Abstract
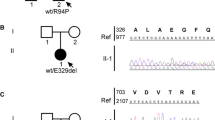
Neurotoxicity is a common side effect of vincristine (VCR) treatment. Severe exacerbations of neuropathy have been reported in patients with Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease (CMT) 1A with duplication of the peripheral myelin protein 22 (PMP22) gene. However, whether or not VCR exacerbates neuropathies through mutations in other CMT-associated genes besides PMP22 duplication has not been well studied. The purpose of this study was to identify mutations in any CMT-associated genes in a patient with hypersensitivity to VCR. We performed clinical, electrophysiological, and genetic examinations of a 23-year-old woman, who was hypersensitive to low-dose VCR, and her healthy mother. DNA analysis was performed using our specially designed resequencing array that simultaneously screens for 28 CMT-associated genes. Electrophysiological studies revealed that the patient and her healthy mother had demyelinating polyneuropathy. Furthermore, they showed the same novel mutation in the early growth response 2 (EGR2) gene. Recognizing pre-existing asymptomatic CMT by electrophysiological studies and genetic analysis before VCR treatment allowed us to prevent severe VCR-induced neuropathy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weiss HD, Walker MD, Wiernik PH (1974) Neurotoxicity of commonly used antineoplastic agents (second of two parts). N Engl J Med 291:127–133
Trobaugh-Lotrario AD, Smith AA, Odom LF (2003) Vincristine neurotoxicity in the presence of hereditary neuropathy. Med Pediatr Oncol 40:39–43
Weimer LH, Podwall D (2006) Medication-induced exacerbation of neuropathy in Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease. J Neurol Sci 242:47–54
Birouk N, Gouider R, Le Guern E, Gugenheim M, Tardieu S, Maisonobe T, Le Forestier N, Agid Y, Brice A, Bouche P (1997) Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease type 1A with 17p11.2 duplication. Clinical and electrophysiological phenotype study and factors influencing disease severity in 119 cases. Brain 120:813–823
Boerkoel CF, Takashima H, Garcia CA, Olney RK, Johnson J, Berry K, Russo P, Kennedy S, Teebi AS, Scavina M, Williams LL, Mancias P, Butler IJ, Krajewski K, Shy M, Lupski JR (2002) Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease and related neuropathies: mutation distribution and genotype–phenotype correlation. Ann Neurol 51:190–201
Yerushalmi R, Levi I, Wygoda M, Ifergane G, Wirguin I (2007) Are platinum-based chemotherapeutic drugs safe for patients with Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease? J Peripher Nerv Syst 12:139–141
Neumann Y, Toren A, Rechavi G, Seifried B, Shoham NG, Mandel M, Kenet G, Sharon N, Sadeh M, Navon R (1996) Vincristine treatment triggering the expression of asymptomatic Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease. Med Pediatr Oncol 26:280–283
Mercuri E, Poulton J, Buck J, Broadbent V, Bamford M, Jungbluth H, Manzur AY, Muntoni F (1999) Vincristine treatment revealing asymptomatic hereditary motor sensory neuropathy type 1A. Arch Dis Child 81:442–443
Uno S, Katayama K, Dobashi N, Hirano A, Ogihara A, Yamazaki H, Usui N, Kobayashi T, Inoue K, Kuraishi Y (1999) Acute vincristine neurotoxicity in a non-Hodgkin's lymphoma patient with Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease. Rinsho Ketsueki 40:414–419
Hildebrandt G, Holler E, Woenkhaus M, Quarch G, Reichle A, Schalke B, Andreesen R (2000) Acute deterioration of Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease IA (CMT IA) following 2 mg of vincristine chemotherapy. Ann Oncol 11:743–747
Naumann R, Mohm J, Reuner U, Kroschinsky F, Rautenstrauss B, Ehninger G (2001) Early recognition of hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy type 1 can avoid life-threatening vincristine neurotoxicity. Br J Haematol 115:323–325
Cil T, Altintas A, Tamam Y, Battaloglu E, Isikdogan A (2009) Low dose vincristine-induced severe polyneuropathy in a Hodgkin lymphoma patient: a case report (vincristine-induced severe polyneuropathy). J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 31:787–789
Ajitsaria R, Reilly M, Anderson J (2008) Uneventful administration of vincristine in Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease type 1X. Pediatr Blood Cancer 50:874–876
Nishikawa T, Kawakami K, Kumamoto T, Tonooka S, Abe A, Hayasaka K, Okamoto Y, Kawano Y (2008) Severe neurotoxicities in a case of Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease type 2 caused by vincristine for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 30:519–521
Porter CC, Carver AE, Albano EA (2009) Vincristine induced peripheral neuropathy potentiated by voriconazole in a patient with previously undiagnosed CMT1X. Pediatr Blood Cancer 52:298–300
Nagarajan R, Svaren J, Le N, Araki T, Watson M, Milbrandt J (2001) EGR2 mutations in inherited neuropathies dominant-negatively inhibit myelin gene expression. Neuron 30:355–368
Scherer SS (1997) The biology and pathobiology of Schwann cells. Curr Opin Neurol 10:386–397
Niemann A, Berger P, Suter U (2006) Pathomechanisms of mutant proteins in Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease. Neuromolecular Med 8:217–242
Swiatek PJ, Gridley T (1993) Perinatal lethality and defects in hindbrain development in mice homozygous for a targeted mutation of the zinc finger gene Krox20. Gene Dev 7:2071–2084
Topilko P, Schneider-Maunoury S, Levi G, Baron-Van Evercooren A, Chennoufi AB, Seitanidou T, Babinet C, Charnay P (1994) Krox-20 controls myelination in the peripheral nervous system. Nature 371:796–799
Warner LE, Mancias P, Butler IJ, McDonald CM, Keppen L, Koob KG, Lupski JR (1998) Mutations in the early growth response 2 (EGR2) gene are associated with hereditary myelinopathies. Nat Genet 18:382–384
Timmerman V, De Jonghe P, Ceuterick C, De Vriendt E, Lofgren A, Nelis E, Warner LE, Lupski JR, Martin JJ, Van Broeckhoven C (1999) Novel missense mutation in the early growth response 2 gene associated with Dejerine–Sottas syndrome phenotype. Neurology 52:1827–1832
Warner LE, Svaren J, Milbrandt J, Lupski JR (1999) Functional consequences of mutations in the early growth response 2 gene (EGR2) correlate with severity of human myelinopathies. Hum Mol Genet 8:1245–1251
Boerkoel C, Takashima H, Bacino C, Daentl D, Lupski J (2001) EGR2 mutation R359W causes a spectrum of Dejerine–Sottas neuropathy. Neurogenetics 3:153–157
Yoshihara T, Kanda F, Yamamoto M, Ishihara H, Misu K, Hattori N, Chihara K, Sobue G (2001) A novel missense mutation in the early growth response 2 gene associated with late-onset Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease type 1. J Neurol Sci 184:149–153
Mikesova E, Huhne K, Rautenstrauss B, Mazanec R, Barankova L, Vyhnalek M, Horacek O, Seeman P (2005) Novel EGR2 mutation R359Q is associated with CMT type 1 and progressive scoliosis. Neuromuscul Disord 15:764–767
Jang SW, LeBlanc SE, Roopra A, Wrabetz L, Svaren J (2006) In vivo detection of Egr2 binding to target genes during peripheral nerve myelination. J Neurochem 98:1678–1687
LeBlanc SE, Ward RM, Svaren J (2007) Neuropathy-associated Egr2 mutants disrupt cooperative activation of myelin protein zero by Egr2 and Sox10. Mol Cell Biol 27:3521–3529
Jang SW, Svaren J (2009) Induction of myelin protein zero by early growth response 2 through upstream and intragenic elements. J Biol Chem 284:20111–20120
Jones EA, Lopez-Anido C, Srinivasan R, Krueger C, Chang LW, Nagarajan R, Svaren J (2011) Regulation of the PMP22 gene through an intronic enhancer. J Neurosci 31:4242–4250
Acknowledgements
We thank the families described in this report for their cooperation. We also thank Ms. A. Yoshimura of Kagoshima University for her excellent technical assistance.
Disclosures
This study was supported in part by grants from the Nervous and Mental Disorders and Research Committee for Charcot–Marie–Tooth Disease, Neuropathy, Ataxic Disease and Research on Applying Health Technology of the Japanese Ministry of Health, Welfare and Labor (H.T). H.T. has received royalty from Athena diagnostics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakamura, T., Hashiguchi, A., Suzuki, S. et al. Vincristine exacerbates asymptomatic Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease with a novel EGR2 mutation. Neurogenetics 13, 77–82 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-012-0313-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-012-0313-1