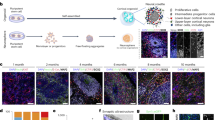
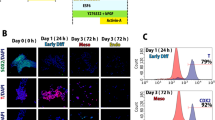
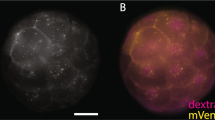
Abstract
In mouse embryos, somite formation occurs every two hours, and this periodic event is regulated by a biological clock called the segmentation clock, which involves cyclic expression of the basic helix-loop-helix gene Hes7. Hes7 expression oscillates by negative feedback and is cooperatively regulated by Fgf and Notch signaling. Both loss of expression and sustained expression of Hes7 result in severe somite fusion, suggesting that Hes7 oscillation is required for proper somite segmentation. Expression of a related gene, Hes1, also oscillates by negative feedback with a period of about two hours in many cell types such as neural progenitor cells. Hes1 is required for maintenance of neural progenitor cells, but persistent Hes1 expression inhibits proliferation and differentiation of these cells, suggesting that Hes1 oscillation is required for their proper activities. Hes1 oscillation regulates cyclic expression of the proneural gene Neurogenin2 (Ngn2) and the Notch ligand Delta1, which in turn lead to maintenance of neural progenitor cells by mutual activation of Notch signaling. Taken together, these results suggest that oscillatory expression with short periods (ultradian oscillation) plays an important role in many biological events.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aulehla, A., and Herrmann, B.G. (2004). Segmentation in vertebrates: clock and gradient finally joined. Genes Dev. 18, 2060–2067.
Baek, J.H., Hatakeyama, J., Sakamoto, S., Ohtsuka, T., and Kageyama, R. (2006). Persistent and high levels of Hes1 expression regulate boundary formation in the developing central nervous system. Development 133, 2467–2476.
Bar-Or, R.L., Maya, R., Segel, L.A., Alon, U., Levine, A.J., and Oren, M. (2000). Generation of oscillations by the p53-Mdm2 feedback loop: a theoretical and experimental study. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 11250–11255.
Bertrand, N., Castro, D.S., and Guillemot, F. (2002). Proneural genes and the specification of neural cell types. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 3, 517–530.
Bessho, Y., Sakata, R., Komatsu, S., Shiota, K., Yamada, S., and Kageyama, R. (2001). Dynamic expression and essential functions of Hes7 in somite segmentation. Genes Dev. 15, 2642–2647.
Bessho, Y., Hirata, H., Masamizu, Y., and Kageyama, R. (2003). Periodic repression by the bHLH factor Hes7 is an essential mechanism for the somite segmentation clock. Genes Dev. 17, 1451–1456.
Bettenhausen, B., Hrabe de Angelis, M., Simon, D., Guenet, J., and Gossler, A. (1995). Transient and restricted expression during mouse embryogenesis of DII1, a murine gene closely related to Drosophila Delta. Development 121, 2407–2418.
Castro, D.S., Skowronska-Krawczyk, D., Armant, O., Donaldson, I.J., Parras, C., Hunt, C., Critchley, J.A., Nguyen, L., Gossler, A., Gottgens, B., et al. (2006). Proneural bHLH and Brn proteins coregulate a neurogenic program through cooperative binding to a conserved DNA motif. Dev. Cell 11, 831–844.
Chen, J., Kang, L., and Zhang, N. (2005). Negative feedback loop formed by Lunatic fringe and Hes7 controls their oscillatory expression during somitogenesis. Genesis 43, 196–204.
Dequéant, M., and Pourquie, O. (2008). Segmental patterning of the vertebrate embryonic axis. Nat. Rev. Genet. 9, 370–382.
Dequéant, M.-L., Glynn, E., Gaudenz, K., Wahl, M., Chen, J., Mushegian, A., and Pourquie, O. (2006). A complex oscillating network of signaling genes underlies the mouse segmentation clock. Science 314, 1595–1598.
Dubrulle, J., and Pourquié, O. (2004). fgf8 mRNA decay establishes a gradient that couples axial elongation to patterning in the vertebrate embryo. Nature 427, 419–422.
Gridley, T. (2006). The long and short of it: somite formation in mice. Dev. Dyn. 235, 2330–2336.
Guillemot, F., and Joyner, A.L. (1993). Dynamic expression of the murine Achaete-Scute homologue Masg-1 in the developing nervous system. Mech. Dev. 42, 171–185.
Hatakeyama, J., Bessho, Y., Katoh, K., Ookawara, S., Fujioka, M., Guillemot, F., and Kageyama, R. (2004). Hes genes regulate size, shape and histogenesis of the nervous system by control of the timing of neural stem cell differentiation. Development 131, 5539–5550.
Hirata, H., Yoshiura, S., Ohtsuka, T., Bessho, Y., Harada, T., Yoshikawa, K., and Kageyama, R. (2002). Oscillatory expression of the bHLH factor Hes1 regulated by a negative feedback loop. Science 298, 840–843.
Hirata, H., Bessho, Y., Kokubu, H., Masamizu, Y., Yamada, S., Lewis, J., and Kageyama, R. (2004). Instability of Hes7 protein is crucial for the somite segmentation clock. Nat. Genet. 36, 750–754.
Hoffmann, A., Levchenko, A., Scott, M., and Baltimore, D. (2002). The IkB-NF-kB signaling module: temporal control and selective gene activation. Science 298, 1241–1245.
Horikawa, K., Ishimatsu, K., Yoshimoto, E., Kondo, S., and Takeda, H. (2006). Noise-resistant and synchronized oscillation of the segmentation clock. Nature 441, 719–723.
Huppert, S.S., Ilagan, M.X.G., De Strooper, B. and Kopan, R. (2005). Analysis of Notch function in presomitic mesoderm suggests a gamma-secretase-independent role for presenilins in somite differentiation. Dev. Cell 8, 677–688.
Ishibashi, M., Ang, S.L., Shiota, K., Nakanishi, S., Kageyama, R., and Guillemot, F. (1995). Targeted disruption of mammalian hairy and Enhancer of split homolog-1 (HES-1) leads to upregulation of neural helix-loop-helix factors, premature neurogenesis, and severe neural tube defects. Genes Dev. 9, 3136–3148.
Jensen, M.H., Sneppen, K., and Tiana, G. (2003). Sustained oscillations and time delays in gene expression of protein Hes1. FEBS Lett. 541, 176–177.
Jiang, Y.-J., Aerne, B.L., Smithers, L., Haddon, C., Ish-Horowicz, D. and Lewis, J. (2000). Notch signaling and the synchronization of the somite segmentation clock. Nature 408, 475–479.
Kageyama, R., Ohtsuka, T., Hatakeyama, J. and Ohsawa, R. (2005). Roles of bHLH genes in neural stem cell differentiation. Exp. Cell Res. 306, 343–348.
Kageyama, R., Ohtsuka, T. and Kobayashi, T. (2007). The Hes gene family: repressors and oscillators that orchestrate embryogenesis. Development 134, 1243–1251.
Kageyama, R., Ohtsuka, T., Shimojo, H. and Imayoshi, I. (2008). Dynamic Notch signaling in neural progenitor cells and a revised view of lateral inhibition. Nat. Neurosci. 11, 1247–1251.
Kamakura, S., Oishi, K., Yoshimatsu, T., Nakafuku, M., Masuyama, N. and Gotoh, Y. (2004). Hes binding to STAT3 mediates crosstalk between Notch and JAK-STAT signaling. Nat. Cell Biol. 6, 547–554.
Lahav, G., Rosenfeld, N., Sigal, A., Geva-Zatorsky, N., Levine, A.J., Elowitz, M.B. and Alon, U. (2004). Dynamics of the p53-Mdm2 feedback loop in individual cells. Nat. Genet. 36, 147–150.
Lewis, J. (2003). Autoinhibition with transcriptional delay: a simple mechanism for the zebrafish somitogenesis oscillator. Curr. Biol. 13, 1398–1408.
Maroto, M., Dale, J.K., Dequeant, M.-L., Petit, A.C. and Pourquie, O. (2005). Synchronised cycling gene oscillations in presomitic mesoderm cells require cell-cell contact. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 49, 309–315.
Masamizu, Y., Ohtsuka, T., Takashima, Y., Nagahara, H., Takenaka, Y., Yoshikawa, K., Okamura, H. and Kageyama, R. (2006). Real-time imaging of the somite segmentation clock: revelation of unstable oscillators in the individual presomitic mesoderm cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 1313–1318.
Monk, N.A.M. (2003). Oscillatory expression of Hes1, p53, and NF-kB driven by transcriptional time delays. Curr. Biol. 13, 1409–1413.
Morimoto, M., Takahashi, Y., Endo, M. and Saga, Y. (2005). The Mesp2 transcription factor establishes segmental borders by suppressing Notch activity. Nature 435, 354–359.
Nelson, D.E., Ihekwaba, A.E., Elliott, M., Johnson, J.R., Gibney, C.A., Foreman, B.E., Nelson, G., See, V., Horton, C.A., Spiller, D.G., et al. (2004). Oscillations in NF-kB signaling control the dynamics of gene expression. Science 306, 704–708.
Nieto, M., Schuurmans, S., Britz, O. and Guillemot, F. (2001). Neural bHLH genes control the neuronal versus glial fate decision in cortical progenitors. Neuron 29, 401–413.
Niwa, Y., Masamizu, Y., Liu, T., Nakayama, R., Deng, C.X. and Kageyama, R. (2007). The initiation and propagation of Hes7 oscillation are cooperatively regulated by Fgf and Notch signaling in the somite segmentation clock. Dev. Cell 13, 298–304.
Ohtsuka, T., Ishibashi, M., Gradwohl, G., Nakanishi, S., Guillemot, F. and Kageyama, R. (1999). Hes1 and Hes5 as Notch effecttors in mammalian neuronal differentiation. EMBO J. 18, 2196–2207.
Pascoal, S., Carvalho, C.R., Rodriguez-Leon, J., Delfini, M.C., Duprez, D., Thorsteinsdottir, S., and Palmeirim, I. (2007). A molecular clock operates during chick autopod proximal-distal outgrowth. J. Mol. Biol. 368, 303–309.
Riedel-Kruse, I.H., Müller, C., and Oates, A.C. (2007). Synchrony dynamics during initiation, failure, and rescue of the segmentation clock. Science 317, 1911–1915.
Ross, S.E., Greenberg, M.E., and Stiles, C.D. (2003). Basic helixloop-helix factors in cortical development. Neuron 39, 13–25.
Serth, K., Schuster-Gossler, K., Cordes, R., and Gossler, A. (2003). Transcriptional oscillation of Lunatic fringe is essential for somitogenesis. Genes Dev. 17, 912–925.
Shimojo, H., Ohtsuka, T., and Kageyama, R. (2008). Oscillations in notch signaling regulate maintenance of neural progenitors. Neuron 58, 52–64.
Sommer, L., Ma, Q. and Anderson, D.J. (1996). neurogenins, a novel family of atonal-related bHLH transcription factors, are putative mammalian neuronal determination genes that reveal progenitor cell heterogeneity in the developing CNS and PNS. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 8, 221–241.
Tomita, K., Moriyoshi, K., Nakanishi, S., Guillemot, F. and Kageyama, R. (2000). Mammalian achaete-scute and atonal homologs regulate neuronal versus glial fate determination in the central nervous system. EMBO J. 19, 5460–5472.
Yoshiura, S., Ohtsuka, T., Takenaka, Y., Nagahara, H., Yoshikawa, K. and Kageyama, R. (2007). Ultradian oscillations of Stat, Smad, and Hes1 expression in response to serum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 11292–11297.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kageyama, R., Niwa, Y. & Shimojo, H. Rhythmic gene expression in somite formation and neural development. Mol Cells 27, 497–502 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-009-0068-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-009-0068-1