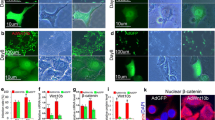
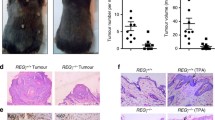
Abstract
Keratinocyte overgrowth after UVB exposure is believed to contribute to skin photoageing and cancer development. However, little is known about the transcription factors that epigenetically regulate keratinocyte response to UVB. Recently, HIF-1α was found to play a role in epidermal homeostasis by controlling the keratinocyte cell cycle, and thus, we hypothesized that HIF-1α is involved in UVB-induced keratinocyte growth. In cultured keratinocytes, HIF-1α was found to be down-regulated shortly after UVB exposure and to be involved in UVB-induced proliferation. In mice repeatedly treated with UVB, the epidermis became hyperplasic and keratinocytes lacked HIF-1α in nuclei. Based on these results, we suggest that the deregulation of HIF-1α is associated with UVB-induced hyperplasia of the epidermis. This work provides insight of the molecular mechanism underlying UV-induced photoageing and skin cancer development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arsham, A.M., Plas, D.R., Thompson, C.B., and Simon, M.C. (2002). Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling is neither required for hypoxic stabilization of HIF-1 alpha nor sufficient for HIF-1-dependent target gene transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 15162–15170.
Cho, Y.S., Bae, J.M., Chun, Y.S., Chung, J.H., Jeon, Y.K., Kim, I.S., Kim, M.S., and Park, J.W. (2008). HIF-1alpha controls keratinocyte proliferation by up-regulating p21(WAF1/Cip1). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1783, 323–333.
Chun, Y.S., Choi, E., Kim, G.T., Lee, M.J., Lee, M.J., Lee, S.E., Kim, M.S., and Park, J.W. (2000). Zinc induces the accumulation of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha, but inhibits the nuclear translocation of HIF-1beta, causing HIF-1 inactivation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 268, 652–656.
El-Abaseri, T.B., Putta, S., and Hansen, L.A. (2006). Ultraviolet irradiation induces keratinocyte proliferation and epidermal hyperplasia through the activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Carcinogenesis 27, 225–231.
Gerald, D., Berra, E., Frapart, Y.M., Chan, D.A., Giaccia, A.J., Mansuy, D., Pouysségur, J., Yaniv, M., and Mechta-Grigoriou, F. (2004) JunD reduces tumor angiogenesis by protecting cells from oxidative stress. Cell 118, 781–794.
Huang, L.E. (2008). Carrot and stick: HIF-alpha engages c-Myc in hypoxic adaptation. Cell Death Differ. 15, 672–677.
Hudson, C.C., Liu, M., Chiang, G.G., Otterness, D.M., Loomis, D.C., Kaper, F., Giaccia, A.J., and Abraham, R.T. (2002). Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha expression and function by the mammalian target of rapamycin. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22, 7004–7014.
Iyer, N.V., Kotch, L.E., Agani, F., Leung, S.W., Laughner, E., Wenger, R.H., Gassmann, M., Gearhart, J.D., Lawler, A.M., Yu, A.Y., et al. (1998). Cellular and developmental control of O2 homeostasis by hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha. Genes Dev. 12, 149–162.
Kaidi, A., Williams, A.C., and Paraskeva, C. (2007). Interaction between beta-catenin and HIF-1 promotes cellular adaptation to hypoxia. Nat. Cell Biol. 9, 210–217.
Kim, H.L., Cho, Y.S., Choi, H., Chun, Y.S., Lee, Z.H., and Park, J.W. (2009). Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha is deregulated by the serum of rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 378, 123–128.
Koshiji, M., Kageyama, Y., Pete, E.A., Horikawa, I., Barrett, J.C., and Huang, L.E. (2004). HIF-1alpha induces cell cycle arrest by functionally counteracting Myc. EMBO J. 23, 1949–1956.
Lang, K.J., Kappel, A., and Goodall, G.J. (2002). Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha mRNA contains an internal ribosome entry site that allows efficient translation during normoxia and hypoxia. Mol. Biol. Cell 13, 1792–1801.
Lee, J.K., Kim, J.H., Nam, K.T., and Lee, S.H. (2003). Molecular events associated with apoptosis and proliferation induced by ultraviolet-B radiation in the skin of hairless mice. J. Dermatol. Sci. 32, 171–179.
Lim, J.H., Chun, Y.S., and Park, J.W. (2008). Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha obstructs a Wnt signaling pathway by inhibiting the hARD1-mediated activation of beta-catenin. Cancer Res. 68, 5177–5184.
Marrot, L., and Meunier, J.R. (2008). Skin DNA photodamage and its biological consequences. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 58, S139–S148.
Matsumura, Y., and Ananthaswamy, H.N. (2002). Molecular mechanisms of photocarcinogenesis. Front. Biosci. 7, d765–d783.
Melnikova, V.O., and Ananthaswamy, H.N. (2005). Cellular and molecular events leading to the development of skin cancer. Mutat. Res. 571, 91–106.
Ouhtit, A., Muller, H.K., Davis, D.W., Ullrich, S.E., McConkey, D., and Ananthaswamy, H.N. (2000). Temporal events in skin injury and the early adaptive responses in ultraviolet-irradiated mouse skin. Am. J. Pathol. 156, 201–207.
Park, H. (1999). Aromatic hydrocarbon nuclear translocator as a common component for the hypoxia- and dioxin-induced gene expression. Mol. Cells 9, 172–178.
Peus, D., Meves, A., Vasa, R.A., Beyerle, A., O’Brien, T., and Pittelkow, M.R. (1999). H2O2 is required for UVB-induced EGF receptor and downstream signaling pathway activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 27, 1197–1202.
Rezvani, H.R., Dedieu, S., North, S., Belloc, F., Rossignol, R., Letellier, T., de Verneuil, H., Taïeb, A., and Mazurier, F. (2007). Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, a key factor in the keratinocyte response to UVB exposure. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 16413–16422.
Schofield, C.J., and Ratcliffe, P.J. (2004). Oxygen sensing by HIF hydroxylases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 5, 343–354.
Wang, G.L., and Semenza, G.L. (1995). Purification and characterization of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 1230–1237.
Wunderlich, L., Paragh, G., Wikonkál, N.M., Bánhegyi, G., Kárpáti, S., and Mandl, J. (2008). UVB induces a biphasic response of HIF-1alpha in cultured human keratinocytes. Exp. Dermatol. 17, 335–342.
Zhong, H., Chiles, K., Feldser, D., Laughner, E., Hanrahan, C., Georgescu, M.M., Simons, J.W., and Semenza, G.L. (2000). Modulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha expression by the epidermal growth factor/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/PTEN/AKT/ FRAP pathway in human prostate cancer cells: implications for tumor angiogenesis and therapeutics. Cancer Res. 60, 1541–1545.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, YS., Kim, CH. & Park, JW. Involvement of HIF-1α in UVB-induced epidermal hyperplasia. Mol Cells 28, 537–543 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-009-0148-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-009-0148-2