Abstract
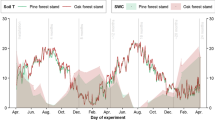
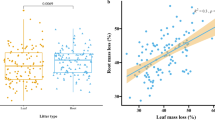
We evaluated the effects of the exotic tree Fraxinus uhdei on decomposition dynamics and nutrient turnover in a montane Hawaiian rainforest. We used reciprocal transplants of litterbags between forests dominated by Fraxinus and by the native Metrosideros polymorpha to distinguish between endogenous (litter quality) and exogenous (for example, microclimate, nutrient availability, microbial and invertebrate communities) effects of Fraxinus on mass loss and nutrient dynamics of decomposing litter. Fraxinus produced greater quantities of litter that was thinner, had higher N and P concentrations, and lower concentrations of lignin and soluble polyphenols. Microbes decomposing Fraxinus litter produced fewer enzymes involved in N and P acquisition and more of those involved in cellulose degradation. Differences in litter quality and microbial activity resulted in a strong effect of litter type on rates of mass loss, whereby Fraxinus litter decomposed and released nutrients at nearly twice the rate of Metrosideros litter (k = 0.82 versus 0.48), regardless of site of decomposition. Although site of decomposition had no effect on rates of litter mass loss, Fraxinus litter decomposed under a Fraxinus canopy mineralized approximately 20% less P after one year than Fraxinus litter decomposed under a Metrosideros canopy. Furthermore, Fraxinus litter decomposed under a Fraxinus canopy immobilized greater amounts of N and P in the early stages of decay, suggesting that the large amounts of N and P in Fraxinus litterfall have raised nutrient availability to decomposers in the forest floor. Greater immobilization of N and P under a Fraxinus canopy may act as a governor on rates of nutrient cycling, limiting the degree to which Fraxinus invasion accelerates N and P cycling in this system.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
R Aerts FS Chapin SuffixIII (2000) ArticleTitleThe mineral nutrition of wild plants revisited: A reevaluation of processes and patterns Adv Ecol Res 30 1–67 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXivVejurw%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0065-2504(08)60016-1
A Ares JH Fownes (2001) ArticleTitleProductivity, resource use, and competitive interactions of Fraxinus uhdei in Hawaii uplands Can J For Res. 31 132–42 Occurrence Handle10.1139/cjfr-31-1-132
RE Benoit RL Starkey J Basaraba (1968) ArticleTitleEffect of purified tannin on decomposition of some organic compounds and plant materials Soil Sci 105 153–8 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaF1cXhtVCitb0%3D Occurrence Handle10.1097/00010694-196803000-00004
F Berendse (1994) ArticleTitleLitter decomposability—a neglected component of plant fitness J Ecol 82 187–90
HA Carcamo TA Abe CE Prescott FB Holl CP Chanway (2000) ArticleTitleInfluence of millipedes on litter decomposition, N mineralization, and microbial communities in a coastal forest in British Columbia, Canada Can J For Res 30 817–26 Occurrence Handle10.1139/cjfr-30-5-817
MM Carreiro RL Sinsabaugh DA Repert DF Parkhurst (2000) ArticleTitleMicrobial enzyme shifts explain litter decay responses to simulated nitrogen deposition Ecology 81 2359–65
FS Chapin SuffixIII H Reynolds CM D’Antonio V Eckhart (1996) The functional role of species in terrestrial ecosystems B Walker W Steffan (Eds) Global change in terrestrial ecosystems Cambridge University Press Cambridge, UK 403–30
DC Coleman DA Crossley (1996) Soil Ecology Academic Press San Diego, CA 205
TE Crews K Kitayama JH Fownes RH Riley DA Herbert D Mueller-Dombois PM Vitousek (1995) ArticleTitleChanges in soil phosphorus fractions and ecosystem dynamics across a long chronosequence in Hawaii Ecology 76 1407–24
JG Ehrenfeld N Scott (2001) ArticleTitleInvasive species and the soil: Effects on organisms and ecosystem processes Ecol Applic 11 1259–60
JG Ehrenfeld P Kourtev WZ Huang (2001) ArticleTitleChanges in soil functions following invasions of exotic understory plants in deciduous forests Ecol Applic 11 1287–300
WM Elliott NB Elliott RL Wyman (1993) ArticleTitleRelative effect of litter and forest type on rate of decomposition Am Midl Naturalist 129 87–95
K Fog (1988) ArticleTitleThe effect of added nitrogen on the rate of decomposition of organic matter Biol Rev 63 433–62
Giambelluca TW, Nullet MA, Schroeder TA. 1986. Rainfall atlas of Hawaii. Department of Land and Natural Resources, Honolulu, HI
ST Gower Y Son (1992) ArticleTitleDifferences in soil and leaf litterfall nitrogen dynamics for 5 forest plantations Soil Sci Soc Am J 56 1959–66 Occurrence Handle10.2136/sssaj1992.03615995005600060051x
RA Hansen (1999) ArticleTitleRed oak litter promotes a microarthropod functional group that accelerates its decomposition Plant Soil 209 37–45 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1004506414711 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXltFGisrc%3D
AF Harrison DR Helliwell (1979) ArticleTitleBioassay for comparing phosphorus availability in soils J Appl Ecol 16 497–505 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3cXktVCktA%3D%3D
S Hattenschwiler AE Hagerman PM Vitousek (2003) ArticleTitlePolyphenols in litter from tropical montane forests across a wide range in soil fertility Biogeochemistry XX XX–XX
SE Hobbie (1992) ArticleTitleEffects of plant species on nutrient cycling Trends Ecol Evol 7 336–9 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0169-5347(92)90126-V
SE Hobbie (2000) ArticleTitleInteractions between litter lignin and soil nitrogen availability during leaf litter decomposition in a Hawaiian montane forest Ecosystems 3 484–94 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s100210000042 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXovFWgt7s%3D
SE Hobbie PM Vitousek (2000) ArticleTitleNutrient limitation of decomposition in Hawaiian forests Ecology 81 1867–77
K Iiyama AFA Wallis (1990) ArticleTitleDetermination of lignin in herbaceous plants by an improved acetyl bromide procedure J Sci Food Agric 51 145–161 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXitFegtrs%3D
RN Mack D Simberloff WM Lonsdale H Evans M Clout FA Bazzaz (2000) ArticleTitleBiotic invasions: Causes, epidemiology, global consequences, and control Ecol Applic 10 689–710
JM Melillo JD Aber AE Linkins A Ricca A Fry KJ Nadelhoffer (1989) ArticleTitleCarbon and nitrogen dynamics along the decay continuum—plant litter to soil organic matter Plant Soil 115 189–98
S Mole PG Waterman (1987) ArticleTitleA critical analysis of techniques for measuring tannins in ecological studies 1: techniques for chemically defining tannins Oecologia 72 137–47
J Neter W Wasserman MH Kutner (1990) Applied linear statistical models EditionNumber3 Richard D. Irwin, Inc. Homewood, IL 1181
LP Olander PM Vitousek (2000) ArticleTitleRegulation of soil phosphatase and chitinase activity by N and P availability Biogeochemistry 49 175–90 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1006316117817 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXis1yjt7Y%3D
JS Olson (1963) ArticleTitleEnergy storage and the balance of producers and decomposers in ecological systems Ecology 44 322–31
J Pastor JD Aber CA McClaugherty JM Melillo (1984) ArticleTitleAboveground production and N and P cycling along a nitrogen mineralization gradient on Blackhawk Island, Wisconsin Ecology 65 256–68 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2cXhtF2qsLo%3D
J Pastor MA Stillwell D Tilman (1987) ArticleTitleLittle bluestem litter dynamics in Minnesota old fields Oecologia 72 327–30
CE Prescott (1995) ArticleTitleDoes nitrogen availability control rates of litter decomposition in forests? Plant Soil 169 83–8
KR Saiya-Cork RL Sinsabaugh DR Zak (2002) ArticleTitleEffects of long term nitrogen deposition on extracellular enzyme activity in an Acer saccharum forest soil Soil Biol Biochem 34 1309–15 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0038-0717(02)00074-3 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XlvVemu7w%3D
NA Scott D Binkley (1997) ArticleTitleFoliage litter quality and annual net N mineralization: Comparison across North American forest sites Oecologia 111 151–9 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s004420050219
TR Seastedt (1984) ArticleTitleThe role of microarthropods in decomposition and mineralization processes Annu Rev Entomol 29 25–46 Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.en.29.010184.000325
RL Sinsabaugh DL Moorhead (1994) ArticleTitleResource allocation to extracellular enzyme production—a model for nitrogen and phosphorus control of litter decomposition Soil Biol Biochem 26 1305–11 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0038-0717(94)90211-9
RL Sinsabaugh RK Antibus AE Linkins CA McClaugherty L Rayburn D Repert T Weiland (1993) ArticleTitleWood decomposition—nitrogen and phosphorous dynamics in relation to extracellular enzyme activity Ecology 74 1586–93 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXlvF2ls78%3D
CW Smith (1985) Impact of alien plants on Hawai’i’s native biota CP Stone JM Scott (Eds) Hawai’i’s terrestrial ecosystems: Preservation and management Cooperative National Park Resources Studies Unit, University of Hawaii Honolulu, HI 180–250
GA Spiers WB McGill (1979) ArticleTitleEffects of phosphorus addition and energy supply on acid-phosphatase production and activity in soils Soil Biol Biochem 11 3–8 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0038-0717(79)90110-X Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE1MXhtlKlt7c%3D
C Theodorou GD Bowen (1990) ArticleTitleEffects of fertilizer on litterfall and nitrogen and phosphorus release from decomposing litter in a Pinus radiata plantation For Ecol Manage 32 87–102 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0378-1127(90)90163-6
N Breemen ParticleVan AC Finzi (1998) ArticleTitlePlant-soil interactions: ecological aspects and evolutionary implications Biogeochemistry 42 1–19
L Vesterdal (1999) ArticleTitleInfluence of soil type on mass loss and nutrient release from decomposing foliage litter of beech and Norway spruce Can J For Res 29 95–105 Occurrence Handle10.1139/cjfr-29-1-95
PM Vitousek (1982) ArticleTitleNutrient cycling and nutrient use efficiency Am Naturalist 119 553–72 Occurrence Handle10.1086/283931
PM Vitousek (1986) Biological invasions and ecosystem properties: can species make a difference? HA Mooney J Drake (Eds) Biological invasions of North America and Hawaii Springer New York 163–76
PM Vitousek (1998) ArticleTitleFoliar and litter nutrients, nutrient resorption, and decomposition in Hawaiian Metrosideros polymorpha Ecosystems 1 401–7 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s100219900033 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXptFensg%3D%3D
Whitesell CD, Wick HL, Honda N. 1971. Growth response of a thinned tropical ash stand in Hawaii after 5 years. USDA Forest Service Research Note PSW−227
JH Zar (1999) Biostatistical Analysis EditionNumber4 Prentice Hall Upper Saddle River, NJ 929
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the Division of Forestry and Wildlife of the State of Hawaii for access to field sites, and Hawaii Volcanoes National Park for logistical support and access to laboratory facilities. We thank Heraldo Farrington, Gordon Holtgrieve, and Steve LeDuc for assistance in the field and Doug Turner for assistance in the laboratory. Robert Sinsabaugh and Don Zak provided advice and lab facilities necessary to conduct enzyme assays. David Foote provided advice and lab facilities for extracting and analyzing arthropods. This research was supported by a USDA-NRI grant to Stanford University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rothstein, D.E., Vitousek, P.M. & Simmons, B.L. An Exotic Tree Alters Decomposition and Nutrient Cycling in A Hawaiian Montane Forest. Ecosystems 7, 805–814 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-004-0009-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-004-0009-y