Abstract
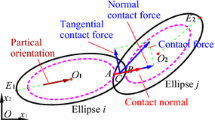
This paper aims to investigate the evolutions of microscopic structures of elliptical particle assemblies in both monotonic and cyclic constant volume simple shear tests using the discrete element method. Microscopic structures, such as particle orientations, contact normals and contact forces, were obtained from the simulations. Elliptical particles with the same aspect ratio (1.4 and 1.7 respectively for the two specimens) were generated with random particle directions, compacted in layers, and then precompressed to a low pressure one-dimensionally to produce an inherently anisotropic specimen. The specimens were sheared in two perpendicular directions (shear mode I and II) in a strain-rate controlled way so that the effects of inherent anisotropy can be examined. The anisotropy of particle orientation increases and the principal direction of particle orientation rotates with the shearing of the specimen in the monotonic tests. The shear mode can affect the way fabric anisotropy rate of particle orientation responds to shear strain as a result of the initial anisotropy. The particle aspect ratio exhibits quantitative influence on some fabric rates, including particle orientation, contact normal and sliding contact normal. The fabric rates of contact normal, sliding contact normal, contact force, strong and weak contact forces fluctuate dramatically around zero after the shear strain exceeds 4 % in the monotonic tests and throughout the cyclic tests. Fabric rates of contact normals and forces are much larger than that of particle orientation. The particle orientation based fabric tensor is harder to evolve than the contact normal or contact force based because the reorientation of particles is more difficult than that of contacts.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oda, M., Nematc-Nasser, S., Mehrabadi, M.M.: A statistical study of fabric in a random assembly of spherical granules. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Mech. Geomech. 6(1), 77–94 (1982)
Satake, M.: Fabric tensor in granular materials. In: Proceedings of the IUTAM Symposium on Deformation and Failure of Granular Materials. Delft, Rotterdam, pp. 63–68 (1982)
Oda, M., Iwashita, K.: Mechanics of Granular Materials. A. A. Balkema, Rotterdam (1999)
Yimsiri, S., Soga, K.: Micromechanics-based stress–strain behaviour of soils at small strains. Géotechnique 50(5), 559–571 (2000)
Chang, C.S., Hicher, P.Y.: An elasto-plastic model for granular materials with microstructural consideration. Int. J. Solids Struct. 42(14), 4258–4277 (2005)
Nemat-Nasser, S.: A micromechanically-based constitutive model for frictional deformation of granular materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 48(6), 1541–1563 (2000)
Rothenburg, L., Bathurst, R.J., Dusseault, M.B.: Micromechanical ideas in constitutive modelling of granular materials. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Micromechanics of Granular Media. Powders Grains, pp. 355–363. A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam (1989)
Ouadfel, H., Rothenburg, L.: Stress–force–fabric’relationship for assemblies of ellipsoids. Mech. Mater. 33(4), 201–221 (2001)
Cundall, P.A., Strack, O.D.L.: A discrete numerical model for granular assemblies. Géotechnique 29(1), 47–65 (1979)
Fonseca, J., Reyes-Aldasoro, C.C., O’Sullivan, C., Coop, M.R.: Experimental investigation into the primary fabric of stress transmitting particles. In: Proceedings of the International Symposium on Geomechanics from Micro to Macro, pp. 1019–1024, Cambridge (2014)
Calvetti, F., Combe, G., Lanier, J.: Experimental micromechanical analysis of a 2D granular material: relation between structure evolution and loading path. Mech. Cohes. Frict. Mater. 2(2), 121–163 (1997)
Kruyt, N.P.: Micromechanical study of fabric evolution in quasi-static deformation of granular materials. Mech. Mater. 44(1), 120–129 (2012)
Yimsiri, S., Soga, K.: DEM analysis of soil fabric effects on behaviour of sand. Géotechnique 60(6), 483–495 (2010)
Kuhn, M.R.: Micro-mechanics of fabric and failure in granular materials. Mech. Mater. 42(9), 827–840 (2010)
O’Sullivan, C., Cui, L.: Fabric evolution in granular materials subject to drained, strain controlled cyclic loading. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Micromechanics of Granular Media, pp. 285–288. AIP, Golden (2009)
Bosko, J.T., Tordesillas, A.: Evolution of Contact Forces, Fabric, and Their Collective Behavior in Granular Media Under Deformation: A DEM Study. Engineering, Construction, and Operations in Challenging Environment, pp. 1–8. ASCE (2006)
Ng, T.-T.: Fabric evolution of ellipsoidal arrays with different particle shapes. J. Eng. Mech. 127(10), 994–999 (2001)
Anandarajah, A.: On influence of fabric anisotropy on the stress–strain behavior of clays. Comput. Geotech. 27(1), 1–17 (2000)
Bathurst, R.J., Rothenburg, L.: Investigation of micromechanical features of idealized granular assemblies using DEM. Eng. Comput. 9(2), 199–210 (1992)
Nouguier-Lehon, C.: Effect of the grain elongation on the behaviour of granular materials in biaxial compression. Comptes Rendus Mécanique 338(10), 587–595 (2010)
Zhao, J.D., Guo, N.: The interplay between anisotropy and strain localisation in granular soils: a multiscale insight. Géotechnique 65(8), 642–656 (2015)
Fu, P.C., Dafalias, Y.F.: Study of anisotropic shear strength of granular materials using DEM simulation. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Mech. Geomech. 35(10), 1098–1126 (2011)
Sazzad, M.M., Suzuki, K.: Micromechanical behavior of granular materials with inherent anisotropy under cyclic loading using 2D DEM. Granul. Matter 12(6), 597–605 (2010)
Kuhn M.R.: OVAL and OVALPLOT: Programs for Analyzing Dense Particle Assemblies with the Discrete Element Method (2006). http://faculty.up.edu/kuhn/oval/doc/oval_0618.pdf
Shodja, H.M., Nezami, E.G.: A micromechanical study of rolling and sliding contacts in assemblies of oval granules. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Mech. Geomech. 27(5), 403–424 (2003)
Mustoe, G.G.W., Miyata, M.: Material flow analyses of noncircular-shaped granular media using discrete element methods. J. Eng. Mech. 127(10), 1017–1026 (2001)
Favier, J.F., Abbaspour-Fard, M.H., Kremmer, M.: Modeling nonspherical particles using multisphere discrete elements. J. Eng. Mech. 127(10), 971–977 (2001)
Ouadfel, H., Rothenburg, L.: An algorithm for detecting inter-ellipsoid contacts. Comput. Geotech. 24(4), 245–263 (1999)
Wang, C.Y., Liang, V.C.: A packing generation scheme for the granular assemblies with planar elliptical particles. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Mech. Geomech. 21(5), 347–358 (1997)
Lin, X.S., Ng, T.-T.: A three-dimensional discrete element model using arrays of ellipsoids. Géotechnique 47(2), 319–329 (1997)
Lin, X.S., Ng, T.-T.: Contact detection algorithms for three-dimensional ellipsoids in discrete element modelling. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Mech. Geomech. 19(9), 653–659 (1995)
Ng, T.-T.: Numerical simulations of granular soil using elliptical particles. Comput. Geotech. 16(2), 153–169 (1994)
Ting, J.M., Khwaja, M., Meachum, L.R., Rowell, J.D.: An ellipsec-based discrete element model for granular materials. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Mech. Geomech. 17(9), 603–623 (1993)
Ting, J.M., Corkum, B.T.: Computational laboratory for discrete element geomechanics. J. Comput. Civil Eng. 6(2), 129–146 (1992)
Ting, J.M.: A robust algorithm for ellipse-based discrete element modelling of granular materials. Comput. Geotech. 13(3), 175–186 (1992)
Rothenburg, L., Bathurst, R.J.: Micromechanical features of granular assemblies with planar elliptical particles. Géotechnique 42(1), 79–95 (1992)
Rothenburg, L., Bathurst, R.J.: Numerical simulation of idealized granular assemblies with plane elliptical particles. Comput. Geotech. 11(4), 315–329 (1991)
Ting, J.M., Meachum, L., Rowell, J.D.: Effect of particle shape on the strength and deformation mechanisms of ellipse-shaped granular assemblages. Eng. Comput. 12(2), 99–108 (1995)
Jiang, M.J., Konrad, J.M., Leroueil, S.: An efficient technique for generating homogeneous specimens for DEM studies. Comput. Geotech. 30(7), 579–597 (2003)
Jiang, M.J., Leroueil, S., Konrad, J.M.: Insight into shear strength functions of unsaturated granulates by DEM analyses. Comput. Geotech. 31(6), 473–489 (2004)
Currary, J.R.: The analysis of two-dimensional orientation data. J. Geol. 64(2), 117–131 (1956)
Thornton, C.: Numerical simulations of deviatoric shear deformation of granular media. Géotechnique 50(1), 43–53 (2000)
Acknowledgments
The work reported here has been supported by the China National Natural Science Foundation with Grant No. 51579178, the National Basic Research Program of China with Grant Nos. 2011CB013504 and 2014CB046901 and State Key Lab. of Disaster Reduction in Civil Engineering with Grant No. SLDRCE14-A-04. The authors also thank Dr. Liqing Li and Mr. Chang Fu for their involvement in the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Micro origins for macro behavior of granular matter.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, M., Li, T. & Shen, Z. Fabric rates of elliptical particle assembly in monotonic and cyclic simple shear tests: a numerical study. Granular Matter 18, 54 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-016-0641-1
Received:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-016-0641-1