Abstract
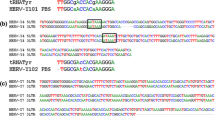
Human endogenous retroviruses (HERVs) have been implicated in the pathogenesis of several human diseases as multi-copy members in the human genome. Their gene expression profiling could provide us with important insights into the pathogenic relationship between HERVs and cancer. In this study, we have evaluated the genomic structure and quantitatively determined the expression patterns in the env gene of a variety of HERV family members located on six specific loci by the RetroTector 10 program, as well as real-time RT-PCR amplification. The env gene transcripts evidenced significant differences in the human tumor/normal adjacent tissues (colon, liver, uterus, lung and testis). As compared to the adjacent normal tissues, high levels of expression were noted in testis tumor tissues for HERV-K, in liver and lung tumor tissues for HERV-R, in liver, lung, and testis tumor tissues for HERV-H, and in colon and liver tumor tissues for HERV-P. These data warrant further studies with larger groups of patients to develop biomarkers for specific human cancers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antony, J.M., Zhu, Y., Izad, M., Warren, K.G., Vodjgani, M., Mallet, F., and Power, C. (2007). Comparative expression of human endogenous retrovirus-W genes in multiple sclerosis. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 23, 1251–1256.
Bessis, D., Moles, J.P., Basset-Seguin, N., Tesniere, A., Arpin, C., and Guilhou, J.J. (2004). Differential expression of a human endogenous retrovirus E transmembrane envelope glycoprotein in normal, psoriatic and atopic dermatitis human skin. British J. Dermatol. 151, 737–745.
Blaise, S., de Parseval, N., Benit, L., and Heidmann, T. (2003). Genomewide screening for fusogenic human endogenous retrovirus envelopes identifies syncytin 2, a gene conserved on primate evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 13013–13018.
Blaise, S., de Parseval, N., and Heidmann, T. (2005). Functional characterization of two newly identified human endogenous retrovirus coding envelope genes. Retrovirology 2, 19.
Blikstad, V., Benachenhou, F., Sperber, G.O., and Blomberg, J. (2008). Evolution of human endogenous retroviral sequences: a conceptual account. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 65, 3348–3365.
Blond, J.L., Lavillette, D., Cheynet, V., Bouton, O., Oriol, G., Chapel-Fernandes, S., Mandrand, B., Mallet, F., and Cosset, F.L. (2000). An envelope glycoprotein of the human endogenous retrovirus HERV-W is expressed in the human placenta and fuses cells expressing the type D mammalian retrovirus receptor. J. Virol. 74, 3321–3329.
Chang, C., Chen, P.T., Chang, G.D., Huang, C.J., and Chen, H. (2004). Functional characterization of the placental fusogenic membrane protein syncytin. Biol. Reprod. 71, 1956–1962.
de Parseval, N., Lazar, V., Casella, J.F., Benit, L., and Heidmann, T. (2003). Survey of human genes of retroviral origin: identification and transcriptome of the genes with coding capacity for complete envelope proteins. J. Virol. 77, 10414–10422.
Dupressoir, A., Marceau, G., Vernochet, C., Benit, L., Kanellopoulos, C., Sapin, V., and Heidmann, T. (2005). Syncytin-A and syncytin-B, two fusogenic placenta-specific murine envelope genes of retroviral origin conserved in Muridae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 725–730.
Esnault, C., Priet, S., Ribet, D., Vernochet, C., Bruls, T., Lavialle, C., Weissenbach, J., and Heidmann, T. (2008). A placenta-specific receptor for the fusogenic, endogenous retrovirus-derived, human syncytin-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 17532–17537.
Frank, O., Verbeke, C., Schwarz, N., Mayer, J., Fabarius, A., Hehlmann, R., Leib-Mosch, C., and Seifarth, W. (2008). Variable transcriptional activity of endogenous retroviruses in human breast cancer. J. Virol. 82, 1808–1818.
Goedert, J.J., Sauter, M.E., Jacobson, L.P., Vessella, R.L., Hilgartner, M.W., Leitman, S.F., Fraser, M.C., and Mueller-Lantzsch, N.G. (1999). High prevalence of antibodies against HERV-K10 in patients with testicular cancer but not with AIDS. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 8, 293–296.
Golan, M., Hizi, A., Resau, J.H., Yaal-Hahoshen, N., Reichman, H., Keydar, I., and Tsarfaty, I. (2008). Human endogenous retrovirus (HERV-K) reverse transcriptase as a breast cancer prognostic marker. Neoplasia 10, 521–533.
Harris, J.R. (1998). Placental endogenous retrovirus (ERV): structural, functional, and evolutionary significance. Bioessays 20, 307–316.
Kim, T.H., Jeon, Y.J., Yi, J.M., Kim, D.S., Huh, J.W., Hur, C.G., and Kim, H.S. (2004). The distribution and expression of HERV families in the human genome. Mol. Cells 18, 87–93.
Kim, H.S., Yi, J.M., Hirai, H., Huh, J.W., Jeong, M.S., Jang, S.B., Kim, C.G., Saitou, N., Hyun, B.H., and Lee, W.H. (2006). Human Endogenous Retrovirus (HERV)-R family in primates: chromosomal location, gene expression, and evolution. Gene 370, 34–42.
Kim, H.S., Kim, D.S., Huh, J.W., Ahn, K., Yi, J.M., Lee, J.R., and Hirai, H. (2008a). Molecular characterization of the HERV-W env gene in humans and primates: expression, FISH, phylogeny, and evolution. Mol. Cells 26, 53–60.
Kim, H.S., Ahn, K., and Kim, D.S. (2008b). Quantitative expression of the HERV-W env gene in human tissues. Arch. Virol. 153, 1587–1591.
Kim, Y.J., Huh, J.W., Kim, D.S., Bae, M.I., Lee, J.R., Ahn, K., Kim, T.O., Song, K.A., and Kim, H.S. (2009). Molecular characterization of the DYX1C1 gene and its application as a cancer biomarker. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 135, 265–270.
Lindeskog, M., Mager, D.L., and Blomberg, J. (1999). Isolation of a human endogenous retroviral HERV-H element with an open env reading frame. Virology 258, 441–450.
Mayer, J., Ehlhardt, S., Seifert, M., Sauter, M., Muller-Lantzsch, N., Mehraein, Y., Zang, K.D., and Meese, E. (2004). Human endogenous retrovirus HERV-K (HML-2) proviruses with Rec pro tein coding capacity and transcriptional activity. Virology 322, 190–198.
Nellaker, C., Yao, Y., Jones-Brando, L., Mallet, F., Yolken, R.H., and Karlsson, H. (2006). Transactivation of elements in the human endogenous retrovirus W family by viral infection. Retrovirology 3, 44.
Prusty, B.K., zur Hausen, H., Schmidt, R., Kimmel, R., and de Villiers, E.M. (2008). Transcription of HERV-E and HERV-Erelated sequences in malignant and non-malignant human haematopoietic cells. Virology 382, 37–45.
Ruprecht, K., Ferreira, H., Flockerzi, A., Wahl, S., Sauter, M., Mayer, J., and Mueller-Lantzsch, N. (2008a). Human endogenous retrovirus family HERV-K (HML-2) RNA transcripts are selectively packaged into retroviral particles produced by the human germ cell tumor line Tera-1 and originate mainly from a provirus on chromosome 22q11.21. J. Virol. 82, 10008–10016.
Ruprecht, K., Mayer, J., Sauter, M., Roemer, K., and Mueller-Lantzsch, N. (2008b). Endogenous retroviruses and cancer. Cell. Mol. Life. Sci. 65, 3366–3382.
Serafino, A., Balestrieri, E., Pierimarchi, P., Matteucci, C., Moroni, G., Oricchio, E., Rasi, G., Mastino, A., Spadafora, C., Garaci, E., et al. (2009). The activation of human endogenous retrovirus K (HERVK) is implicated in melanoma cell malignant transformation. Exp. Cell Res. 315, 849–862.
Sperber, G.O., Airola, T., Jern, P., and Blomberg, J. (2007). Automated recognition of retroviral sequences in genomic data-RetroTector. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, 4964–4976.
Tanaka, S., Ikeda, H., Otsuka, N., Yamamoto, Y., Sugaya, T., and Yoshiki, T. (2003). Tissue specific high level expression of a full length human endogenous retrovirus genome transgene, HERV-R, under control of its own promoter in rats. Transgenic Res. 12, 319–328.
Tristem, M. (2000). Identification and characterization of the novel human endogenous retrovirus families by phylogenetic screening of the human genome mapping project database. J. Virol. 74, 3715–3730.
Wang-Johanning, F., Liu, J., Rycaj, K., Huang, M., Tsai, K., Rosen, D.G., Chen, D.T., Lu, D.W., Barnhart, K.F., and Johanning, G.L. (2007). Expression of multiple human endogenous retrovirus surface envelope proteins in ovarian cancer. Int. J. Cancer 120, 81–90.
Wang-Johanning, F., Radvanyi, L., Rycaj, K., Plummer, J.B., Yan, P., Sastry, K.J., Piyathilake, C.J., Hunt, K.K., and Johanning, G.L. (2008). Human endogenous retrovirus K triggers an antigen-specific immune response in breast cancer patients. Cancer Res. 68, 5869–5877.
Yi, J.M., and Kim, H.S. (2004). Expression analysis of endo-genous retroviral elements belonging to the HERV-F family from human tissues and cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 211, 89–96.
Yi, J.M., and Kim, H.S. (2007a). Molecular phylogenetic analysis of the human endogenous retrovirus E (HERV-E) family in human tissues and human cancers. Genes Genet. Syst. 82, 89–98.
Yi, J.M., and Kim, H.S. (2007b). Expression and phylogenetic analyses of human endogenous retrovirus HC2 belonging to the HERV-T family in human tissues and cancer cells. J. Hum. Genet. 52, 285–296.
Yi, J.M., Kim, T.H., Huh, J.W., Park, K.S., Jang, S.B., Kim, H.M., and Kim, H.S. (2004a). Human endogenous retroviral elements belonging to the HERV-S family from human tissues, cancer cells, and primates: expression, structure, phylogeny and evolution. Gene 342, 283–392.
Yi, J.M., Kim, H.M., and Kim, H.S. (2004b). Expression of the human endogenous retrovirus HERV-W family in various human tissues and cancer cells. J. Gen. Virol. 85, 1203–1210.
Yi, J.M., Schuebel, K., and Kim, H.S. (2006a). Molecular genetic analyses of human endogenous retroviral elements belonging to the HERV-P family in primates, human tissues, and cancer cells. Genomics 89, 1–9.
Yi, J.M., Kim, H.M., and Kim, H.S. (2006b). Human endogenous retrovirus HERV-H family in human tissues and cancer cells: expression, identification, and phylogeny. Cancer Lett. 231, 228–239.
Yi, J.M., Schuebel, K., and Kim, H.S. (2007). Molecular genetic analyses of human endogenous retroviral elements belonging to the HERV-P family in primates, human tissues, and cancer cells. Genomics 89, 1–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Ahn, K., Kim, HS. Structural and quantitative expression analyses of HERV gene family in human tissues. Mol Cells 28, 99–103 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-009-0107-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-009-0107-y