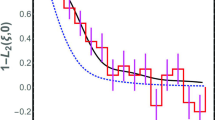
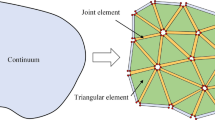
Abstract
We study the influence of particle shape anisotropy on the occurrence of avalanches in sheared granular media. We use molecular dynamic simulations to calculate the relative movement of two tectonic plates. Our model considers irregular polygonal particles constituting the material within the shear zone. We find that the magnitude of the avalanches is approximately independent of particle shape and in good agreement with the Gutenberg–Richter law, but the aftershock sequences are strongly influenced by the particle anisotropy yielding variations on the exponent characterizing the empirical Omori’s law. Our findings enable one to identify the presence of anisotropic particles at the macro-mechanical level only by observing the avalanche sequences of real faults. In addition, we calculate the probability of occurrence of an avalanche for given values of stiffness or frictional strength and observe also a significant influence of the particle anisotropy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolt B.A.: Earthquakes. W.H. Freeman, New York (2005)
Sykes L.R., Shaw B.E., Scholz C.H.: Rethinking earthquake prediction. Pure Appl. Geophys. 155, 207–232 (1999)
Donzé F., Mora P., Magnier S.-A.: Numerical simulation of faults and shear zones. Geophys. J. Int. 116, 46–52 (1994)
Mora P., Place D.: Stress correlation function evolution in lattice solid elasto-dynamic models of shear and fracture zones and earthquake prediction. Pure Appl. Geophys. 159, 2413–2427 (2002)
Ramos, O., Altshuler, E., Maløy, K.J.: Predicting power law distributed avalanches: implications for earthquake forecast. Private report (2007)
Summers R., Byerlee J.D.: A note on the effect of fault gouge composition on the stability of frictional sliding. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 14, 155–160 (1977)
Marone C.: Laboratory-derived friction laws and their application to seismic faulting. Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 26, 643–696 (1998)
Mair K., Frye K.M., Marone C.: Influence of grain characteristics on the friction of granular shear zones. J. Geophys. Res. 107, 2219 (2002)
Mora P., Place D.: Simulation of the frictional stick-slip instability. Pageoph 143, 61 (1994)
Tillemans H.J., Herrmann H.J.: Simulating deformations of granular solids under shear. Physica A 217, 261–288 (1995)
Mora P., Place D.: The weakness of earthquake faults. Geophys. Res. Lett. 26, 123–126 (1999)
Alonso-Marroquín F., Vardoulakis I., Herrmann H.J., Weatherley D., Mora P.: Effect of rolling on dissipation in fault gouges. Phys. Rev. E 74, 031306 (2006)
Scholz C.H.: The Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2002)
Turcotte D.L., Schubert G.: Geodynamics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2002)
Abe S., Latham S., Mora P.: Dynamic rupture in a 3-d particle-based simulation of a rough planar fault. Pure Appl. Geophys. 163, 1881–1892 (2006)
Wilson B., Dewers T., Reches Z., Brune J.: Particle size and energetics of gouge from earthquake rupture zone. Nature 434, 749–752 (2005)
Mora P., Place D.: Numerical simulation of earthquake faults with gouge: toward a comprehensive explanation for the heat flow paradox. J. Geophys. Res. 103, 21067–21089 (1998)
Peña, A.A., Lizcano, A., Alonso-Marroquín, F., Herrmann, H.J.: Biaxial test simulations using a packing of polygonal particles. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Meth. Geomech. (2007) (accepted)
Peña A.A., García-Rojo R., Herrmann H.J.: Influence of particle shape on sheared dense granular media. Granul. Matter 9, 279–291 (2007)
Kanamori H., Brodsky E.E.: The physics of earthquakes. Phys. Today 54, 34–40 (2001)
Sethna J.P., Dahmen K.A., Myers C.R.: Crackling noise. Nature 410, 242–250 (2001)
Gutenberg B., Richter C.F.: Seismicity of the Earth and Associated Phenomena. Princeton University Press, Princeton (1954)
Omori F.: On the aftershocks of earthquakes. J. Coll. Sci. Imper. Univ. Tokyo 7, 111 (1895)
Pöschel T., Schwager T.: Computational Granular Dynamics. Springer, Berlin (2005)
Chakrabarti K.B., Benguigui L.G.: Statistical Physics of Fracture and Breakdown in Disordered Systems. Clarendon, Oxford (1997)
Papoulis A.: Probability, Random Variables, and Stochastic Processes. McGraw-Hill, Boston (2002)
Peña A.A., Lind P.G., Herrmann H.J.: Modeling slow deformation of polygonal particles using DEM. Particuology 6, 506–514 (2008)
Peña, A.A., Lind, P.G., McNamara, S., Herrmann, H.J.: Numerical improvement of the discrete element method applied to shear of granular media. Acta Mech. (2009) (in press)
Nasuno S., Kudrolli A., Bank A., Gollub J.P.: Time-resolved studies of stick-slip friction in sheared granular layers. Phys. Rev. E 58, 2161–2171 (1998)
Feder H.J.S., Feder J.: Self-organized criticality in a stick-slip process. Phys. Rev. Lett. 66, 2669–2672 (1991)
Staron L., Radjai F.: Friction versus texture at the approach of a granular avalanche. Phys. Rev. E 72, 041308 (2005)
Staron L., Vilotte J.P., Radjai F.: Preavalanche instabilities in a granular pile. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 204302 (2002)
Radjai F., Jean M., Moreau J.J., Roux S.: Force distribution in dense two-dimensional granular systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 274 (1996)
Radjai F., Wolf D.E., Jean M., Moreau J.J.: Bimodal character of stress transmission in granular packings. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 61–64 (1998)
Majmudar T.S., Behringe R.P.: Contact force measurements and stress-induced anisotropy in granular materials. Nature 435, 1079–1082 (2005)
Staron, L., Radjai, F., Vilotte, J.P.: Granular micro-structure and avalanche precursors. J. Stat. Mech. P07014 (2006)
Alonso-Marroquin, F., Peña, A.A., Herrmann, H.J., Mora, P.: Simulation of shear bands using polygonal particles. Discrete Element Methods (DEM) Conference, Brisbane, Australia, pp. 1–8 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peña, A.A., McNamara, S., Lind, P.G. et al. Avalanches in anisotropic sheared granular media. Granular Matter 11, 243–252 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-009-0136-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-009-0136-4