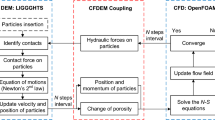
Abstract
Geomaterials are mixtures of solids with voids which are filled by fluids such as air and water. Due to the strong coupling between phases, pore pressures can be generated if loading is applied fast enough. In the case of loose metastable materials, unstable behavior and catastrophic failure can happen. An important case is that of fast catastrophic landslides with large velocities caused by high pore pressures in their lower part. The purpose of this paper is to present mathematical, constitutive and rheological models which describe the most relevant phenomena, together with discretization techniques.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagnold R.A.: Experiments on a gravity-free dispersion of large solid spheres in a Newtonian fluid under shear. Proc. Royal Soc. A 225, 49–63 (1954)
Been K., Jefferies M.: A state parameter for sands. Géotechnique 35, 99–112 (1985)
Biot M.A.: Theory of elasticity and consolidation for a porous anisotropic solid. J. Appl. Phys. 26, 182–185 (1955)
Castro, G.: Liquefaction of sands, Ph.D. thesis, Harvard University, Harvard Soil Mechanics Series no. 81 (1969)
Chen C.L., Ling C.H.: Granular-flow rheology: role of shear-rate number in transition regime. J. Eng. Mech. ASCE 122(5), 469–481 (1996)
Coulomb, C.A.: Essai sur une application des régles de maxi- mis et minimis à quelques problémes de statique relatifs a l’architecture”. Mémoires de Mathématique et de Physique, présentés à l’Académie Royale des Sciences par Divers Savants et lus dans ses Assemblées, 7, Paris, France, 343–382 (1773)
Coussy O.: Mechanics of Porous Media. Wiley, Chichester (1995)
Darve F.: Liquefaction phenomenon of granular materials and constitutive instability. Int. J. Eng. Comp. 7, 5–28 (1995)
Darve F., Laouafa F.: Instabilities in granular materials and application to landslides. Mech. Coh.-Frict. Mater. 5(8), 627–652 (2000)
Darve F., Laouafa F.: Modelling of slope failure by a material instability mechanism. Comput. Geotech. 29, 301–325 (2001)
de Boer R.: Theory of Porous Media. Springer, Berlin (2000)
Dikau R., Cavallin A., Jager S.: Databases and GIS for landslide research in Europe. Geomorphology 15(3–4), 227–239 (1996)
Di Prisco C., Matiotti R., Nova R.: Theoretical investigation of undrained stability of shallow submerged slopes. Geotechnique 45, 479–496 (1995)
Evans, S.G., Bent, A.L.: The las Colinas Landslide, Santa Tecla: a highly destructive flowslide triggered by the Jan 13, 2001, El Salvador earthquake. In: Rose W.T., et al. (eds.) Natural Hazards in El Salvador: Geological Society of America Special Paper 375, pp. 25–37 (2004)
Fernández Merodo J.A., Pastor M., Mira P., Tonni L., Herreros I., González E., Tamagnini R.: Modelling of diffuse failure mechanisms of catastrophic landslides. Comp. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 193, 2911–2939 (2004)
Fisher R.A.: On the capillary forces in an ideal soil; correction of formulas by W.B. Haines. J. Agric. Sci. 16, 492–505 (1926)
Gallipoli D., Gens A., Sharma R., Vaunat J.: An elastoplastic model for unsaturated soil incorporating the effects of suction and degree of saturation on mechanical behaviour. Géotechnique 53(1), 123–135 (2003)
Gens, A., Nova, R.: Conceptual bases for a constitutive model for bonded soils and weak rocks. In: Proceedings of International Symposium on Geotechnical Engineering of Hard Soils-Soft Rocks, pp. 485–494. Rótterdam, Balkema (1993)
Haines W.B.: Studies in the physical properties of soils. A note on the cohesion developed by capillary forces in an ideal soil. J. Agric. Sci. 15, 529–535 (1925)
Hanes D.M., Inman D.L.: Observations of rapidly flowing granular-fluid materials. J. Fluid Mech. 150, 357–380 (1985)
Herschel W.H., Bulkley R.: Konsistenzmessungen von Gummi-Benzollösungen. Kolloid Zeitschrift 39, 291–300 (1926)
Houlsby G.T.: The work input to an unsaturated granular material. Géotechnique 47(1), 193–196 (1997)
Hutchinson J.N.: A sliding-consolidation model for flow slides. Can. Geotech. J. 23, 115–126 (1986)
Iverson R.M.: Differential equations governing slip-induced pore pressure fluctuations in a water-saturated granular medium. Math. Geol. 25(8), 1027–1048 (1993)
Iverson R.I., Denlinger R.P.: Flow of variably fluidized granular masses across three dimensional terrain. 1. Coulomb mixture theory. J. Geophys. Res. 106(N0.B1), 537–552 (2001)
Iverson R.M., LaHusen R.G.: Dynamic pore-pressure fluctuations in rapidly shearing granular materials. Science 246, 796–799 (1989)
Konagai, K., Johansson, J., Mayorca, P., Uzuoka, R., Yamamoto, T., Miyajima, M., Pulido, N., Sassa, K., Fujuoka, H., Duran, F.: Las Colinas landslide, Santa Tecla: rapid and long-traveling soil flow caused by the January 13th, 2001, El Salvador earthquake. In: Rose, W.I, Bommer, J.J., Lopez, D.L., Carr, M.J., Major, J.J. (eds.) Natural Hazards in El Salvador, pp. 25–37 (2004)
Lagioia R., Nova R.: An experimental and theoretical study of the behaviour of a calcarenite in triaxial compression. Geotechnique 45(4), 633–648 (1995)
Lewis R.W., Schrefler B.A.: The Finite Element Method in the Deformation and Consolidation of Porous Media. Wiley, Chichester (1987)
Li X.L.: Modelling of dilative shear failure. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 123, 609–616 (1997)
Li X.L., Dafalias Y.F.: Dilatancy for cohesionless soils. Géotechnique 50, 449–460 (2000)
Lotti, C.C.: E.Hydro, Informe Final. Análisis Evaluación Modelos Numéricos Equlibrio Límite”. Anexo 2.2.1.1 (2001) (in spanish)
Maâtouk A., Leroueil S., LaRochelle P.: Yielding and critical state of a collapsible unsaturated silty soil. Geotechnique 45(3), 465–477 (1995)
Manzanal, D.: Constitutive model based on generalized plasticity incorporating state parameter for saturated and unsaturated sand (Spanish). PhD Thesis School of Civil Engineering, Polytechnic University of Madrid (2008)
Nicot F., Wan R., (eds): Micromécanique de la rupture dans les milieux granulaires. Hermes Science Lavoisier, France (2008)
Nova R.: Controllability of the incremental response of soil specimens subjected to arbitrary loading programmes. J. Mech. Behav. Mater. 5, 193–201 (1994)
Pastor, M., Zienkiewicz, O.C.: A generalized plasticity, hierarchical model for sand under monotonic and cyclic loading. In 2nd International Symposium on Numerical Models in Geomechanic, Ghent, pp. 131–149 (1986)
Pastor M., Zienkiewicz O.C., Leung K.H.: Simple model for transient soil loading in earthquake analysis. II: non-associative models for sands. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Meth. Geomech. 9, 477–498 (1985)
Pastor M., Zienkiewicz O.C., Chan A.H.C.: Generalized plasticity and the modelling of soil behaviour. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Meth. Geomech. 14, 151–190 (1990)
Pastor M., Quecedo M., Merodo J.A.F., Herreros M.I., Gonzalez E., Mira P.: Modelling tailings dams and mine waste dumps failures. Géotechnique 52(8), 579–591 (2002)
Pastor M., Quecedo M., González E., Herreros I, Fernández Merodo J.A., Mira P.: Modelling of landslides: (II) propagation. In: Darve, F., Vardoulakis , I. (eds) Degradations and Instabilities in Geomaterials, pp. 319–367. Springer Wien, New York (2004)
Pastor, M., Blanc, T., Pastor, M.J.: A depth integrated viscoplastic model for dilatant saturated cohesive-frictional fluidized mixtures: application to fast catastrophic landslides. J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech. (in press, 2009)
Pastor M., Haddad B., Sorbino G., Cuomo S., Drempetic V.: A depth integrated coupled SPH model for flow-like landslides and related phenomena. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Meth. Geomech. 33(2), 143–172 (2009)
Quecedo M., Pastor M., Herreros I.: Numerical modelling of impulse wave generated by fast landslides. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Eng. 59, 1633–1656 (2004)
Roscoe K.H., Poorooshasb H.B.: A fundamental principle of similarity in model tests for earth pressure problems. Conf. Asiatique Mécanique des Sols 1, 134–140 (1963)
Sassa, K., Fukuoka, H., Wang, G.: Activities of APERIF: areal prediction of earthquake and rain induced rapid and long travelling flow phenomena. In: Fukuoka, H. (ed.) Proceedings of the Kansai Branch Symposium, Japan Landslide Society, ISBN 4-9900618-9-6 C3051, pp. 61–78 (in Japanese) (2002)
Savage S.B., Hutter K.: The dynamics of avalanches of granular materials from initiation to runout. Part I: analysis. Acta Mech. 86, 201–223 (1991)
Schneider, L., Hutter, K.: Solid-Fluid Mixtures of Frictional Materials in Geophysical Context Based on a Concise Thermodynamic Analysis. Advances in geophysical and environmental mechanics and mathematics series, Springer, New York (2009, to appear)
Seed H.B., Lee K.H.: Undained strength characteristics of cohesionless soils. J. Soil Mech. Found. Div. Proc. ASCE 93(6), 333–360 (1967)
Sivakumar, V.: A critical state framework for unsaturated soil. Ph.D. thesis Department of Civil and Structural Engineering, University of Sheffield (1993)
Spencer A.J.M.: Continuum Mechanics. Longman, London (1980)
Tamagnini R.: An extended Cam-Clay model for unsaturated soils with hydraulic hysteresis. Géotechnique 54(2), 223–228 (2004)
Tamagnini R., Pastor M.: A thermodynamically based model for unsaturated soils: a new framework for generalized plasticity. In: Mancuso, (eds) 2nd International Workshop on Unsaturated Soils, pp. 1–14. Naples, Italy (2004)
Uriel, A.O.: Discussion to spec. session 2, problems of non linear soil mechanics. In: Proceedings of the 8th International Conference Soil Mechanics Foundation Engineering Moscow, vol. 4.3, pp. 78–80 (1973)
Uriel, A.O., Merino, M.: Harmonic response of sands in shear. In: Third International Conference on Numerical Methods Geomechanics pp. 2–6, Aachen (1979)
Voellmy A.: Über die Zerstörungskraft von Lawinen. Schweizerische Bauzeitung 73, 212–285 (1955)
Wan R.G., Guo P.J.: A simple constitutive model for granular soils: modified stress-dilatancy approach. Comput. Geotech. 22(2), 109–133 (1998)
Wroth C.P., Bassett N.: A stress-strain relationship for the shearing behaviour of sand. Géotechnique 15, 32–56 (1965)
Zienkiewicz O.C., Mroz Z.: Generalized plasticity formulation and applications to geomechanics. In: Desai, C.S., Gallagher, R.H. (eds) Mechanics of Engineering Materials, pp. 655–679. John Wiley, Sons (1984)
Zienkiewicz O.C., Shiomi T.: Dynamic behaviour of saturated porous-media - The generalized Biot formulation and its numerical solution. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Meth. Geomech. 8(1), 71–96 (1984)
Zienkiewicz O.C., Chang C.T., Bettess P.: Drained, undrained, consolidating and dynamic behaviour assumptions in soils. Géotechnique 30(4), 385–395 (1980)
Zienkiewicz O.C., Leung K.H., Pastor M.: Simple model for transient soil loading in earthquake analysis. I: basic model and its application. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Meth. Geomech. 9, 453–476 (1985)
Zienkiewicz O.C., Chan A.H.C., Pastor M., Schrefler B.A., Shiomi T.: Computational geomechanics. John Wiley, Sons (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pastor, M., Manzanal, D., Fernández Merodo, J.A. et al. From solids to fluidized soils: diffuse failure mechanisms in geostructures with applications to fast catastrophic landslides. Granular Matter 12, 211–228 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-009-0152-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-009-0152-4