Abstract
Purpose
To prospectively evaluate the use of a continuous Nitinol containing memory frame patch during a TIPP-technique in the open repair of inguinal and femoral hernias.
Methods
Over a 3-year period all consecutive adult patients that needed treatment for an inguinal or femoral hernia were treated by the TIPP repair using the Rebound Shield mesh. Intra-operatively the type and size of the hernia were evaluated according to the EHS classification, as well as the size of the mesh used. Baseline characteristics for all patients were evaluated considering age, gender, BMI and American society of Anesthesiologists score. Standard X-ray was performed to evaluate mesh position. All patients were evaluated for post-operative pain using the visual analogue scale (VAS 0–10 scale).
Results
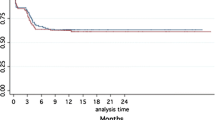
In total 289 groin hernias were operated using a nitinol containing patch in 235 patients. The mean operating time was 38 min for unilateral hernias and 59 min for bilateral hernias. The median follow-up is 21.2 months (14–33 months) during which three patients died, unrelated to the groin hernia repair. At the time of re-evaluation 12 patients (5.0 %) complained of chronic pain, with a VAS score higher than 3 after 3 months (range 3–10). Two of these patients already had severe pain pre-operatively. A total of 3 recurrences (2.9 %) were noted with strong correlation with X-ray findings.
Conclusion
A nitinol memory frame containing mesh is a valuable tool to achieve complete deployment of a large pore mesh in a TIPP repair for inguinal hernias with acceptable morbidity and a low recurrence rate.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bay-Nielsen M, Perkins FM, Kehlet H (2001) Pain and functional impairment 1 year after inguinal herniorrhaphy: a nationwide questionnaire study. Ann Surg 233(1):1–7 (Epub 2001/01/05)
Hynes DM, Stroupe KT, Luo P, Giobbie-Hurder A, Reda D, Kraft M et al (2006) Cost effectiveness of laparoscopic versus open mesh hernia operation: results of a Department of Veterans Affairs randomized clinical trial. J Am College Surg 203(4):447–457 (Epub 2006/09/27)
Berrevoet F, Sommeling C, de Gendt S, Breusegem C, de Hemptinne B (2009) The preperitoneal memory-ring patch for inguinal hernia: a prospective multicentric feasibility study. Hernia J Hernias Abdom Wall Surg 13(3):243–249 (Epub 2009/02/10)
Pelissier EP (2006) Inguinal hernia: preperitoneal placement of a memory-ring patch by anterior approach. Preliminary experience. Hernia: J Hernias Abdom Wall Surg 10(3):248–252 (Epub 2006/06/08)
Berrevoet F, Maes L, Reyntjens K, Rogiers X, Troisi R, de Hemptinne B (2010) Transinguinal preperitoneal memory ring patch versus Lichtenstein repair for unilateral inguinal hernias. Langenbeck’s archives of surgery/Deutsche Gesellschaft fur Chirurgie 395(5):557–562 (Epub 2009/08/01)
Brown RB (2011) NiTiNol hernia device stability in inguinal hernioplasty without fixation. JSLS J Soc Laparoendosc Surg/Soc Laparoendosc Surg 15(2):160–164 (Epub 2011/09/10)
Simons MP, Aufenacker T, Bay-Nielsen M, Bouillot JL, Campanelli G, Conze J et al (2009) European Hernia Society guidelines on the treatment of inguinal hernia in adult patients. Hernia : J Hernias Abdom Wall Surg 13(4):343–403 (Epub 2009/07/29)
Koning GG, Andeweg CS, Keus F, van Tilburg MW, van Laarhoven CJ, Akkersdijk WL (2012) The transrectus sheath preperitoneal mesh repair for inguinal hernia: technique, rationale, and results of the first 50 cases. Hernia: J Hernias Abdom Wall Surg 16(3):295–299 (Epub 2011/12/02)
Koning GG, Keus F, Koeslag L, Cheung CL, Avci M, van Laarhoven CJ et al (2012) Randomized clinical trial of chronic pain after the transinguinal preperitoneal technique compared with Lichtenstein’s method for inguinal hernia repair. Br J Surg 99(10):1365–1373 (Epub 2012/09/11)
Koning GG, Vriens PW (2012) Anterior preperitoneal repair of extremely large inguinal hernias: An alternative technique. Int J Surg Case Rep 3(2):45–48 (Epub 2012/01/31)
Maillart JF, Vantournhoudt P, Piret-Gerard G, Farghadani H, Mauel E (2011) Transinguinal preperitoneal groin hernia repair using a preperitoneal mesh preformed with a permanent memory ring: a good alternative to Lichtenstein’s technique. Hernia: J Hernias Abdom Wall Surg 15(3):289–295 (Epub 2011/02/01)
Callesen T, Bech K, Kehlet H (1999) Prospective study of chronic pain after groin hernia repair. Br J Surg 86(12):1528–1531 (Epub 1999/12/14)
Nienhuijs SW, Boelens OB, Strobbe LJ (2005) Pain after anterior mesh hernia repair. J Am College Surg 200(6):885–889 (Epub 2005/06/01)
Poobalan AS, Bruce J, King PM, Chambers WA, Krukowski ZH, Smith WC (2001) Chronic pain and quality of life following open inguinal hernia repair. Br J Surg 88(8):1122–1126 (Epub 2001/08/08)
Poobalan AS, Bruce J, Smith WC, King PM, Krukowski ZH, Chambers WA (2003) A review of chronic pain after inguinal herniorrhaphy. Clin J Pain 19(1):48–54 (Epub 2003/01/07)
Aasvang EK, Brandsborg B, Christensen B, Jensen TS, Kehlet H (2008) Neurophysiological characterization of postherniotomy pain. Pain 137(1):173–181 (Epub 2007/11/03)
Willaert W, De Bacquer D, Rogiers X, Troisi R, Berrevoet F (2012) Open Preperitoneal Techniques versus Lichtenstein Repair for elective Inguinal Hernias. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 7:CD008034 (Epub 2012/07/13)
Lundstrom KJ, Sandblom G, Smedberg S, Nordin P (2012) Risk factors for complications in groin hernia surgery: a national register study. Ann Surg 255(4):784–788 (Epub 2012/03/16)
Hsu W, Chen CS, Lee HC, Liang HH, Kuo LJ, Wei PL et al (2012) Preservation versus division of ilioinguinal nerve on open mesh repair of inguinal hernia: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. World J Surg 36(10):2311–2319 (Epub 2012/05/31)
Kingsnorth A, Gingell-Littlejohn M, Nienhuijs S, Schule S, Appel P, Ziprin P et al (2012) Randomized controlled multicenter international clinical trial of self-gripping Parietex ProGrip polyester mesh versus lightweight polypropylene mesh in open inguinal hernia repair: interim results at 3 months. Hernia: J Hernias Abdom Wall Surg 16(3):287–294 (Epub 2012/03/29)
Pelissier EP (2009) Preperitoneal memory-ring patch for inguinal hernia. Re: Preperitoneal memory-ring patch for inguinal hernia: a prospective multicentric feasibility study, Berrevoet et al. (2009) Hernia (in press) doi:10.1007/s10029-009-0475-4. Hernia: J Hernias Abdom Wall Surg 13(4):451–452 Epub 2009/03/21
Torres-Villalobos G, Sorcic L, Ruth GR, Andrade R, Martin-del-Campo LA, Anderson JK (2010) Evaluation of the rebound hernia repair device for laparoscopic hernia repair. JSLS: J Soc Laparoendosc Surg Soc Laparoendosc Surg 14(1):95–102 (Epub 2010/06/10)
Shabalovskaya SA (2002) Surface, corrosion and biocompatibility aspects of Nitinol as an implant material. Bio-med Mater Eng 12(1):69–109 (Epub 2002/02/16)
Early M, Kelly D (2011) The consequences of the mechanical environment of peripheral arteries for nitinol stenting. Med Biol Eng Comput. 49:1279–1288
Pound BG (2010) Corrosion behaviour of nitinol in blood serum and PBS containing amino acids. J Biomed Mater Res Part B: Appl Biomater 94B:287–295
Conflict of interest
FB declares no conflict of interest that directly relates to this study; AV declares no conflict of interest; JB declares no conflict of interest; RT declares no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berrevoet, F., Vanlander, A., Bontinck, J. et al. Open preperitoneal mesh repair of inguinal hernias using a mesh with nitinol memory frame. Hernia 17, 365–371 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10029-013-1110-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10029-013-1110-y