of podophyllotoxin for the treatment of genital warts. Semin. Dermatol. 9, 148–151.
Boldt, S., Weidle, U.H., and Kolch, W. (2002). The role of MAPK pathways in the action of chemotherapeutic drugs. Carcinogenesis 23, 1831–1838.
Bu, J., Ma, P.C., Chen, Z.Q., Zhou, W.Q., Fu, Y.J., Li, L.J., and Li, C.R. (2008). Inhibition of MITF and tyrosinase by paeonol-stimulated JNK/SAPK to reduction of phosphorylated CREB. Am. J. Chin. Med. 36, 245–263.
Chang, L., and Karin, M. (2001). Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature 410, 37–40.
Chijiwa, T., Mishima, A., Hagiwara, M., Sano, M., Hayashi, K., Inoue, T., Naito, K., Toshioka, T., and Hidaka, H. (1990). Inhibition of forskolin-induced neurite outgrowth and protein phosphorylation by a newly synthesized selective inhibitor of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, N-[2-(p-bromocinnamylamino) ethyl]-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide (H-89), of PC12D pheochromocytoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 5267–5272.
Choi, H.J., Park, Y.G., and Kim, C.H. (2007). Lactosylceramide alpha2,3-sialyltransferase is induced via a PKC/ERK/CREB-dependent pathway in K562 human leukemia cells. Mol. Cells 23, 138–144.
Conkright, M.D., Guzman, E., Flechner, L., Su, A.I., Hogenesch, J.B., and Montminy, M. (2003). Genome-wide analysis of CREB target genes reveals a core promoter requirement for cAMP responsiveness. Mol. Cell 11, 1101–1108.
Cramer, T., Juttner, S., Plath, T., Mergler, S., Seufferlein, T., Wang, T.C., Merchant, J., and Hocker, M. (2008). Gastrin transactivates the chromogranin A gene through MEK-1/ERK- and PKC-dependent phosphorylation of Sp1 and CREB. Cell Signal. 20, 60–72.
Dai, K., Kobayashi, R., and Beach, D. (1996). Physical interaction of mammalian CDC37 with CDK4. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 22030–22034.
Damayanthi, Y., and Lown, J.W. (1998). Podophyllotoxins: current status and recent developments. Curr. Med. Chem. 5, 205–252.
Deak, M., Clifton, A.D., Lucocq, L.M., and Alessi, D.R. (1998). Mitogen- and stress-activated protein kinase-1 (MSK1) is directly activated by MAPK and SAPK2/p38, and may mediate activation of CREB. EMBO J. 17, 4426–4441.
Du, K., and Montminy, M. (1998). CREB is a regulatory target for the protein kinase Akt/PKB. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 32377–32379.
Ferraris, J.D., Persaud, P., Williams, C.K., Chen, Y., and Burg, M.B. (2002). cAMP-independent role of PKA in tonicity-induced transactivation of tonicity-responsive enhancer/ osmotic response element-binding protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 16800–16805.
Francis, H., Glaser, S., Demorrow, S., Gaudio, E., Ueno, Y., Venter, J., Dostal, D., Onori, P., Franchitto, A., Marzioni, M., et al. (2008). Small mouse cholangiocytes proliferate in response to H1 histamine receptor stimulation by activation of the IP3/CaMK I/CREB pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 295, C499–513.
Gordaliza, M., Castro, M.A., Garcia-Gravalos, M.D., Ruiz, P., Miguel del Corral, J.M., and San Feliciano, A. (1994). Antineoplastic and antiviral activities of podophyllotoxin related lignans. Arch. Pharm. 327, 175–179.
Gordaliza, M., Garcia, P.A., del Corral, J.M., Castro, M.A., and Gomez-Zurita, M.A. (2004). Podophyllotoxin: distribution, sources, applications and new cytotoxic derivatives. Toxicon 44, 441–459.
Gudi, T., Lohmann, S.M., and Pilz, R.B. (1997). Regulation of gene expression by cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase requires nuclear translocation of the kinase: identification of a nuclear localization signal. Mol. Cell Biol. 17, 5244–5254.
Gullingsrud, J., Kim, C., Taylor, S.S., and McCammon, J.A. (2006). Dynamic binding of PKA regulatory subunit RI alpha. Structure 14, 141–149.
Hande, K.R. (1998). Etoposide: four decades of development of a topoisomerase II inhibitor. Eur. J. Cancer 34, 1514–1521.
Huang, T.S., Lee, C.C., Chao, Y., Shu, C.H., Chen, L.T., Chen, L.L., Chen, M.H., Yuan, C.C., and Whang-Peng, J. (1999). A novel podophyllotoxin-derived compound GL331 is more potent than its congener VP-16 in killing refractory cancer cells. Pharm. Res. 16, 997–1002.
Igarashi, Y. (1997). Functional roles of sphingosine, sphingosine 1-phosphate, and methylsphingosines: in regard to membrane sphingolipid signaling pathways. J. Biochem. 122, 1080–1087.
Jia, W.P. (2005). Gene symbol: mc4r. Disease: obesity. Hum. Genet. 118, 548.
Johannessen, M., Delghandi, M.P., and Moens, U. (2004). What turns CREB on? Cell Signal. 16, 1211–1227.
Johnson, G.L., and Lapadat, R. (2002). Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and p38 protein kinases. Science 298, 1911–1912.
Kaplan, I.W. (1942). Condylomata acuminata. New Orleans Med. Surg. J. 94, 388–390.
Kitamura, T., Kimura, K., Jung, B.D., Makondo, K., Sakane, N., Yoshida, T., and Saito, M. (2002). Proinsulin C-peptide activates cAMP response element-binding proteins through the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in mouse lung capillary endothelial cells. Biochem. J. 3, 737–744.
Kurosu, T., Hernandez, A.I., Wolk, J., Liu, J., and Schwartz, J.H. (2009). Alpha/beta-tubulin are A kinase anchor proteins for type I PKA in neurons. Brain Res. 1251, 53–64.
Lee, E.J., Lee, S.H., Jung, J.W., Lee, W., Kim, B.J., Park, K.W., Lim, S.K., Yoon, C.J., and Baik, J.H. (2001). Differential regulation of cAMP-mediated gene transcription and ligand selectivity by MC3R and MC4R melanocortin receptors. Eur. J. Biochem. 268, 582–591.
Liang, M.H., Wendland, J.R., and Chuang, D.M. (2008). Lithium inhib- its Smad3/4 transactivation via increased CREB activity induced by enhanced PKA and AKT signaling. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 37, 440–453.
Lin, S., Huang, H.C., Chen, L.L., Lee, C.C., and Huang, T.S. (2001). GL331 induces down-regulation of cyclin D1 expression via enhanced proteolysis and repressed transcription. Mol. Pharmacol. 60, 768–775.
Loos, R.J., Lindgren, C.M., Li, S., Wheeler, E., Zhao, J.H., Prokopenko, I., Inouye, M., Freathy, R.M., Attwood, A.P., Beckmann, J.S., et al. (2008). Common variants near MC4R are associated with fat mass, weight and risk of obesity. Nat. Genet. 40, 768–775.
Lu, Y.F., Kandel, E.R., and Hawkins, R.D. (1999). Nitric oxide signaling contributes to late-phase LTP and CREB phosphorylation in the hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 19, 10250–10261.
Mages, H.W., Rilke, O., Bravo, R., Senger, G., and Kroczek, R.A. (1994). NOT, a human immediate-early response gene closely related to the steroid/thyroid hormone receptor NAK1/TR3. Mol. Endocrinol. 8, 1583–1591.
McEvoy, A.N., Murphy, E.A., Ponnio, T., Conneely, O.M., Bresnihan, B., FitzGerald, O., and Murphy, E.P. (2002). Activation of nuclear orphan receptor NURR1 transcription by NF-“kappa”B and cyclic adenosine 5′-monophosphate response element-binding protein in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue. J. Immunol. 168, 2979–2987.
Merrill, A.H., Jr., and Stevens, V.L. (1989). Modulation of protein kinase C and diverse cell functions by sphingosine—a pharmacologically interesting compound linking sphingolipids and signal transduction. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1010, 131–139.
Moeenrezakhanlou, A., Nandan, D., Shephard, L., and Reiner, N.E. (2007). 1alpha,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol activates binding of CREB to a CRE site in the CD14 promoter and drives promoter activity in a phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase-dependent manner. J. Leukoc. Biol. 81, 1311–1321.
Mountjoy, K.G., Robbins, L.S., Mortrud, M.T., and Cone, R.D. (1992). The cloning of a family of genes that encode the melanocortin receptors. Science 257, 1248–1251.
Niu, J., Vaiskunaite, R., Suzuki, N., Kozasa, T., Carr, D.W., Dulin, N., and Voyno-Yasenetskaya, T.A. (2001). Interaction of heterotrimeric G13 protein with an A-kinase-anchoring protein 110 (AKAP110) mediates cAMP-independent PKA activation. Curr. Biol. 11, 1686–1690.
Pei, L., Waki, H., Vaitheesvaran, B., Wilpitz, D.C., Kurland, I.J., and Tontonoz, P. (2006). NR4A orphan nuclear receptors are transcriptional regulators of hepatic glucose metabolism. Nat. Med. 12, 1048.
Pilz, R.B., and Casteel, D.E. (2003). Regulation of Gene Expression by Cyclic GMP. Circ. Res. 93, 1034–1046.
Qi, S.N., Yoshida, A., Wang, Z.R., and Ueda, T. (2004). GP7 can induce apoptotic DNA fragmentation of human leukemia cells through caspase-3-dependent and -independent pathways. Int. J. Mol. Med. 13, 163–167.
Qi, S.N., Jing, Y.X., Dong, G.X., Chen, Y., Yoshida, A., and Ueda, T. (2007). GP7 induces internucleosomal DNA fragmentation independent of caspase activation and DNA fragmentation factor in NB4 cells. Oncol. Rep. 18, 273–277.
Qiu, L., Zhou, C., Sun, Y., Di, W., Scheffler, E., Healey, S., Wanebo, H., Kouttab, N., Chu, W., and Wan, Y. (2006). Paclitaxel and ceramide synergistically induce cell death with transient activation of EGFR and ERK pathway in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 16, 907–913.
Raingeaud, J., Gupta, S., Rogers, J.S., Dickens, M., Han, J., Ulevitch, R.J., and Davis, R.J. (1995). Pro-inflammatory cytokines and environmental stress cause p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation by dual phosphorylation on tyrosine and threonine. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 7420–7426.
Sackett, D.L. (1993). Podophyllotoxin, steganacin and combretastatin: natural products that bind at the colchicine site of tubulin. Pharmacol. Ther. 59, 163–228.
Samarakoon, R., Higgins, C.E., Higgins, S.P., and Higgins, P.J. (2009). Differential requirement for MEK/ERK and SMAD signaling in PAI-1 and CTGF expression in response to microtubule disruption. Cell Signal. 21, 986–995.
Sato, K., Suematsu, A., Nakashima, T., Takemoto-Kimura, S., Aoki, K., Morishita, Y., Asahara, H., Ohya, K., Yamaguchi, A., Takai, T., et al. (2006). Regulation of osteoclast differentiation and function by the CaMK-CREB pathway. Nat. Med. 12, 1410–1416.
Schmid-Alliana, A., Menou, L., Manie, S., Schmid-Antomarchi, H., Millet, M.A., Giuriato, S., Ferrua, B., and Rossi, B. (1998). Micro-tubule integrity regulates src-like and extracellular signalregulated kinase activities in human pro-monocytic cells. Importance for interleukin-1 production. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 3394–3400.
Shabb, J.B. (2001). Physiological substrates of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Chem. Rev. 101, 2381–2411.
Shaywitz, A.J., and Greenberg, M.E. (1999). CREB: a stimulusinduced transcription factor activated by a diverse array of extracellular signals. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 68, 821–861.
Shtil, A.A., Mandlekar, S., Yu, R., Walter, R.J., Hagen, K., Tan, T.H., Roninson, I.B., and Kong, A.N.T. (1999). Differential regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinases by microtubule-binding agents in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 18, 377–384.
Stepanova, L., Leng, X., Parker, S.B., and Harper, J.W. (1996). Mammalian p50Cdc37 is a protein kinase-targeting subunit of Hsp90 that binds and stabilizes Cdk4. Genes Dev. 10, 1491–1502.
Stone, A.A., and Chambers, T.C. (2000). Microtubule inhibitors elicit differential effects on MAP kinase (JNK, ERK, and p38) signaling pathways in human KB-3 carcinoma cells. Exp. Cell Res. 254, 110–119.
Swarthout, J.T., Tyson, D.R., Jefcoat, S.C., and Partridge, N.C. (2002). Induction of transcriptional activity of the cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element binding protein by parathyroid hormone and epidermal growth factor in osteoblastic cells. J. Bone Miner. Res. 17, 1401–1407.
Tai, Y., Feng, S., Ge, R., Du, W., Zhang, X., He, Z., and Wang, Y. (2008). TRPC6 channels promote dendritic growth via the CaMKIV-CREB pathway. J. Cell Sci. 121, 2301–2307.
Tseng, C.J., Wang, Y.J., Liang, Y.C., Jeng, J.H., Lee, W.S., Lin, J.K., Chen, C.H., Liu, I.C., and Ho, Y.S. (2002). Microtubule damaging agents induce apoptosis in HL 60 cells and G2/M cell cycle arrest in HT 29 cells. Toxicology 175, 123–142.
Tyson, D.R., Swarthout, J.T., Jefcoat, S.C., and Partridge, N.C. (2002). PTH induction of transcriptional activity of the cAMP response element-binding protein requires the serine 129 site and glycogen synthase kinase-3 activity, but not casein kinase II sites. Endocrinology 143, 674–682.
Vaughan, C.K., Mollapour, M., Smith, J.R., Truman, A., Hu, B., Good, V.M., Panaretou, B., Neckers, L., Clarke, P.A., Workman, P., et al. (2008). Hsp90-dependent activation of protein kinases is regulated by chaperone-targeted dephosphorylation of Cdc37. Mol. Cell 31, 886–895.
Wilstermann, A.M., Bender, R.P., Godfrey, M., Choi, S., Anklin, C., Berkowitz, D.B., Osheroff, N., and Graves, D.E. (2007). Topoisomerase II — drug interaction domains: identification of substituents on etoposide that interact with the enzyme. Biochemistry 46, 8217–8225.
Zhong, H., SuYang, H., Erdjument-Bromage, H., Tempst, P., and Ghosh, S. (1997). The transcriptional activity of NF-kappaB is regulated by the IkappaB-associated PKAc subunit through a cyclic AMP-independent mechanism. Cell 89, 413–424.
Zhu, T., Fang, L.Y., and Xie, X. (2008). Development of a universal high-throughput calcium assay for G-protein-coupled receptors with promiscuous G-protein Galpha15/16. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 29, 507–516.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y.Q., Xie, X. Podophyllotoxin induces CREB phosphorylation and CRE-driven gene expression via PKA but not MAPKs. Mol Cells 29, 41–50 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-010-0015-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-010-0015-1