Abstract
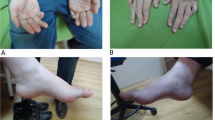
We recently identified a new locus for spastic paraplegia type 47 (SPG47) in a consanguineous Arabic family with two affected siblings with progressive spastic paraparesis, intellectual disability, seizures, periventricular white matter changes and thin corpus callosum. Using exome sequencing, we now identified a novel AP4B1 frameshift mutation (c.664delC) in this family. This mutation was homozygous in both affected siblings and heterozygous in both parents. The mutant allele was absent in 316 Caucasian and 200 ethnically matched control chromosomes. We propose that AP4B1 mutations cause SPG47 and should be considered in early onset spastic paraplegia with intellectual disability.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Salinas S, Proukakis C, Crosby A, Warner TT (2008) Hereditary spastic paraplegia: clinical features and pathogenetic mechanisms. Lancet Neurol 7:1127–1138
Blumkin L, Lerman-Sagie T, Lev D, Yosovich K, Leshinsky-Silver E (2011) A new locus (SPG47) maps to 1p13.2-1p12 in an Arabic family with complicated autosomal recessive hereditary spastic paraplegia and thin corpus callosum. J Neurol Sci 305:67–70
Goecks J, Nekrutenko A, Taylor J (2011) Galaxy: a comprehensive approach for supporting accessible, reproducible, and transparent computational research in the life sciences. Genome Biol 11:R86
Lunter G, Goodson M (2011) Stampy: a statistical algorithm for sensitive and fast mapping of Illumina sequence reads. Genome Res 21:936–939
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G, Durbin R, 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup (2009) The sequence alignment/map format and SAM tools. Bioinforma, Oxf 25:2078–2079
Wang K, Li M, Hakonarson H (2011) ANNOVAR: functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res 38:e164
Abou Jamra R, Philippe O, Raas-Rothschild A, Eck SH, Graf E, Buchert R, Borck G, Ekici A, Brockschmidt FF, Nöthen MM, Munnich A, Strom TM, Reis A, Colleaux L (2011) Adaptor protein complex 4 deficiency causes severe autosomal-recessive intellectual disability, progressive spastic paraplegia, shy character, and short stature. Am J Hum Genet 88:788–795
Moreno-De-Luca A, Helmers SL, Mao H, Burns TG, Melton AM, Schmidt KR, Fernhoff PM, Ledbetter DH, Martin CL (2011) Adaptor protein complex-4 (AP-4) deficiency causes a novel autosomal recessive cerebral palsy syndrome with microcephaly and intellectual disability. J Med Genet 48:141–144
Verkerk AJ, Schot R, Dumee B, Schellekens K, Swagemakers S, Bertoli-Avella AM, Lequin MH, Dudink J, Govaert P, van Zwol AL, Hirst J, Wessels MW, Catsman-Berrevoets C, Verheijen FW, de Graaff E, de Coo IF, Kros JM, Willemsen R, Willems PJ, van der Spek PJ, Mancini GM (2009) Mutation in the AP4M1 gene provides a model for neuroaxonal injury in cerebral palsy. Am J Hum Genet 85:40–52
Acknowledgments
This study has been supported by a grant of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SCHO 754/5-1) and funding from the e-rare program to EUROSPA (01GM0807) and an EC grant (TECHGENE; FP7-Health 2007-B223143).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Peter Bauer, Esther Leshinsky-Silver, and Lubov Blumkin contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bauer, P., Leshinsky-Silver, E., Blumkin, L. et al. Mutation in the AP4B1 gene cause hereditary spastic paraplegia type 47 (SPG47). Neurogenetics 13, 73–76 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-012-0314-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-012-0314-0