Abstract
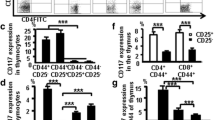
Tacrolimus is a widely used T cell targeted immunosuppressive drug, known as a calcineurin inhibitor. However, the exact pharmacological effects of tacrolimus on CD4+ T cells have yet to be elucidated. This study investigated the effects of tacrolimus on CD4+ T cell subsets. Mouse or human CD4+ T cells were cultured with immobilized anti-CD3/CD28 antibodies in the presence of tacrolimus. The cell division of CD4+ T cells was analyzed using a flow cytometer according to the expression of Foxp3. The gene expression patterns of tacrolimus-exposed T cells were examined by quantitative PCR. In the case of conventional CD4+ T cells (Tconv cells), tacrolimus inhibited T cell receptor stimulation-induced cell division. In contrast, the cell division of regulatory CD4+ T cells (Treg cells) was even promoted in the presence of tacrolimus, especially in humans. Tacrolimus did not promote conversion of Tconv to Treg cells in mice. Furthermore, tacrolimus modified the expression levels of Foxp3-regulated T cell receptor signal related-genes, PTPN22 and Itk, in human Treg cells. Immunosuppressive effect of tacrolimus may be attributed to the relatively enhanced proliferation of Treg cells in association with altered gene expression levels of TCR signaling molecules.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan, S.E., Crome, S.Q., Crellin, N.K., Passerini, L., Steiner, T.S., Bacchetta, R., Roncarolo, M.G., and Levings, M.K. (2007). Activation-induced FOXP3 in human T effector cells does not suppress proliferation or cytokine production. Int. Immunol. 19, 345–354.
Baecher-Allan, C., and Hafler, D.A. (2004). Suppressor T cells in human diseases. J. Exp. Med. 200, 273–276.
Battaglia, M., Stabilini, A., and Roncarolo, M.G. (2005). Rapamycin selectively expands CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ regulatory T cells. Blood 105, 4743–4748.
Begovich, A.B., Carlton, V.E., Honigberg, L.A., Schrodi, S.J., Chokkalingam, A.P., Alexander, H.C., Ardlie, K.G., Huang, Q., Smith, A.M., Spoerke, J.M.et al. (2004). A missense single-nucleotide polymorphism in a gene encoding a protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTPN22) is associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 75, 330–337.
Bennett, C.L., Christie, J., Ramsdell, F., Brunkow, M.E., Ferguson, P.J., Whitesell, L., Kelly, T.E., Saulsbury, F.T., Chance, P.F., and Ochs, H.D. (2001). The immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome (IPEX) is caused by mutations of FOXP3. Nat. Genet. 27, 20–21.
Bottini, N., Musumeci, L., Alonso, A., Rahmouni, S., Nika, K., Rostamkhani, M., MacMurray, J., Meloni, G.F., Lucarelli, P., Pellecchia, M. et al. (2004). A functional variant of lymphoid tyrosine phosphatase is associated with type I diabetes. Nat. Genet. 36, 337–338.
Brunkow, M.E., Jeffery, E.W., Hjerrild, K.A., Paeper, B., Clark, L.B., Yasayko, S.A., Wilkinson, J.E., Galas, D., Ziegler, S.F., and Ramsdell, F. (2001). Disruption of a new forkhead/winged-helix protein, scurfin, results in the fatal lymphoproliferative disorder of the scurfy mouse. Nat. Genet. 27, 68–73.
Chen, W., Jin, W., Hardegen, N., Lei, K.J., Li, L., Marinos, N., McGrady, G., and Wahl, S.M. (2003). Conversion of peripheral CD4+CD25- naive T cells to CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells by TGF-beta induction of transcription factor Foxp3. J. Exp. Med. 198, 1875–1886.
Dumont, F.J. (2000). FK506, an immunosuppressant targeting calcineurin function. Curr. Med. Chem. 7, 731–748.
Gomez-Rodriguez, J., Readinger, J.A., Viorritto, I.C., Mueller, K.L., Houghtling, R.A., and Schwartzberg, P.L. (2007). Tec kinases, actin, and cell adhesion. Immunol. Rev. 218, 45–64.
Granelli-Piperno, A., Nolan, P., Inaba, K., and Steinman, R.M. (1990). The effect of immunosuppressive agents on the induction of nuclear factors that bind to sites on the interleukin 2 promoter. J. Exp. Med. 172, 1869–1872.
Gregersen, P.K., and Batliwalla, F. (2005). PTPN22 and rheumatoid arthritis: gratifying replication. Arthritis Rheum. 52, 1952–1955.
Gregersen, P.K., Lee, H.S., Batliwalla, F., and Begovich, A.B. (2006). PTPN22: setting thresholds for autoimmunity. Semin Immunol. 18, 214–223.
Haxhinasto, S., Mathis, D., and Benoist, C. (2008). The AKT-mTOR axis regulates de novo differentiation of CD4+Foxp3+ cells. J. Exp. Med. 205, 565–574.
Hori, S., Nomura, T., and Sakaguchi, S. (2003). Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science 299, 1057–1061.
Kiani, A., Rao, A., and Aramburu, J. (2000). Manipulating immune responses with immunosuppressive agents that target NFAT. Immunity 12, 359–372.
Mantel, P.Y., Ouaked, N., Ruckert, B., Karagiannidis, C., Welz, R., Blaser, K., and Schmidt-Weber, C.B. (2006). Molecular mechanisms underlying FOXP3 induction in human T cells. J. Immunol. 176, 3593–3602.
Marson, A., Kretschmer, K., Frampton, G.M., Jacobsen, E.S., Polansky, J.K., MacIsaac, K.D., Levine, S.S., Fraenkel, E., von Boehmer, H., and Young, R.A. (2007). Foxp3 occupancy and regulation of key target genes during T-cell stimulation. Nature 445, 931–935.
Orozco, G., Sanchez, E., Gonzalez-Gay, M.A., Lopez-Nevot, M.A., Torres, B., Caliz, R., Ortego-Centeno, N., Jimenez-Alonso, J., Pascual-Salcedo, D., Balsa, A., et al. (2005). Association of a functional single-nucleotide polymorphism of PTPN22, encoding lymphoid protein phosphatase, with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 52, 219–224.
Sadlack, B., Merz, H., Schorle, H., Schimpl, A., Feller, A.C., and Horak, I. (1993). Ulcerative colitis-like disease in mice with a disrupted interleukin-2 gene. Cell 75, 253–261.
Sakaguchi, S. (2004). Naturally arising CD4+ regulatory t cells for immunologic self-tolerance and negative control of immune responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 22, 531–562.
Schaeffer, E.M., Debnath, J., Yap, G., McVicar, D., Liao, X.C., Littman, D.R., Sher, A., Varmus, H.E., Lenardo, M.J., and Schwartzberg, P.L. (1999). Requirement for Tec kinases Rlk and Itk in T cell receptor signaling and immunity. Science 284, 638–641.
Setoguchi, R., Hori, S., Takahashi, T., and Sakaguchi, S. (2005). Homeostatic maintenance of natural Foxp3(+) CD25(+) CD4(+) regulatory T cells by interleukin (IL)-2 and induction of autoimmune disease by IL-2 neutralization. J. Exp. Med. 201, 723–735.
Shimizu, J., Yamazaki, S., Takahashi, T., Ishida, Y., and Sakaguchi, S. (2002). Stimulation of CD25(+)CD4(+) regulatory T cells through GITR breaks immunological self-tolerance. Nat. Immunol. 3, 135–142.
Tocci, M.J., Matkovich, D.A., Collier, K.A., Kwok, P., Dumont, F., Lin, S., Degudicibus, S., Siekierka, J.J., Chin, J., and Hutchinson, N.I. (1989). The immunosuppressant FK506 selectively inhibits expression of early T cell activation genes. J. Immunol. 726, 718–726.
Tran, D.Q., Ramsey, H., and Shevach, E.M. (2007). Induction of FOXP3 expression in naive human CD4+FOXP3 T cells by Tcell receptor stimulation is transforming growth factor-beta dependent but does not confer a regulatory phenotype. Blood 110, 2983–2990.
Walker, M.R., Kasprowicz, D.J., Gersuk, V.H., Benard, A., Van Landeghen, M., Buckner, J.H., and Ziegler, S.F. (2003). Induction of FoxP3 and acquisition of T regulatory activity by stimulated human CD4+CD25- T cells. J. Clin. Invest. 112, 1437–1443.
Walker, M.R., Carson, B.D., Nepom, G.T., Ziegler, S.F., and Buckner, J.H. (2005). De novo generation of antigen-specific CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells from human CD4+CD25- cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 4103–4108.
Wildin, R.S., Ramsdell, F., Peake, J., Faravelli, F., Casanova, J.L., Buist, N., Levy-Lahad, E., Mazzella, M., Goulet, O., Perroni, L. et al. (2001). X-linked neonatal diabetes mellitus, enteropathy and endocrinopathy syndrome is the human equivalent of mouse scurfy. Nat. Genet. 27, 18–20.
Yocum, D.E., Furst, D.E., Bensen, W.G., Burch, F.X., Borton, M.A., Mengle-Gaw, L.J., Schwartz, B.D., Wisememandle, W., and Mekki, Q.A. (2004). Safety of tacrolimus in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: long-term experience. Rheumatology 43, 992–999.
Yu, X., Sun, J.P., He, Y., Guo, X., Liu, S., Zhou, B., Hudmon, A., and Zhang, Z.Y. (2007). Structure, inhibitor, and regulatory mechanism of Lyp, a lymphoid-specific tyrosine phosphatase implicated in autoimmune diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 19767–19772.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kogina, K., Shoda, H., Yamaguchi, Y. et al. Tacrolimus differentially regulates the proliferation of conventional and regulatory CD4+ T cells. Mol Cells 28, 125–130 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-009-0114-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-009-0114-z