Abstract
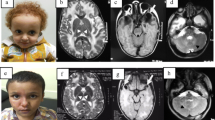
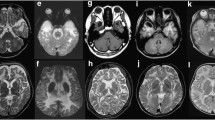
Megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts is an autosomal recessive disease characterized by early onset macrocephaly; developmental delay; motor disability in the form of progressive spasticity and ataxia; seizures; cognitive decline; and characteristic magnetic resonance imaging findings. Mutations in two genes, MLC1 (22q13.33; 75 % of patients) or HEPACAM (11q24; 20 % of patients), are associated with the disease. We describe an adult MLC patient with moderate clinical symptoms. MLC1 cDNA analysis from lymphoblasts showed a strong transcript reduction and identified a 246-bp pseudoexon containing a premature stop codon between exons 10 and 11, due to a homozygous c.895-226 T>G deep-intronic mutation. This category of mutations is often overlooked, being outside of canonically sequenced genomic regions. The mutation c.895-226 T>G has a leaky effect on splicing leaving part of the full-length transcript. Its role on splicing was confirmed using a minigene assay and an antisense morpholinated oligonucleotide targeted to the aberrant splice site in vitro, which partially abrogated the mutation effect.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
van der Knaap MS, Barth PG, Stroink H, van Nieuwenhuizen O, Arts WF, Hoogenraad F, Valk J (1995) Leukoencephalopathy with swelling and a discrepantly mild clinical course in eight children. Ann Neurol 37(3):324–334
Costello DJ, Eichler AF, Eichler FS (2009) Leukodystrophies: classification, diagnosis, and treatment. Neurologist 15(6):319–328. doi:10.1097/NRL.0b013e3181b287c800127893-200911000-00004
Leegwater PA, Boor PK, Yuan BQ, van der Steen J, Visser A, Konst AA, Oudejans CB, Schutgens RB, Pronk JC, van der Knaap MS (2002) Identification of novel mutations in MLC1 responsible for megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts. Hum Genet 110(3):279–283
Lopez-Hernandez T, Ridder MC, Montolio M, Capdevila-Nortes X, Polder E, Sirisi S, Duarri A, Schulte U, Fakler B, Nunes V, Scheper GC, Martinez A, Estevez R, van der Knaap MS (2011) Mutant GlialCAM causes megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts, benign familial macrocephaly, and macrocephaly with retardation and autism. Am J Hum Genet 88(4):422–432. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.02.009
Teijido O, Casaroli-Marano R, Kharkovets T, Aguado F, Zorzano A, Palacin M, Soriano E, Martinez A, Estevez R (2007) Expression patterns of MLC1 protein in the central and peripheral nervous systems. Neurobiol Dis 26(3):532–545. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2007.01.016
Lopez-Hernandez T, Sirisi S, Capdevila-Nortes X, Montolio M, Fernandez-Duenas V, Scheper GC, van der Knaap MS, Casquero P, Ciruela F, Ferrer I, Nunes V, Estevez R (2011) Molecular mechanisms of MLC1 and GLIALCAM mutations in megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts. Hum Mol Genet 20(16):3266–3277. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddr238
Teijido O, Martinez A, Pusch M, Zorzano A, Soriano E, Del Rio JA, Palacin M, Estevez R (2004) Localization and functional analyses of the MLC1 protein involved in megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts. Hum Mol Genet 13(21):2581–2594. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddh291ddh291
Ridder MC, Boor I, Lodder JC, Postma NL, Capdevila-Nortes X, Duarri A, Brussaard AB, Estevez R, Scheper GC, Mansvelder HD, van der Knaap MS (2011) Megalencephalic leucoencephalopathy with cysts: defect in chloride currents and cell volume regulation. Brain 134(Pt 11):3342–3354. doi:10.1093/brain/awr255
Favre-Kontula L, Rolland A, Bernasconi L, Karmirantzou M, Power C, Antonsson B, Boschert U (2008) GlialCAM, an immunoglobulin-like cell adhesion molecule is expressed in glial cells of the central nervous system. Glia 56(6):633–645. doi:10.1002/glia.20640
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Reese MG, Eeckman FH, Kulp D, Haussler D (1997) Improved splice site detection in Genie. J Comput Biol 4(3):311–323
Akashi YJ, Nakazawa K, Sakakibara M, Miyake F, Koike H, Sasaka K (2003) The clinical features of Takotsubo cardiomyopathy. QJM 96(8):563–573
Corrigan A, Arenas M, Escuredo E, Fairbanks L, Marinaki A (2011) HPRT deficiency: identification of twenty-four novel variants including an unusual deep intronic mutation. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 30(12):1260–1265. doi:10.1080/15257770.2011.590172
Vache C, Besnard T, le Berre P, Garcia-Garcia G, Baux D, Larrieu L, Abadie C, Blanchet C, Bolz HJ, Millan J, Hamel C, Malcolm S, Claustres M, Roux AF (2011) Usher syndrome type 2 caused by activation of an USH2A pseudoexon: implications for diagnosis and therapy. Hum Mutat. doi:10.1002/humu.21634
Costa C, Pruliere-Escabasse V, de Becdelievre A, Gameiro C, Golmard L, Guittard C, Bassinet L, Bienvenu T, Georges MD, Epaud R, Bieth E, Giurgea I, Aissat A, Hinzpeter A, Costes B, Fanen P, Goossens M, Claustres M, Coste A, Girodon E (2011) A recurrent deep-intronic splicing CF mutation emphasizes the importance of mRNA studies in clinical practice. J Cyst Fibros 10(6):479–482. doi:10.1016/j.jcf.2011.06.011
Castaman G, Giacomelli SH, Mancuso ME, D’Andrea G, Santacroce R, Sanna S, Santagostino E, Mannucci PM, Goodeve A, Rodeghiero F (2011) Deep intronic variations may cause mild hemophilia A. J Thromb Haemost 9(8):1541–1548. doi:10.1111/j.1538-7836.2011.04408.x
Ilja Boor PK, de Groot K, Mejaski-Bosnjak V, Brenner C, van der Knaap MS, Scheper GC, Pronk JC (2006) Megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts: an update and extended mutation analysis of MLC1. Hum Mutat 27(6):505–512. doi:10.1002/humu.20332
Aartsma-Rus A, den Dunnen JT, van Ommen GJ (2010) New insights in gene-derived therapy: the example of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1214:199–212. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05836.x
Lu QL, Yokota T, Takeda S, Garcia L, Muntoni F, Partridge T (2011) The status of exon skipping as a therapeutic approach to Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Mol Ther 19(1):9–15. doi:10.1038/mt.2010.219
Bugiani M, Moroni I, Bizzi A, Nardocci N, Bettecken T, Gartner J, Uziel G (2003) Consciousness disturbances in megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts. Neuropediatrics 34(4):211–214. doi:10.1055/s-2003-42209
Serkov SV, Pronin IN, Bykova OV, Maslova OI, Arutyunov NV, Muravina TI, Kornienko VN, Fadeeva LM, Marks H, Bonnemann C, Schiffmann R, van der Knaap MS (2004) Five patients with a recently described novel leukoencephalopathy with brainstem and spinal cord involvement and elevated lactate. Neuropediatrics 35(1):1–5
Kaczorowska M, Kuczynski D, Jurkiewicz E, Scheper GC, van der Knaap MS, Jozwiak S (2006) Acute fright induces onset of symptoms in vanishing white matter disease—case report. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 10(4):192–193
Vermeulen G, Seidl R, Mercimek-Mahmutoglu S, Rotteveel JJ, Scheper GC, van der Knaap MS (2005) Fright is a provoking factor in vanishing white matter disease. Ann Neurol 57(4):560–563
Leegwater PA, Yuan BQ, van der Steen J, Mulders J, Konst AA, Boor PK, Mejaski-Bosnjak V, van der Maarel SM, Frants RR, Oudejans CB, Schutgens RB, Pronk JC, van der Knaap MS (2001) Mutations of MLC1 (KIAA0027), encoding a putative membrane protein, cause megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts. Am J Hum Genet 68(4):831–838
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. D. Coviello for the pSPL3 vector (Invitrogen) and Prof. Nicola Migone for critical discussion. We are indebted to the patient and family members who collaborated in the study. This work was supported by Compagnia di San Paolo, Progetto finalizzato Neuroscienze entitled “Identification of a novel gene responsible for a form of adult-onset autosomal dominant leukodystrophy.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Alessandro Brussino and Alfredo Brusco contributed equally to the work.
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 58 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mancini, C., Vaula, G., Scalzitti, L. et al. Megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts type 1 (MLC1) due to a homozygous deep intronic splicing mutation (c.895-226T>G) abrogated in vitro using an antisense morpholino oligonucleotide. Neurogenetics 13, 205–214 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-012-0331-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-012-0331-z