Abstract
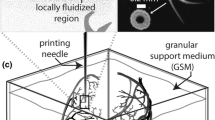
We present the results of direct observation of material rearrangement due to penetration of a solid rod (penetrometer) through a granular medium. Two different techniques and their advantages are discussed in this paper. We investigate the motion of material within the bulk around the rod. Transparent, polydisperse, and irregularly shaped silica particles immersed in index matching fluid are used for detailed imaging of the interior of a granular pile. Motion of material is observed by confocal microscopy from the bottom boundary up to 100 particle diameters in height. Image analysis indicates that rearrangements spread furthest not directly under the penetrometer but in a ring around the penetrometer. In addition, the direction of preformed stress chains in the material influences the particle rearrangements. Material compressed from one side exhibits anisotropic particle rearrangements under penetrometer testing. Laser sheet scanning allows for direct imaging of individual particle motion with greater accuracy, but works best for spherical particles only.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolton M. (1979). A Guide to Soil Mechanics. Macmillan Education Ltd, New York
Friedmann, S.J., Kwon, G., Losert, W.: Granular mem- ory and its effect on the triggering and distribution of rock avalanche events. J. Geophys. Res. 108(B8), ECV8–1–11 (2005)
Geng J., Howell D., Longhi E., Behringer R.P. (2001). Footprints in sand: the response of a granular material to local perturbations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87(3): 03556
Hill K.M., Kakalios J. (1997). Axial segregation of granular media rotated in a drum mixer: pattern evolution. Phys. Rev. E. 56(4): 4386–4393
Iskander M.G., Liu J., Sadek S. (2002). Transparent amorphous silica to model clay. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. 128(3): 262–273
Khakhar D.V., Orpe A.V., Hajra S.K. (2003). Segregation of granular materials in rotating cylinders. Physica A 318(1-2): 129–136
Louge M.Y. (2003). Model for dense granular flows down bumpy inclines. Phys. Rev. E. 67(6): 61303/1–61303/11
Majmudar T.S., Behringer R.P. (2005). Contact force measurements and stress-induced anisotropy in granular materials. Nature 435(7045): 1079–1082
MiDi G. (2004). On dense granular flows. Eur. Phys. J. E. 14: 341–365
Sadek S., Iskander M.G., Liu J. (2003). Accuracy of digital image correlation for measuring deformations in transparent media. J. Comput. Civil. Eng. 17: 88–96
Stone, M.B., Barry, R., Bernstein, D.P., Pelc, M.D., Tsui, Y.K., Schiffer, P.: Local jamming via penetration of a granular medium. Phys. Rev. E. 70(4), 41301–1–10 (2004)
Stone M.B., Bernstein D.P., Barry R., Pelc M.D., Tsui Y., Schiffer P. (2004). Getting to the bottom of granular medium. Nature 427: 503–504
Stone, M.B., Bernstein, D.P., Barry, R., Pelc, M.D., Tsui, Y.,Schiffer, P.: Unpublished (2004)
Terzaghi K., Peck R.B. (1967). Soil Mechanics in Engineering Practice, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Toiya M., Stambaugh J., Losert W. (2004). Transient and oscillatory granular shear flow. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93(8): 088001/1–088001/4
Tsai J.C., Voth G.A., Gollub J.P. (1999). Mixing of granular materials: a test-bed for dynammical system for pattern formation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 9(8): 1467–1484
Utter B., Behringer R.P. (2004). Self-diffusion in dense gran- ular shear flows. Phys. Rev. E. 69(3): 31308/1–31308/12
van den Berg P. (1994). Analysis of Soil Penetration. Delft University Press, Delft
Vanel L., Howell D., Clark D., Behringer R.P., Clement E. (1999). Memories in sand: experimental tests of construction history of stress distributions under sandpiles. Phys. Rev. E. 60: R5040–R5043
Welker A.L., Bowders J.J., Gilbert R.B. (1999). Applied research using a transparent material with hydraulic properties similar to soil. Geotech. Test. J. 22(3): 266–270
Yu H.S., Mitchell J.K. (1998). Analysis of cone resistance: review of methods. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. 124: 140–149
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toiya, M., Hettinga, J. & Losert, W. 3D Imaging of particle motion during penetrometer testing. Granular Matter 9, 323–329 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-007-0044-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-007-0044-4