Abstract
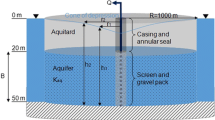
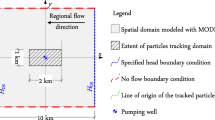
A recent analytical model developed to compute the residence time of fluid flowing in an unconfined aquifer towards a single pumping well is examined. The solution is scaled and presented practically as a nomograph showing the relationship between the residence time, flow length and draw-down. In addition, a similar scaling process is undertaken for the same problem occurring in a confined aquifer so that the error introduced by approximating an unconfined system as a confined system can be understood over a wide range of conditions.
Résumé
On analyse un modèle analytique récent pour calculer le temps de résidence d’un fluide pendant son écoulement vers un puits de pompage dans une nappe libre. La solution a été mise-à-l’échelle et présenté d’une manière pratique, comme une nomogramme qui exprime la relation entre le temps de résidence, la distance de l› écoulement et le rabattement. De plus, on a utilisé un procédé similaire de mise-à-l’échelle pour le même problème dans une nappe captive affin que l’erreur introduite par l’approximation d’une nappe libre par une nappe captive peut être interprétée pour une grande classe de conditions.
Resumen
Se examina un modelo analítico, recientemente desarrollado, para calcular el tiempo de residencia de un fluido, el cual está fluyendo dentro de un acuífero libre hacia un pozo de bombeo único. La solución después de ser ajustada, se presenta prácticamente como un nomograma, mostrando la relación entre el tiempo de residencia, la longitud del flujo y el abatimiento. Adicionalmente, un proceso similar de ajuste fue realizado para el mismo problema, pero bajo condiciones de acuífero confinado, por tanto el error causado por hacer la aproximación de un sistema libre como si fuera un sistema confinado, puede llegar a ser entendido para un rango amplio de condiciones.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bear J (1972) Dynamics of fluids in porous media. Elsevier, New York
Clement TP Wise WR Molz FJ, Wen M (1996) A comparison of modeling approaches for steady-state unconfined flow. J Hydrol 181:189–209
Freeze RA, Cherry JA (1979) Groundwater. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey
Haitjema HM (1995) Analytic Element Modeling of Groundwater Flow. Academic Press, San Diego, California
Muskat M (1937) The flow of homogeneous fluids through porous media. McGraw Hill, New York
Simpson MJ Clement TP, Yeomans FE (2003a) Analytical model for computing residence times near a pumping well. Ground Water 41:351–354
Simpson MJ Clement TP, Gallop TA (2003b) Laboratory and numerical investigation of flow and transport near a seepage-face boundary. Ground Water 41:690–700
Theis CV (1937) The relationship between the lowering of the piezometric surface and the rate and duration of discharge of a well using ground-water storage. Trans Am Geophys Union 16:519–524
Acknowledgement
The review suggestions of Changyuan Tang, Maki Tsujimura and Perry Olcott were appreciated. In addition, Kerry Landman’s initial suggestions were helpful.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simpson, M.J. Computing residence times for flow towards a pumping well: nomograph solution and validity of the small draw-down approximation. Hydrogeol J 13, 889–894 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-004-0369-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-004-0369-6