Abstract.
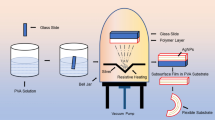
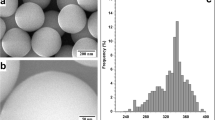
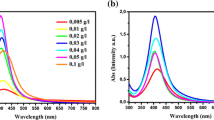
A new metallorganic silver precursor, Ag(hfa)tetraglyme, has been used to produce silver aggregates into polymeric thin film matrices by thermal reduction in a temperature range between 200 °C and 300 °C. Here we present a characterization of the metal aggregates into polyimide thin films (0.1–1 μm). The size of the metallic particles has been measured by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). A narrow particles size distribution centered around a radius value of ∼16 nm has been observed. X-ray diffraction (XRD) performed on this sample confirms the presence of metallic silver. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) has been used to determine the elemental composition at the particle surface. A partial oxidation of the metal particles, probably due to the air contamination or to interaction with oxygen of the polymeric matrix, has been observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 1 September 1998 / Received in final form: 5 November 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fragalà, M., Compagnini, G., Malandrino, G. et al. Silver nanoparticles dispersed in polyimide thin film matrix. Eur. Phys. J. D 9, 631–633 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100530050515
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100530050515