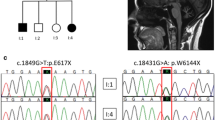
Abstract.
We studied five families with pediatric-onset recessive spastic ataxia from Turkey. The clinical characteristics and linkage studies are compatible with autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay (ARSACS). SACS mutations are responsible for ARSACS in Québec families. In four of the five families tested we detected new disease-causing mutations using automated sequencing of SACS. Our study raises to 12 the number of SACS mutations detected in ARSACS patients with origins around the Mediterranean basin.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouchard J-P, Barbeau A, Bouchard R, Bouchard RW (1978) Autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguanay. Can J Neurol Sci 5:61–69
Jetté R, Gauvreau D, Guérien M (1991) Aux origines d’une région: le peuplement fondateur de Charlevoix avant 1850. In: Bouchard G, De Braekeleer M (eds) Histoire d’un génome: population et génétique dans l’est du Québec. Presses de l’Université du Québec, Sillery, pp 75–107
Gauvreau D, Guérien M, Hamel M (1991) De Charlevoix au Saguenay: mesure et caractéristiques du mouvement migratoire avant 1911. In: Bouchard G, De Braekeleer M (eds) Histoire d’un génome: population et génétique dans l’est du Québec. Presses de l’Université du Québec, Sillery, pp 145–162
De Braekeleer M (1991) Hereditary disorders in Saguenay-Lac-St-Jean (Quebec, Canada). Hum Hered 41:141–146
De Braekeleer M, Giasson F, Mathieu J, Roy M, Bouchard J-P, Morgan K (1993) Genetic epidemiology of autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay in Northeastern Quebec. Genet Epidemiol 10:17–25
Bouchard J-P (1991) Recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay. In: Jong JMBV de (ed) Hereditary neuropathies and spinocerebellar atrophies. Handbook of Clinical Neurology, vol 16. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, pp 451–459
Bouchard J-P, Richter A, Mathieu J, Brunet D, Hudson TJ, Morgan K, Melançon SB (1998) Autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay. Neuromusc Disord 8:474–479
Richter Rioux J, Bouchard J-P, Mercier J, Mathieu J, Ge B, Poirier J, Julien D, Gyapay G, Weissenbach J, Hudson TJ, Melançon SB, Morgan K (1999) Location score and haplotype analysis of the locus for autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay in chromosome region 13 q 11. Am J Hum Genet 64:768–775
Engert JC, Bérubé P, Mercier J, Doré C, Lepage P, Ge B, Bouchard J-P, Mathieu J, Melançon SB, Schalling M, Lander ES, Morgan K, Hudson TJ, Richter A (2000) ARSACS, a spastic ataxia common in northeastern Quebec, is caused by mutations in a new gene encoding an 11.5 kb ORF. Nat Genet 24:120–125
Chaigne D, Brauer E, Ruh D, Jouart D, Juif JG (1993) L’ataxie spastique autosomique récessive: étude clinique, neurophysiologique, ophtalmologique et IRM de deux cas familiaux (abstract). Rev Neurol (Paris) 149:585
Mrissa N, Belal S, Hamida CB, Amouri R, Turki I, Mrissa R, Hamida MB, Hentati F (2000) Linkage to chromosome 13 q 11–12 of an autosomal recessive cerebellar ataxia in a Tunisian family. Neurology 54:1408–1414
Pascual-Castroviejo I, Pascual-Pascual SI, Viano J, Martinez V (2000) Charlevoix-Saguenay type recessive spastic ataxia. A report of a Spanish case. Rev Neurol 31:36–38
Gücüyener K, Özgül K, Paternotte C, Erdem H, Prud’homme JF, Özgüç M, Topaloğlu H (2001) Autosomal recessive spastic atatxia in two unrelated Turkish families. Neuropediatrics 23:142–146
Euch-Fayache G, Lalani I, Amouri R, Turki I, Ouahchi K, Hung WY, Belal S, Siddique T, Hentati F (2003) Phenotypic features and genetic findings in Sacsin-related autosomal recessive ataxia in Tunisia Arch Neurol 60:982–988
Aparicio S, Chapman J, Stupka E, Putnam N, Chia JM, Dehal P, et al (2002) Whole-genome shotgun assembly and analysis of the genome of Fugu rubripes. Science 297:1301–1310
Grynberg M, Erlandsen H, Godzik A (2003) HEPN: a common domain in bacterial drug resistance and human neurodegenerative proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 28:224–226
Grieco GS, Malandrini A, Comanducci G, Leuzzi V, Valoppi M, Tessa A, Palmeri S, Benedetti L, Pierallini A, Gambelli S, Federico A, Pierelli F, Bertini E, Casali C, Santorelli FM (2004) Novel SACS mutations in autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay type. Neurology 62:103–106
Criscuolo C, Banfi S, Orio M, Gasparini P, Monticelli A, Scarano V, Santorelli FM, Perretti A, Santoro L, De Michele G, Filla A (2004) A novel mutation in SACS gene in a family from southern Italy. Neurology 62:100–102
Ogawa T, Takiyama Y, Sakoe K, Mori K, Namekawa M, Shimazaki H, Nakano I, Nishizawa M (2004) Identification of a SACS gene missense mutation in ARSACS. Neurology 62:107–109
Gomez CM (2004) ARSACS goes global. Neurology 62:10–11
Acknowledgements.
These studies were supported by a research grant (MOP-14668) from the Canadian Institutes of Health (to A.R.) and Association Française contre les Myopathies (to H.T.). The experiments described in this paper comply with the current laws of the countries (Turkey and Canada) in which they were performed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Richter, A.M., Ozgul, R.K., Poisson, V.C. et al. Private SACS mutations in autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay (ARSACS) families from Turkey. Neurogenetics 5, 165–170 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-004-0179-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-004-0179-y