Abstract
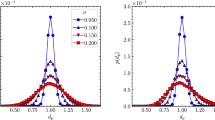
In its simplest statistical-mechanical description, a granular fluid can be modeled as composed of smooth inelastic hard spheres (with a constant coefficient of normal restitution α) whose velocity distribution function obeys the Enskog–Boltzmann equation. The basic state of a granular fluid is the homogeneous cooling state, characterized by a homogeneous, isotropic, and stationary distribution of scaled velocities, F(c). The behavior of F(c) in the domain of thermal velocities (c ~ 1) can be characterized by the two first non-trivial coefficients (a 2 and a 3) of an expansion in Sonine polynomials. The main goals of this paper are to review some of the previous efforts made to estimate (and measure in computer simulations) the α-dependence of a 2 and a 3, to report new computer simulations results of a 2 and a 3 for two-dimensional systems, and to investigate the possibility of proposing theoretical estimates of a 2 and a 3 with an optimal compromise between simplicity and accuracy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campbell C.S.: Rapid granular flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 22, 57 (1990)
Goldhirsch I.: Rapid granular flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 35, 267 (2003)
Brilliantov N., Pöschel T.: Kinetic Theory of Granular Gases. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2004)
Brey J.J., Dufty J.W., Santos A.: Dissipative dynamics for hard spheres. J. Stat. Phys. 87, 1051 (1997)
Haff P.K.: Grain flow as a fluid-mechanical phenomenon. J. Fluid Mech. 134, 401 (1983)
van Noije T.P.C., Ernst M.H.: Velocity distributions in homogeneous granular fluids: the free and the heated case. Granul. Matter 1, 57 (1998)
Esipov S.E., Pöschel T.: The granular phase diagram. J. Stat. Phys. 86, 1385 (1997)
Abramowitz M., Stegun I.A. (eds) Handbook of Mathematical Functions, Ch. 22. Dover, New York (1972)
Noskowicz S.H., Bar-Lev O., Serero D., Goldhirsch I.: Computer-aided kinetic theory and granular gases. Europhys. Lett. 79, 60001 (2007)
Goldshtein A., Shapiro M.: Mechanics of collisional motion of granular materials. Part 1. General hydrodynamic equations. J. Fluid Mech. 282, 75 (1995)
Brey J.J., Ruiz-Montero M.J., Cubero D.: Homogeneous cooling state of a low-density granular flow. Phys. Rev. E 54, 3664 (1996)
Garzó V., Dufty J.W.: Homogeneous cooling state for a granular mixture. Phys. Rev. E 60, 5706 (1999)
Montanero J.M., Santos A.: Computer simulation of uniformly heated granular fluids. Granul. Matter 2, 53 (2000)
Brilliantov N., Pöschel T.: Deviation from Maxwell distribution in granular gases with constant restitution coefficient. Phys. Rev. E 61, 2809 (2000)
Huthmann M., Orza J.A.G., Brito R.: Dynamics of deviations from the Gaussian state in a freely cooling homogeneous system of smooth inelastic particles. Granul. Matter 2, 189 (2000)
Montanero J.M., Garzó V.: Monte Carlo simulation of the homogeneous cooling state for a granular mixture. Granul. Matter 4, 17 (2002)
Coppex F., Droz M., Piasecki J., Trizac E.: On the first Sonine correction for granular gases. Physica A 329, 114 (2003)
Brilliantov N., Pöschel T.: Breakdown of the Sonine expansion for the velocity distribution of granular gases. Europhys. Lett. 74, 424 (2006)
Brilliantov N., Pöschel T.: Erratum: breakdown of the Sonine expansion for the velocity distribution of granular gases. Europhys. Lett. 75, 188 (2006)
Ahmad S.R., Puri S.: Velocity distributions in a freely evolving granular gas. Europhys. Lett. 75, 56 (2006)
Ahmad S.R., Puri S.: Velocity distributions and aging in a cooling granular gas. Phys. Rev. E 75, 031302 (2007)
Brey J.J., Dufty J.W., Kim C.S., Santos A.: Hydrodynamics for granular flow at low density. Phys. Rev. E 58, 4638 (1998)
Garzó V., Santos A., Montanero J.M.: Modified Sonine approximation for the Navier-Stokes transport coefficients of a granular gas. Physica A 376, 94 (2007)
Bird G.: Molecular Gas Dynamics and the Direct Simulation of Gas Flows. Clarendon, Oxford (1994)
Alexander F.J., Garcia A.L.: The direct simulation Monte Carlo method. Comp. Phys. 11, 588 (1997)
Williams D.R.M., MacKintosh F.C.: Driven granular media in one dimension: correlations and equation of state. Phys. Rev. E 54, R9 (1996)
Williams D.R.M.: Driven granular media and dissipative gases: correlations and liquid-gas phase transitions. Physica A 233, 718 (1996)
Swift M.R., Boamfǎ M., Cornell S.J., Maritan A.: Scale invariant correlations in a driven dissipative gas. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 4410 (1998)
Santos A., Ernst M.H.: Exact steady-state solution of the Boltzmann equation: a driven one-dimensional inelastic Maxwell gas. Phys. Rev. E 68, 011305 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santos, A., Montanero, J.M. The second and third Sonine coefficients of a freely cooling granular gas revisited. Granular Matter 11, 157–168 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-009-0132-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-009-0132-8