Abstract
The force analysis of overconstrained PMs is relatively complex and difficult, for which the methods have always been a research hotspot. However, few literatures analyze the characteristics and application scopes of the various methods, which is not convenient for researchers and engineers to master and adopt them properly. A review of the methods for force analysis of both passive and active overconstrained PMs is presented. The existing force analysis methods for these two kinds of overconstrained PMs are classified according to their main ideas. Each category is briefly demonstrated and evaluated from such aspects as the calculation amount, the comprehensiveness of considering limbs’ deformation, and the existence of explicit expressions of the solutions, which provides an important reference for researchers and engineers to quickly find a suitable method. The similarities and differences between the statically indeterminate problem of passive overconstrained PMs and that of active overconstrained PMs are discussed, and a universal method for these two kinds of overconstrained PMs is pointed out. The existing deficiencies and development directions of the force analysis methods for overconstrained systems are indicated based on the overview.
Similar content being viewed by others
1 Introduction
Compared with parallel mechanisms (PMs) with six degrees of freedom (DoFs), lower mobility PMs have increasingly drawn attention from researchers and engineers in the robotics community in recent years, since 100 percent flexibility (i.e., six DoFs) is not required in many instances [1]. In terms of the relationship between the number of constraints and that of DoFs possessed by the moving platform of a PM, the lower mobility PMs can be divided into two categories: PMs in which the moving platform suffers exactly 6–n (n represents the number of DoFs) constraints, for example, the 3-RPS PM [2], 3-UPU PM [3,4,5], 3-RCC PM [6], and so on [7], and those in which the moving platform suffers more than 6–n constraints supplied by all supporting limbs, for example, the 3-RRC PM [8], 2UPR + SPR PM [9,10,11], and 3-PRC PM [12, 13]. The latter category of lower mobility PMs are called overconstrained PMs [14, 15], and they contain common or redundant constraints that can be removed without changing the kinematics of the mechanisms [16, 17]. The overconstrained PMs have the merits of higher stiffness and larger loading capacity with respect to general lower mobility PMs, which are also called passive overconstrained PMs, as the joint reactions are related to system stiffness [18].
It is well known that redundantly actuated PMs [19,20,21] have been investigated and utilized extensively, since redundant actuations can avoid kinematic singularities [22,23,24,25,26,27], enlarge load capability [28,29,30], improve dynamic characteristics [31, 32], and eliminate backlash [33, 34] of the mechanisms. The distribution of driving forces/torques of a redundantly actuated PM belongs to the statically indeterminate problem. From this view, the multi-robot cooperation system [35, 36], walking machines with multiple legs [37, 38], and mechanical hands grasping an object [39, 40] can also be regarded as redundantly actuated PMs to some extent. As an actuator redundancy can transform a mechanism into an overconstrained mechanism, the redundantly actuated PMs are also overconstrained PMs. These kinds of PMs are called active overconstrained PMs, since the driving forces/torques can be distributed arbitrarily according to different optimization goals [18].
Redundant constraints exist in both active overconstrained and passive overconstrained PMs. Although they have no effect on the kinematics [41], they increase the complexity and difficulty of the force analysis of these two kinds of overconstrained PMs. The objective of force analysis of passive overconstrained PMs is to determine the driving forces/torques and constraint forces/moments that balance the external loads. In the case that only driving forces/torques are required, the methods for force analysis of non-overconstrained PMs are applicable to this kind of mechanisms, such as, the Newton–Euler formulation [42, 43], the virtual work principle [44, 45], the Lagrangian formulation [9, 46], and so on [47, 48]. In many cases, for example, when we want to take the influence of friction in joints into consideration, the constraint forces/moments need to be calculated. Bi et al. [10], built a complete and solvable dynamic model of a passive overconstrained PM by extending the Newton–Euler formulation. This method is computationally intensive because of the high-rank coefficient matrix of the simultaneous equations. Wojtyra et al. [17, 49,50,51,52], proposed several mathematical and simulation methods to find the reactions for which joints can be uniquely determined. The corresponding physical interpretation is not considered in those methods. Vertechy et al. [53], Wang et al. [54], Yao et al. [55], and Hu et al. [56], studied the force analysis of passive overconstrained PMs under the condition that the deformations along different axes generated at the end of each supporting limb by the corresponding driving forces/torques and constraint forces/moments are independent of each other. The coupled deformations of each limb generated by the driving forces/torques and constraint forces/moments within the same limb are ignored. Based on the screw theory, Huang et al. [57], presented an approach for the kinetostatics of passive overconstrained PMs with collinear constraint forces or coaxial constraint moments. However, this approach is not suitable for the passive overconstrained PMs with general constraints. Xu et al. [58], defined the stiffness matrix of the limb’s constraint or overconstraint wrenches, based on which a general method was proposed for the force analysis of passive overconstrained PMs. This method requires an accurate judgment of the overconstraint wrenches and the non-overconstraint wrenches. On the basis of the work shown in Ref. [58] the weighted generalized inverse method was proposed for solving the statically indeterminate problem of passive overconstrained PMs by the authors [59], in which the gravity of limbs was not considered. Besides, there are several other approaches presented in Refs. [60,61,62,63,64].
In theory, there are an infinite number of possible solutions to the statically indeterminate problem of active overconstrained PMs. At present, a variety of optimization goals have been proposed to distribute the driving forces/torques of active overconstrained PMs, such as minimizing the driving forces/torques [29, 65], energy consumption [36, 66, 67], potential energy of the system [37, 68, 69], internal forces [18, 40, 70], and improving the traction/load sharing [71]. In essence, the driving forces/torques distribution of active overconstrained PMs under different optimization goals is just a constrained optimization problem, however, the existing methods have not formed a unified one. The pseudo-inverse method is widely applied when the minimum driving forces/torques are selected as the objective [30, 33, 72]. A weighted coefficient method was proposed by Huang et al. [73], to solve the load distribution of a redundantly actuated walking machine, in which the values of the weighted coefficients can be given arbitrarily according to different optimization goals. Afterwards, the weighted coefficient method [73] was further developed into a weighted generalized inverse method in Ref. [59]. In addition to the abovementioned methods, there are other approaches for force analysis of active overconstrained PMs [74,75,76].
The force analysis of overconstrained PMs presents research difficulties. At present, the approaches proposed to solve this problem have different characteristics. It is difficult to quickly find a suitable method for force analysis of the corresponding overconstrained system. In this paper, the methods for force analysis of both active overconstrained and passive overconstrained PMs are reviewed and discussed in detail, to provide an important reference for researchers and engineers who would like to solve the statically indeterminate problem of overconstrained systems.
2 Methods for Force Analysis of Passive Overconstrained PMs
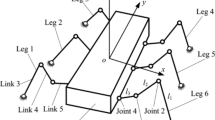
The schematic of a general passive overconstrained PM with n DOFs is shown in Fig. 1. Assume that the t supporting limbs supply m constraint forces/moments to the moving platform in total. For a passive overconstrained PM, there exists m > 6–n. Let A υ , B υ , C υ , …, denote the joints of the υth (υ = 1, 2, …, t) supporting limb from the moving platform to the base in sequence. Assume that the friction in the kinematic joints is ignored, and the stiffness of the moving platform is much greater than that of the supporting limbs.
Owing to the existence of redundant constraints, the force and moment equilibrium equations of a passive overconstrained PM are insufficient to determine all the driving forces/torques and constraint forces/moments. Hence, a certain number of supplementary equations are required. The typical methods for force analysis of passive overconstrained PMs can be divided into six categories.
2.1 Traditional Method
Main ideas: The force and moment equilibrium equations of all movable bodies are established based on the Newton–Euler formulation in sequence. Then, a certain number of compatibility equations of deformation are supplemented to obtain a set of complete and solvable equations. Thus, the driving forces/torques and constraint forces/moments can be solved by combining the force and moment equilibrium equations and the compatibility equations of deformation [10], which is explained briefly in the following paragraphs.
Based on the Newton–Euler formulation the force and moment equilibrium equations of the moving platform of a passive overconstrained PM can be established as
where F and M denote the three-dimensional external force and moment vectors exerted on the moving platform expressed in the coordinate system {O} attached at the moving platform, respectively, f υ (υ = 1, 2, …, t) and t υ represent the three-dimensional reaction force and moment vectors of joint A υ connecting the moving platform and the υth limb, respectively, which are expressed in the local coordinate system {o υ } of the υ-th limb, \({}_{o\upsilon }^{O} {\varvec{R}}\) is the rotational transformation matrix of {o υ } with respect to {O}, g is the gravity vector expressed in the global coordinate system, \({}_{g}^{O} {\varvec{R}}\) is the rotational transformation matrix of the global system with respect to {O}, m O is the mass of the moving platform, r Oυ is the position vector from origin O to the center of joint A υ expressed in {O}, and h O and n O denote the inertia force and moment vectors of the moving platform expressed in {O}, respectively.
The force and moment equilibrium equations of the link A υ B υ close to the moving platform in the υth limb can be built as
where f Bυ and t Bυ represent the three-dimensional reaction force and moment vectors of joint B υ , respectively, \({}_{g}^{o\upsilon } {\varvec{R}}\) is the rotational transformation matrix of the global system with respect to {o υ }, m υ1 is the mass of the link A υ B υ , r oA and r oB are the position vectors from the origin o υ to the centers of the joints A υ and B υ , respectively, and h υ1 and n υ1 denote the inertia force and moment vectors of the link A υ B υ , respectively. f Bυ , t Bυ , r oA , r oB , h υ1 and n υ1 are expressed in the local coordinate system {o υ }.
Similarly, the force and moment equilibrium equations of other links of the t limbs can be formulated. It should be noted that, for different types of joints, the number of unknown reactions is different, for example, one of the three reaction moments of a rotational joint (R) is zero, while for a translational joint (P), one of the three reaction forces is zero.
Assuming that the moving platform is rigid, the deformations of supporting limbs have to be compatible with each other to satisfy the geometric constraints. Hence, the compatibility equations of the deformations generated in the axes of redundant constraint forces and moments can be expressed as [10]
where δ u,υ and δ u,υ+1 denote the linear deformations generated at the ends of the υth and the (υ + 1)th limbs in the axis of the uth redundant constraint force, respectively, and ψ v,υ and ψ v,υ+1 represent the angular deformations generated at the ends of the υth and (υ + 1)th limbs in the axis of the vth redundant constraint moment, respectively.
Then all driving forces/torques and constraint forces/moments can be solved by combining Eqs. (1), (2), and (3).
Discussion: This is a traditional method applicable to the statically indeterminate problem of general passive overconstrained PMs. However, it is computationally intensive because of the high-rank coefficient matrix of the simultaneous equations. Furthermore, it is difficult to obtain the explicit expressions of the solutions by this method.
2.2 Method Based on the Judgment of Constraint Jacobian Matrix
Main ideas: The judgments of the independent and dependent rows of the constraint Jacobian matrix are used to find which joint reactions of a mechanism with redundant constraints can be uniquely determined [17, 49,50,51,52].
Generally, a kinematic joint imposes a certain number of constraints on the relative motion between the two bodies it connects. If a mechanism is described by N coordinates, the constraint conditions imposed by the bth kinematic joint can be expressed as
where q 1, q 2, …, q N denote the N coordinates.
Then the equations describing the μ constraints imposed by all the joints of the mechanism can be arranged as
The constraint Jacobian matrix of the constraint equations can be obtained on the basis of Eq. (5):
For a mechanism with redundant constraints, the rank of matrix \({\varvec{\Phi}}_{{\varvec{q}}} \left( {\varvec{q}} \right)\) must be less than μ. That is to say, one or more rows of \({\varvec{\Phi}}_{{\varvec{q}}} \left( {\varvec{q}} \right)\) can be expressed as a linear combination of other rows. The independent rows of \({\varvec{\Phi}}_{q} \left( {\varvec{q}} \right)\) can be identified by a variety of mathematical methods [17, 49,50,51,52], such as the concept of direct sum, the singular value decomposition, the QR decomposition. For an overconstrained rigid body mechanism, the reaction forces/moments corresponding to the independent constraint equations are unique, despite that all joint reactions cannot be uniquely determined. In order to obtain the unique solutions to all joint reactions, it is necessary to consider the flexibility of passive overconstrained mechanisms. Wojtyra et al. [52], discussed which parts should be modeled as flexible bodies to guarantee unique joint reactions in overconstrained mechanisms.
Discussion: Based on the constraint Jacobian matrix of a passive overconstrained mechanism, several methods were proposed to isolate the joint reactions that can be uniquely determined. Those methods were proposed from a purely mathematical perspective, i.e., the corresponding physical interpretation was not considered. Besides, the analytical expressions of joint reactions cannot be obtained by this kind of method.
2.3 Method under the Condition of Decoupled Deformations
Main ideas: Assuming that the υth (υ = 1, 2, …, t) supporting limb of a passive overconstrained PM contains N υ driving forces/torques and constraint forces/moments in total, as shown in Fig. 1, the elastic deformations generated at the end of the υth limb by the N υ driving forces/torques and constraint forces/moments are considered to be decoupled to each other [53,54,55,56]. In this case, the stiffness of each supporting limb can be expressed as a scalar quantity or a diagonal matrix. The steps of this method can be summarized as follows:
The force and moment equilibrium equations of the moving platform of a passive overconstrained PM can be formulated as
where \({\not\!{\varvec{S}}}_{F}\) denotes the six-dimensional external load imposed on the moving platform, G is the coefficient matrix mapping the driving forces/torques and constraint forces/moments to the external loads, and f is the vector composed of the magnitudes of the n driving forces/torques and m constraint forces/moments.
Let k j be the stiffness between the jth driving force/torque or constraint force/moment and the elastic deformation generated at the end of the corresponding limb under the action of the jth driving force/torque or constraint force/moment. There exists
where f j denotes the magnitude of the jth driving force/torque or constraint force/moment, and δ j represents the elastic deformation generated at the end of the corresponding limb by f j .
Rearranging Eq. (8) in the form of matrix yields
where
The relationship between the elastic deformations generated at the end of supporting limbs and the six-dimensional micro-displacement X of the moving platform as the result of external loads can be derived as
Rearranging Eq. (10) in the form of matrix leads to
From Eqs. (7) to (11) we can get
from which the n driving forces/torques and m constraint forces/moments can be obtained.
It should be noted that the driving force/torque or constraint force/moment along an arbitrary direction can be decomposed along or perpendicular to the axis of the corresponding limb.
Discussion: This method gives the analytical expression of the solutions of the driving forces/torques and the constraint forces/moments of passive overconstrained PMs. However, the coupled deformations generated at the ends of the supporting limbs by the driving forces/torques and constraint forces/moments are ignored.
2.4 Method Based on Resultant Constraint Wrenches
Main ideas: The resultant forces/moments of the collinear constraint forces or coaxial constraint moments are dealt with first. Then, the constraint forces/moments can be obtained by distributing the resultant forces/moments according to the stiffness proportion of the supporting limbs with collinear constraint forces or coaxial constraint moments [57].
Assume that a passive overconstrained PM has p collinear constraint forces and q coaxial constraint moments, and the remaining (m–p–q) constraints are independent. Based on the screw theory, the force and moment equilibrium equations between the actuation wrenches, the resultant constraint wrench of the p collinear constraint forces and that of the q coaxial constraint moments, and the remaining constraint wrenches can be built as
where
\({\not\!{\hat{{\varvec{S}}}}}_{{{\text{r,}}F}}\) and \({\not\!{\hat{{\varvec{S}}}}}_{{{\text{r,}}M}}\) denote the unit screws of the ith actuation wrench, the kth independent constraint wrench, the resultant constraint wrench and the resultant constraint couple, respectively, w i , f k , f p and f q represent the magnitudes of the ith actuation wrench, the kth independent constraint wrench, the resultant constraint wrench and the resultant constraint couple, respectively. All screws are expressed in the global system.
If G b is non-singular, the magnitudes of the actuation wrenches, the independent constraint wrenches, the resultant constraint wrench, and the resultant constraint couple can be solved from Eq. (13) as
According to the hypothesis given in Ref. [57], we assume that the stiffness proportion of the (γ + 1)th and the γth supporting limbs with collinear constraint forces is η γ , and that of the (λ + 1)th and the λth supporting limbs with coaxial constraint moments is η λ . In view that the constraint forces and moments are in direct proportion to the stiffness of the corresponding limbs, the complementary equations can be given as
where f p,γ and f q,λ are the magnitudes of the γth collinear constraint force and the λth collinear constraint moment, respectively.
The magnitudes of the resultant constraint forces and moments have been solved from Eq. (14) as
Combining Eqs. (15) and (16), the magnitudes of each collinear constraint force and coaxial constraint moment can be solved. Thus, the reactions of the joints connecting the moving platform and supporting limbs can be easily determined based on the relationship between them and the actuation and constraint wrenches. The reactions of other joints can be solved by establishing the force and moment equilibrium equations of the corresponding link one by one.
Discussion: In general, a kinematic joint possesses more than one constraint reaction, for example, there exist 5, 4, 4 and 3 constraint reactions for an R joint, universal joint (U), cylindrical joint (C), and spherical joint (S), respectively. If we adopt traditional methods to build the force and moment equilibrium equations of all movable bodies and complementary equations, the rank of the coefficient matrix of those equations will be very large. This method, which is based on resultant constraint wrenches, can avoid the high-rank matrix, reduce a certain number of unknowns, and ensure that the number of simultaneous equilibrium equations is not more than six each time. However, it is only suitable for solving the driving forces/torques and constraint forces/moments of passive overconstrained PMs with collinear constraint forces or coaxial constraint moments.
2.5 Method Based on the Stiffness Matrix of Limb’s Overconstraint or Constraint Wrenches
Main ideas: Based on the characteristics of the elastic deformations generated at the ends of supporting limbs, the passive overconstrained PMs are classified into two classes: the limb stiffness decoupled and coupled overconstrained PMs. Stiffness matrices of the limb’s overconstraint and constraint wrenches that correspond to the two types of mechanisms are defined, which help to establish the compatibility equations about the deformations generated at the ends of supporting limbs and the micro-displacements of the moving platform [58]. Then, the driving forces/torques and constraint forces/moments of the two kinds of overconstrained PMs are solved by combining the force and moment equilibrium equations and the compatibility equations of deformation.
A brief review of the methods for force analysis of the limb stiffness decoupled and coupled overconstrained PMs follows.
For a limb stiffness decoupled overconstrained PM, the force and moment equilibrium equations of the moving platform can be expressed as
where
\({\not\!{\hat{{\varvec{S}}}}}_{{{\text{a}},i}}\)(i = 1, 2, …, n), \({\not\!{\hat{{\varvec{S}}}}}_{{{\text{r,}}\varepsilon }}\)(ε = 1, 2, …, l), and \({\not\!{\hat{{\varvec{S}}}}}_{{{\text{r}},\sigma }}^{{\text{e}}}\) (σ = 1, 2, …, d) represent the unit screws of the ith actuation wrench, εth non-overconstraint wrench, and σth equivalent constraint wrench of the (m–l) overconstraint wrenches, respectively. w a,i , f r,ε , and \(f_{{{\text{r,}}\sigma }}^{\text{e}}\) are the magnitudes of the ith actuation wrench, εth non-overconstraint wrench, and σth equivalent constraint wrench, respectively. Details about the non-overconstraint wrenches, overconstraint wrenches, and equivalent ones of overconstraint wrenches are given in Ref. [58].
Then the magnitudes of the actuation wrenches, the non-overconstraint wrenches, and the equivalent constraint wrenches can be solved from Eq. (17) as
Assume that the (m–l) overconstraint wrenches are distributed in ς supporting limbs. The relationship between the magnitudes of the equivalent constraint wrenches and those of the overconstraint wrenches can be expressed as
According to the definition of the stiffness matrix of the supporting limb’s overconstraint wrenches [58], we can know that
The elastic deformations generated at the end of the sth supporting limb in the axes of overconstraint wrenches can be formulated as
where X e is the vector composed of the elastic deformations in the axes of equivalent constraint wrenches.
Then, the magnitudes of the overconstraint wrenches can be solved by combining Eqs. (19), (20) and (21) as
So far, Eqs. (18) and (22) give the analytical expressions of the magnitudes of all actuation wrenches, non-overconstraint wrenches, and overconstraint wrenches.
For a limb stiffness coupled overconstrained PM, assuming that the υth supporting limb supplies N υ constraint wrenches (including actuation wrenches) to the moving platform, the force and moment equilibrium equations of the moving platform can be expressed as
where
According to the definition of the stiffness matrix of the supporting limb’s constraint wrenches [58] there exists
The compatibility equation about the elastic deformations generated at the end of each limb in the axes of constraint wrenches and the six-dimensional micro-displacement of the moving platform is
Thus, the magnitudes of all the constraint wrenches (including the actuation wrenches) can be solved by combining Eqs. (23), (24) and (25) as
which is just the general expression of the magnitudes of all actuation and constraint wrenches.
Then, the actual reactions of all kinematic joints can be easily obtained according to the relationship between them and the magnitudes of the actuation and constraint wrenches shown in Ref. [58].
Discussion: It can be seen from Eqs. (18), (22), and (26) that, for the statically indeterminate problem of the limb stiffness decoupled overconstrained PMs, only the elastic deformations generated at the end of supporting limbs in the axes of overconstraint wrenches need to be considered, while for that of the limb stiffness coupled overconstrained PMs, the elastic deformations generated at the end of supporting limbs in the axes of all constraint wrenches, including actuation wrenches, should be taken into account. This method has clear steps, few computational requirements, and gives the explicit analytical expressions of the solutions to the statically indeterminate problem of general passive overconstrained PMs.
2.6 Weighted Generalized Inverse Method
Main ideas: A simple method is proposed in Ref. [59] by resorting to the definition of the weighted generalized inverse of a non-square matrix [77], which is suitable for solving the statically indeterminate problem of both the limb stiffness decoupled and coupled passive overconstrained PMs.
Based on the weighted generalized inverse of the matrix mapping the driving forces/torques and constraint forces/moments to the external loads, the solutions of the statically indeterminate problem of a general passive overconstrained PM can be derived as [59]
where the weighted matrix B is the inverse matrix of a block diagonal matrix composed of the stiffness matrices of each limb’s constraint wrenches.
In the case that each supporting limb only supplies one driving force/torque or constraint force/moment, the stiffness of each limb is just a scalar quantity, and the weighted matrix B becomes a diagonal matrix, which is consistent with the work done in Refs. [53, 54].
Discussion: The method based on the weighted generalized inverse supplies a simpler and more effective way to solve the statically indeterminate problem of passive overconstrained PMs. Moreover, it can be seen from Eq. (27) that the elements of the weighted matrix B are the stiffness matrices of the limbs’ constraint wrenches, which shows that the solutions of the driving forces/torques and constraint forces/moments of passive overconstrained PMs are unique.
In addition to the above mentioned methods, there are other approaches of handling redundant constraints of a passive overconstrained PM, for example, the pseudo-inverse method [60] and the augmented Lagrangian formulation [61, 62]. Furthermore, Zahariev et al. [63], proposed a method for dynamic analysis of multibody systems in overconstrained and singular configurations, in which some closed chains are transformed into open branches and the missing links are substituted by stiff forces.
3 Methods for Force Analysis of Active Overconstrained PMs
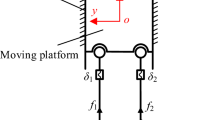
The schematic of a general active overconstrained PM with n DOFs and ζ actuated joints is shown in Fig. 2, where ζ > n. Assume that the active overconstrained PM shown in Fig. 2 contains t supporting limbs and the υth supporting limb contains l υ links. Without loss of generality, each limb can possess more than one actuator.
As there are theoretically infinite sets of solutions to the statically indeterminate problem of active overconstrained PMs, the key to the force analysis of this kind of overconstrained PMs is to find the optimal distribution of all driving forces/torques. The typical methods for solving this problem fall into four categories.
3.1 Pseudo-inverse Method
The force and moment equilibrium equations of an active overconstrained PM can be written in the form [40, 42, 72]
where f act consists of ζ driving forces/torques, G act is the coefficient matrix, and F extr is the generalized external force vector composed of inertia forces/moments, weight, and external loads encountered in the components of the mechanism.
As the matrix G act is singular, the pseudo-inverse of G act is used to find the minimum norm of f act in some situations [27, 30, 72]:
In this way, the minimum driving forces/torques of an active overconstrained PM can be obtained.
3.2 Weighted Coefficient Method
The distribution of the driving forces/torques of an active overconstrained PM under different optimization goals [65,66,67,68,69] can be viewed as a constrained optimization problem, i.e., the minimum set of solutions of the objective function under the constraints of force and moment balance need to be solved. The weighted coefficient method proposed by Huang et al. [73] and Zhao et al. [78], can achieve a variety of optimization goals. It is taken as representative of this method and is briefly reviewed in the following paragraphs:
Select n joints among the ζ actuated joints as the generalized coordinates. The driving forces/torques of the (ζ–n) actuated joints, external loads, inertia forces/moments, and gravity applied on the moving platform and each supporting link can be expressed with respect to the generalized coordinates. Thus, the dynamic equilibrium equations of an active overconstrained PM can be rearranged as [73, 78]
where τ non is composed of the driving forces/torques of the generalized joints, i.e., the n non-redundant driving forces/torques, and τ over consists of the driving forces/torques of the non-generalized joints, i.e., the remaining (ζ–n) redundant driving forces/torques. \({\not\!{\varvec{S}}}_{F,h}^{\upsilon }\) and \({\not\!{\varvec{S}}}_{F}\) denote the resultant force vectors of the external loads, gravity, and inertia force/moment acted on the h-link of the υth limb and the moving platform, respectively. They are expressed in the corresponding local coordinates. \(\left( {{\varvec{G}}_{h}^{\text{non}} } \right)^{\upsilon }\), \({\varvec{G}}_{F}^{\text{non}}\), and \({\varvec{G}}_{\text{over}}^{\text{non}}\) represent the transformation matrices of \({\not\!{\varvec{S}}}_{F,h}^{\upsilon }\), \({\not\!{\varvec{S}}}_{F,h}^{\upsilon }\), and τ over from the corresponding local coordinates to the generalized coordinates, respectively.
In order to obtain the optimal distribution of all driving forces/torques, the objective function of optimization can be constructed as [73, 78]
where
in which W i and W ξ (ξ = n+1, n + 2, …, ζ) are weighted coefficients.
By solving the minimum values of the objective function shown in Eq. (31) under the constraint condition of Eq. (30) we get
where \({\not\!{\varvec{S}}}_{F,M} = \left( {\sum\limits_{\upsilon = 1}^{t} {\sum\limits_{h = 1}^{{M_{\upsilon } }} {\left( {{\varvec{G}}_{h}^{\text{non}} } \right)^{\upsilon } {\not\!{\varvec{S}}}_{F,h}^{\upsilon } } + {\varvec{G}}_{F}^{\text{non}} {\not\!{\varvec{S}}}_{F} } } \right)\).
Substituting Eq. (32) into Eq. (30) yields
Rearranging Eqs. (32) and (33) yields
which is the analytical expression of the optimal distribution of driving forces/torques of a general active overconstrained PM. Different optimization goals can be achieved by changing the values of the weighted matrices W non and W over, for example:
(1) Let W i and W ξ be the velocities of the ith and ξth actuated joints, respectively. The driving forces/torques are distributed with the minimum input energy of the actuators [36, 66, 67].
(2) Let W i = W ξ = 1. Then, the minimum driving forces/torques of the mechanism can be obtained [40, 65].
(3) Let \(W_{i} = K_{i}^{ - 1}\) and \(W_{\xi } = K_{\xi }^{ - 1}\), where K i and K ξ represent the stiffness of the ith and ξth actuated joints, respectively. The driving forces/torques are distributed with the minimum elastic potential energy of the mechanism [37, 68, 69].
3.3 Method Based on the Optimal Internal Forces
For an active overconstrained PM, the solution to its statically indeterminate problem shown in Eq. (28) can be broken into a particular solution and a homogeneous solution [19, 39], as follows:
where the special solution f spcl satisfies
and the homogeneous solution f homo meets
It can be seen from Eq. (35) that the solutions of driving forces/torques may involve the components corresponding to the null space of the coefficient matrix G act, which are known as the internal forces. Hence, two kinds of methods are proposed for the statically indeterminate problem of active overconstrained PMs from the perspective of dealing with the internal forces. The first method is that the driving forces/torques are distributed without internal forces [18, 35, 70]. A number of studies have shown that the internal forces can be utilized to change the stiffness [79], improve the motion accuracy [32], increase the load-carrying capacity [19], and eliminate the backlash [34] of active overconstrained PMs, so the second method is that the driving forces/torques are distributed by utilizing the advantages of internal forces [19, 32, 34].
3.4 Weighted Generalized Inverse Method
If \({\varvec{A}} \in {\varvec{C}}^{{x \times \left( {y + z} \right)}}\) and A = [U V], where U and V are composed of the first y columns and the last z columns of A, respectively. The weighted generalized inverse of the matrix A can be expressed as [80]
\(\begin{aligned} & {\text{where}}\;{\varvec{H}} = {\varvec{C}}_{{{\varvec{P}},{\varvec{K}}1}}^{ + } + \left( {{\varvec{I}} - {\varvec{C}}_{{{\varvec{P}},{\varvec{Q}}y}}^{ + } {\varvec{C}}} \right){\varvec{K}}_{1}^{{ - 1}} \left( {{\varvec{D}}^{*} {\varvec{Q}}_{y} - {\varvec{L}}^{*} } \right){\varvec{U}}_{{{\varvec{P}},{\varvec{Q}}y}}^{ + } , \\ & {\varvec{K}}_{1} = {\varvec{Q}}_{z} + {\varvec{D}}^{*} {\varvec{Q}}_{y} {\varvec{D}} - \left( {{\varvec{D}}^{*} {\varvec{L}} + {\varvec{L}}^{*} {\varvec{D}}} \right) - {\varvec{L}}^{*} \left( {{\varvec{I}} - {\varvec{U}}_{{{\varvec{P}},{\varvec{Q}}y}}^{ + } {\varvec{U}}} \right){\varvec{Q}}_{y}^{{ - 1}} {\varvec{L}}, \\ & {\varvec{C}} = \left( {{\varvec{I}} - {\varvec{UU}}_{{{\varvec{P}},{\varvec{Q}}y}}^{ + } } \right){\varvec{V}}, \\ & {\varvec{D}} = {\varvec{U}}_{{{\varvec{P}},{\varvec{Q}}y}}^{ + } {\varvec{V}}, \\ \end{aligned}\)
\({\varvec{A}}_{{{\varvec{P}},{\varvec{Q}}}}^{ + }\) represents the weighted generalized inverse matrix of A with P and Q as the weighted factors, I is an identity matrix, P is a x × x positive definite matrix, and Q is a (y + z) × (y + z) positive definite matrix that can be partitioned as
\({\varvec{Q}} = \left( {\begin{array}{*{20}c} {{\varvec{Q}}_{y} } & {\mathbf{L}} \\ {{\varvec{L}}^{*} } & {{\varvec{Q}}_{z} } \\ \end{array} } \right)\), in which the sign “*” denotes the conjugate and transpose operations.
Using Eq. (36), we found that the solution of the driving forces/torques shown in Eq. (34) can be obtained directly using the weighted generalized inverse of the matrix mapping the driving forces/torques to the generalized external force [59]. Therefore, the weighted generalized inverse can be applied to distribute the driving forces/torques of active overconstrained PMs:
where S is the weighted diagonal matrix whose elements are determined by the specific optimization goal.
Moreover, there are other approaches for the force distribution problem of active overconstrained PMs. A partitioned actuator set control method was proposed by Gardner et al. [71], to improve the traction or load sharing among the actuators. A scaling factor method and an analytical method were presented in Ref. [74] to determine the wrench capabilities of active overconstrained PMs. Nahon et al. [75], summarized three methods for solving the optimal force distribution problem of this kind of PMs: the weighted pseudo-inverse, explicit Lagrange multipliers, and direct substitution.
4 Discussion
The force analyses of both active and passive overconstrained PMs belong to the statically indeterminate problem. A large number of methods have been proposed for the force analysis of these two kinds of overconstrained PMs, among which the weighted generalized inverse method is the simplest and most common. That is to say, the solutions of the statically indeterminate problems of both active and passive overconstrained PMs can be solved by
For the passive overconstrained PMs, f consists of the magnitudes of all constraint wrenches (including actuation wrenches), \({\varvec{G}}_{f}^{F}\) is the coefficient matrix mapping the driving forces/torques and constraint forces/moments to the external loads, and the weighted matrix W is composed of the stiffness matrices of each limb’s constraint wrenches, which cannot be actively selected. As a result, the solutions of the driving forces/torques and constraint forces/moments of passive overconstrained PMs are unique. For the active overconstrained PMs, f is composed of the magnitudes of all driving forces/torques, \({\varvec{G}}_{f}^{F}\) is the coefficient matrix mapping the driving forces/torques to the generalized external loads, and the elements of the weighted matrix W can be actively given according to different optimization goals. Therefore, there are an infinite number of solutions of the driving forces/torques of active overconstrained PMs.
5 Conclusions and Outlook
The existence of redundant constraints or actuations makes the force analysis of both passive overconstrained PMs (i.e., the PMs with redundant or common constraints) and active ones (i.e., the redundantly actuated PMs) belong to a statically indeterminate problem, which is extremely difficult and particularly complicated to solve. The various approaches proposed for the force analysis of these two kinds of overconstrained PMs are divided into six categories and four categories, respectively, in this paper, among which:
(1) The pseudo-inverse method was used to solve the force analysis of these two kinds of overconstrained PMs. However, for the passive overconstrained PMs, the solutions are obtained without physical meaning, and for the active overconstrained PMs, the driving forces/torques are solved with the minimum values.
(2) The common method used to solve the statically indeterminate problem of passive overconstrained PMs involves combining the force and moment equilibrium equations and the compatibility equations of deformation of the mechanisms, and that used to solve the driving forces/torques of active overconstrained PMs involves establishing a specific optimization goal and then solving the minimum values of the objective function under the constraint of force and moment equilibrium equations.
(3) The weighted generalized inverse method can be applied to solve the statically indeterminate problem of both passive and active overconstrained PMs. For the passive overconstrained PMs, the weighted matrix consists of the stiffness matrices of each limb’s constraint wrenches, and for the active overconstrained PMs, it is determined by the optimization goals.
In recent decades, sustained efforts have been made to find a simple and general method to solve the driving forces/torques and constraint forces/moments of passive overconstrained PMs, and to distribute the driving forces/torques of active overconstrained PMs. It can be seen from this paper that the weighted generalized inverse method is the simplest and most universal one at present.
However, the existing theoretical methods for force analysis of overconstrained PMs are basically proposed without considering the actual characteristics of the mechanisms, such as joint clearance and friction, the real stiffness models of supporting limbs. Therefore, the force analysis of typical overconstrained systems (for example, the parallel machine tool XT 700) under the condition of the actual characteristics will become a research hotspot. In addition, the establishment of systematic experimental platforms to verify the theoretical methods will be another important research direction.
References
S A Joshi, L W Tsai. Jacobian analysis of limited-DOF parallel manipulators. Journal of Mechanical Design, Transactions of the ASME, 2002, 124(2): 254–258.
A Sokolov, P Xirouchakis. Dynamics analysis of a 3-DOF parallel manipulator with R-P-S joint structure. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2007, 42(5): 541–557.
L W Tsai, S Joshi. Kinematics and optimization of a spatial 3-UPU parallel manipulator. Journal of Mechanical Design, Transactions of the ASME, 2000, 122(4): 439–446.
R D Gregorio. Kinematics of the 3-UPU wrist. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2003, 38(3): 253–263.
Y LU, Y Shi, B Hu. Kinematic analysis of two novel 3UPU I and 3UPU II PKMs. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2008, 56(4): 296–305.
M Callegari, M C Palpacelli, M Principi. Dynamics modelling and control of the 3-RCC translational platform. Mechatronics, 2006, 16(10): 589–605.
J F Li, J S Wang. Inverse kinematic and dynamic analysis of a 3-DOF parallel mechanism. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2003, 16(1): 54–58.
Y M Qian. Position equation establishment and kinematics analysis of 3-RRC parallel mechanism. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2014, 664: 349–354.
T Bonnemains, H Chanal, B C Bouzgarrou, et al. Dynamic model of an overconstrained PKM with compliances: the Tripteor X7. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2013, 29(1): 180–191.
Z M Bi, B Kang. An inverse dynamic model of over-constrained parallel kinematic machine based on Newton–Euler formulation. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, Transactions of the ASME, 2014, 136(4): 041001-(1–9).
Z M Bi. Kinetostatic modeling of Exechon parallel kinematic machine for stiffness analysis. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2014, 71(1): 325–335.
Y M Li, Q S Xu. Dynamic modeling and robust control of a 3-PRC translational parallel kinematic machine. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2009, 25(3): 630–640.
Y M Li, S Staicu. Inverse dynamics of a 3-PRC parallel kinematic machine. Nonlinear Dynamic, 2012, 67(2): 1031–1041.
C Mavroidis, B Roth. Analysis of overconstrained mechanisms. Journal of Mechanical Design, Transactions of the ASME, 1995, 117(1): 69–74.
Y F Fang, L W Tsai. Enumeration of a class of overconstrained mechanisms using the theory of reciprocal screws. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2004, 39(11): 1175–1187.
E J Haug. Computer-aided kinematics and dynamics of mechanical systems. vol. 1: basic methods. Allyn and Bacon, 1989.
M Wojtyra. Joint reaction forces in multibody systems with redundant constraints. Multibody System Dynamics, 2005, 14(1): 23–46.
Y D Xu, J T Yao, Y S Zhao. Internal forces analysis of the active overconstrained parallel manipulators. International Journal of Robotics and Automation, 2015, 30(5): 511–518.
J Wu, X L Chen, L P Wang, et al. Dynamic load-carrying capacity of a novel redundantly actuated parallel conveyor. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2014, 78(1): 241–250.
C Z Wang, Y F Fang, S Guo. Multi-objective optimization of a parallel ankle rehabilitation robot using modified differential evolution algorithm. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015, 28(4): 702–715.
Y D Xu, J T Yao, Y S Zhao. Inverse dynamics and internal forces of the redundantly actuated parallel manipulators. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2012, 51: 172–184.
F Firmani, R P Podhorodeski. Force-unconstrained poses for a redundantly-actuated planar parallel manipulator. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2004, 39(5): 459–476.
B Dasgupta, T S Mruthyunjaya. Force redundancy in parallel manipulators: theoretical and practical issues. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 1998, 33(6): 727–742.
J A Saglia, J S Dai, D G Caldwell. Geometry and kinematic analysis of a redundantly actuated parallel mechanism that eliminates singularities and improves dexterity. Journal of Mechanical Design, Transactions of the ASME, 2008, 130(12): 1786–1787.
S H Li, Y M Liu, H L Cui, et al. Synthesis of branched chains with actuation redundancy for eliminating interior singularities of 3T1R parallel mechanisms. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2016, 29(2): 250–259.
J Kim, F C Park, J R Sun, et al. Design and analysis of a redundantly actuated parallel mechanism for rapid machining. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 2001, 17(4): 423–434.
H Cheng, Y K Yiu, Z X Li. Dynamics and control of redundantly actuated parallel manipulators. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2003, 8(4): 483–491.
Y J Zhao, F Gao, W M Li, et al. Development of a 6-DOF parallel seismic simulator with novel redundant actuation. Mechatronics, 2009, 19(3):422–427.
J M Tao, J Y S Luh. Coordination of two redundant robots. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, May 14–19, 1989: 425–430.
S B Nokleby, R Fisher, R P Podhorodeski, et al. Force capabilities of redundantly-actuated parallel manipulators. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2005, 40(5): 578–599.
Y J Zhao, F Gao. Dynamic performance comparison of the 8PSS redundant parallel manipulator and its non-redundant counterpart—the 6PSS parallel manipulator. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2009, 44(5): 991–1008.
H Liang, W Y Chen, H F Li. Research on the method of improving accuracy of parallel machine tools. Key Engineering Materials, 2009, 407–408: 85–88.
J Wu, J S Wang, L P Wang, et al. Dynamics and control of a planar 3-DOF parallel manipulator with actuation redundancy. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2009, 44(4): 835–849.
A Müller. Internal preload control of redundantly actuated parallel manipulators–its application to backlash avoiding control. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2005, 21(4): 668–677.
I D Walker, R A Freeman, S I Marcus. Internal object loading for multiple cooperating robot manipulators. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, May 14–19, 1989: 606–611.
Y F Zheng, J Y S Luh. Optimal load distribution for two industrial robots handling a single object. Proceedings of the 1988 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Philadelphia, PA, USA, April 24–29, 1988: 344–349.
X C Gao, S M Song, C Q Zheng. Generalized stiffness matrix method for force distribution of robotic systems with indeterminacy. Journal of Mechanical Design, Transactions of the ASME, 1993, 115(3): 585–591.
Y S Zhao, L Lu, T S Zhao, et al. Dynamic performance analysis of six-legged walking machines. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2000, 35(1): 155–163.
T Yoshikawa, K Nagai. Manipulating and grasping forces in manipulation by multifingered hands. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 1991, 7(1): 67–77.
M A Nahon, J Angeles. Optimization of dynamic forces in mechanical hands. Journal of Mechanisms, Transmissions, and Automation in Design, 1991, 113(2): 167–173.
X W Kong. Standing on the shoulders of giants: a brief note from the perspective of kinematics. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2017, 30(1): 1–2.
J Wu, J S Wang, T M Li, et al. Dynamic analysis of the 2-DOF planar parallel manipulator of a heavy duty hybrid machine tool. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2007, 34(3): 413–420.
Y W Li, J S Wang, L P Wang, et al. Inverse dynamics and simulation of a 3-DOF spatial parallel manipulator. 2003 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Taipei, Taiwan, China, September 14–19, 2003: 4092–4097.
Y Lu, Y Shi, Z Huang, et al. Kinematics/statics of a 4-DOF over-constrained parallel manipulator with 3 legs. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2009, 44(8): 1497–1506.
J Gallardo, J M Rico, A Frisoli, et al. Dynamics of parallel manipulators by means of screw theory. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2003, 38(11): 1113–1131.
D G Raffaele, P C Vicenzo. Dynamics of a class of parallel wrists. Journal of Mechanical Design, Transactions of the ASME, 2004, 126(3): 436–441.
S Staicu, D Zhang. A novel dynamic modelling approach for parallel mechanisms analysis. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2008, 24(1): 167–172.
S Staicu, D Zhang, R Rugescu. Dynamic modelling of a 3-DOF parallel manipulator using recursive matrix relations. Robotica, 2006, 24(1): 125–130.
M Wojtyra. Joint reactions in rigid body mechanisms with dependent constraints. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2009, 44(12): 2265–2278.
J Fraczek, M Wojtyra. On the unique solvability of a direct dynamics problem for mechanisms with redundant constraints and coulomb friction in joints. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2011, 46(3): 312–334.
M Wojtyra, J Fraczek. Solvability of reactions in rigid multibody systems with redundant nonholonomic constraints. Multibody System Dynamics, 2013, 30(2): 153–171.
M Wojtyra, J Fraczek. Joint reactions in rigid or flexible body mechanisms with redundant constraints. Bulletin of the Polish Academy of Sciences: Technical Sciences, 2012, 60(3): 617–626.
R Vertechy, V Parenti-Castelli. Static and stiffness analyses of a class of over-constrained parallel manipulators with legs of type US and UPS. 2007 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Roma, Italy, April 10–14, 2007: 561–567.
Z J Wang, J T Yao, Y D Xu, et al. Hyperstatic analysis of a fully pre-stressed six-axis force/torque sensor. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2012, 57: 84–94.
J T Yao, Y L Hou, J Chen, et al. Theoretical analysis and experiment research of a statically indeterminate pre-stressed six-axis force sensor. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2009, 150(1): 1–11.
B Hu, Z Huang. Kinetostatic model of overconstrained lower mobility parallel manipulators. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2016, 86(1): 309–322.
Z Huang, Y Zhao, J F Liu. Kinetostatic analysis of 4-R(CRR) parallel manipulator with overconstraints via reciprocal-screw theory. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2010, 2010(2): 1652–1660.
Y D Xu, W L Liu, J T Yao, et al. A method for force analysis of the overconstrained lower mobility parallel mechanism. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2015, 88: 31–48.
W L Liu, Y D Xu, J T Yao, et al. The weighted Moore-Penrose generalized inverse and the force analysis of overconstrained parallel mechanisms. Multibody System Dynamics, 2017, 39(4): 363–383.
M Wojtyra, J Fraczek. Comparison of selected methods of handling redundant constraints in multibody systems simulations. Journal of Computational and Nonlinear Dynamics, 2013, 8(2): 021007-(1–9).
E Bayo, R Ledesma. Augmented lagrangian and mass-orthogonal projection methods for constrained multibody dynamics. Nonlinear Dynamics, 1996, 9: 113–130.
W Blajer. Augmented Lagrangian formulation: geometrical interpretation and application to systems with singularities and redundancy. Multibody Systems Dynamics, 2002, 8(2): 141–159.
E Zahariev, J Cuadrado. Dynamics of mechanisms in overconstrained and singular configurations. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2011, 41(1): 3–18.
S M Song, X C Gao. Mobility equation and the solvability of joint forces/torques in dynamic analysis. American Society of Mechanical Engineers, Design Engineering Division (Publication) DE, 1990, 24: 191–197.
J P Merlet. Redundant parallel manipulators. Laboratory Robotics and Automation, 1996, 8(1): 17–24.
D E Orin, S Y Oh. Control of force distribution in robotic mechanisms containing closed kinematic chains. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement and Control, Transactions of the ASME, 1981, 103(2): 134–141.
M Nahon, J Angeles. Minimization of power losses in cooperating manipulators. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement and Control, Transactions of the ASME, 1992, 114(2): 213–219.
D R Kerr, M Griffis, D J Sanger, et al. Redundant grasps, redundant manipulators, and their dual relationships. Journal of Robotic Systems, 1992, 9(7): 973–1000.
J Wu, T M Li, B Q Xu. Force optimization of planar 2-DOF parallel manipulators with actuation redundancy considering deformation. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 2013, 227(6): 1371–1377.
I D Walker, R A Freeman, S I Marcus. Analysis of motion and internal loading of objects grasped by multiple cooperating manipulators. International Journal of Robotics Research, 1991, 10(4): 396–409.
J F Gardner, K Srinivasan, K J Waldron. A solution for the force distribution problem in redundantly actuated closed kinematic chains. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement and Control, Transactions of the ASME, 1990, 112(3): 523–526.
V R Kumar, K J Waldron. Force distribution in closed kinematic chains. IEEE Journal of Robotics and Automation, 1988, 4(6): 657–664.
Z Huang, Y S Zhao. Accordance and optimization-distribution equations of the over-determinate inputs of walking machines. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 1994, 29(2): 327–332.
V Garg, S B Nokleby, J A Carretero. Wrench capability analysis of redundantly actuated spatial parallel manipulators. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2009, 44(5): 1070–1081.
M A Nahon, J Angeles J. Force optimization in redundantly-actuated closed kinematic chains. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, May 14–19, 1989: 951–956.
M Nahon, J Angeles. Real-time force optimization in parallel kinematic chains under inequality constraints. Proceedings of the 1991 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Sacramento, CA, USA, April 9–11, 1991: 2198–2203.
Z P Xiong, Y Y Qin. Note on the weighted generalized inverse of the product of matrices. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Computing, 2011, 35(1): 469–474.
Y S Zhao, J Y Ren, Z Huang. Dynamic loads coordination for multiple cooperating robot manipulators. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2000, 35(7): 985–995.
M A Adli, H Hanafusa. Contribution of internal forces to the dynamics of closed chain mechanisms. Robotica, 1995, 13(5): 507–514.
G R Wang, B Zheng. The weighted generalized inverses of a partitioned matrix. Applied Mathematics and Computation (New York), 2004, 155(1): 221–233.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51675458, 51275439), and Youth Top Talent Project of Hebei Province Higher Education of China (Grant No. BJ2017060).
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, WL., Xu, YD., Yao, JT. et al. Methods for Force Analysis of Overconstrained Parallel Mechanisms: A Review. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 30, 1460–1472 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10033-017-0199-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10033-017-0199-9