Abstract
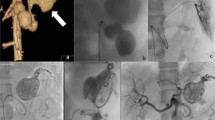
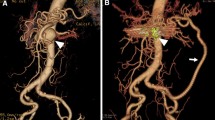
Visceral artery aneurysms (VAA) can be treated by revascularization, ligation, or, most often, endovascular techniques depending on clinical presentation, hemodynamic status, and location. From 1975 to 2002 a total of 42 VAA in 34 patients were treated. The lesion involved the splenic artery (SA; 19), pancreaticoduodenal artery (PDA; 6), celiac trunk (CT; 5), superior mesenteric artery (SNA; 4), common hepatic artery (CHA; 3), gastroduodenal artery (GDA; 2), left hepatic artery (LHA; 1), a branch of the inferior mesenteric artery (BIMA; 1), and a branch of the SMA (BSMA; 1). Twenty-seven VAA in 21 patients (64%) were uncomplicated (group I) and 15 VAA in 13 patients (36%) had ruptured (group II) (PDA; 6; CT, 3; SA, 1; CHA, 1; LHA, 1; BSMA, 1; BIMA, 1). In group I VAA were treated by embolization (n = 11), splenectomy (n = 6), bypass (n = 7), ligation (n = 2), and aneurysmorraphy (n = 1). No deaths were observed. The morbidity rate associated with surgical treatment was 12% including hepatic bypass thrombosis without ischemic complications in two cases. The morbidity rate associated with endovascular treatment was 18% including cholecystitis in one case and bile duct stenosis in one case. The VAA recanalization rate following embolization was 9%. In group II, 12 VAA (80%) were treated by ligation in association with splenectomy in two cases and left hepatectomy in one case. Only one bypass procedure was performed and embolization was used to treat two VAA (1 SMA and 1 PDA). The mortality rate was 20% (3/15). The morbidity rate associated with surgical treatment was 46% (6/13) including bile duct stenosis in one case, ischemic cholecystitis in one case, duodenal fistula in one case, pancreatic fistula in one case, bile tract fistula in one case, and colonic ischemia in one case. No patient died after endovascular treatment and the morbidity rate was 50% (1/2) with duodenal stenosis occurring in one case. In sum, VAA can rupture. Emergency cases can be treated by ligation in most cases or by embolization if the hemodynamic status of the patient allows. Regardless of treatment technique, the morbidity and mortality rate remains high after rupture, especially in cases involving PDA. Embolization can be proposed as a first-line treatment for most VAA. Because of the risk of rupture, endovascular or open repair is warranted for VAA and has a favorable prognosis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
YP Panayiotopoulos R Assadourian PR Taylor (1996) ArticleTitleAneurysms of the visceral and renal arteries Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 78 412–419
A Hossain ED Reis SP Dave et al. (2001) ArticleTitleVisceral artery aneurysms: experience in a tertiary-care center Am. Surg. 67 432–437
C Carmeci J McClenathan (2000) ArticleTitleVisceral artery aneurysms as seen in a community hospital Am. J. Surg. 179 486–489
F Muscari A Barret X Chaufour et al. (2002) ArticleTitleManagement of visceral artery aneurysms. Retrospective study of 23 cases Ann. Chir. 127 281–288
SC Carr DM Mahvi JR Hoch et al. (2001) ArticleTitleVisceral artery aneurysm rupture J. Vasc. Surg. 33 806–811
O Rokke K Sondenaa SR Amundsen et al. (1997) ArticleTitleSuccessful management of eleven splanchnic artery aneurysms Eur. J. Surg. 163 411–417
DG Neschis SD Safford MA Golden (1998) ArticleTitleManagement of pancreaticoduodenal artery aneurysms presenting as catastrophic intra-abdominal bleeding Surgery 123 8–12
TS Yeh YY Jan LB Jeng et al. (1997) ArticleTitleMassive extra-enteric gastrointestinal hemorrhage secondary to splanchnic artery aneurysms Hepatogastroenterology 44 1152–1156
WH Wagner AD Allins RL Treiman et al. (1997) ArticleTitleRuptured visceral artery aneurysms Ann. Vasc. Surg. 11 342–347
H Satoh T Morisaki H Kishikawa (1989) ArticleTitleA case of a postoperative aneurysm of the common hepatic artery which ruptured into the remnant stomach after a radical gastrectomy Jpn. J. Surg. 19 241–245
JA Carr JS Cho AD Shepard et al. (2000) ArticleTitleVisceral pseudoaneurysms due to pancreatic pseudocysts: rare but lethal complications of pancreatitis J. Vasc. Surg. 32 722–730
B Majerus V Alexandrescu E Shutsha et al. (1998) ArticleTitleSpontaneous rupture of the pancreaticoduodenal artery: three cases Dig. Surg. 15 266–269
MA Abbas WM Stone RJ Fowl et al. (2002) ArticleTitleSplenic artery aneurysms: two decades experience at Mayo Clinic Ann. Vasc. Surg. 16 442–449
MJ Dougherty P Gloviczki KJ Cherry SuffixJr et al. (1993) ArticleTitleHepatic artery aneurysms: evaluation and current management Int. Angiol. 12 178–184
WM Stone M Abbas KJ Cherry et al. (2002) ArticleTitleSuperior mesenteric artery aneurysms: is presence an indication for intervention? J. Vasc. Surg. 36 234–237
MM Marshall P Muiesan P Srinivasan et al. (2001) ArticleTitleHepatic artery pseudoaneurysms following liver transplantation: incidence, presenting features and management Clin. Radiol. 56 579–587
M Imamura N Shiiya T Murashita et al. (1998) ArticleTitlePancreaticoduodenal artery aneurysm with celiac trunk occlusion: report of a case J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 39 565–567
M Porcellini V Iaccarino B Bernardo et al. (1996) ArticleTitleVisceral artery aneurysms secondary to collateral circulation Minerva Cardioangiol. 44 443–445
OW Brown LH Hollier PC Pairolero RA McCready (1983) ArticleTitleUncommon visceral artery aneurysms South Med. J. 76 1000–1001
D Melliere JP Becquemin M Kassab F Souadka (1989) ArticleTitleAneurysms of digestive arteries. What are the indications? J. Mal. Vasc. 14 206–212
SG Mattar AB Lumsden (1995) ArticleTitleThe management of splenic artery aneurysms: experience with 23 cases Am. J. Surg. 169 580–584
JA Smith DG Macleish NA Collier (1989) ArticleTitleAneurysms of the visceral arteries Aust. N. Z. J. Surg. 59 329–334
SC Carr WH Pearce RL Vogelzang et al. (1996) ArticleTitleCurrent management of visceral artery aneurysms Surgery 120 627–634 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiD3Mrnt1Y%3D Occurrence Handle8862370
S Ersoz S Ozbas O Basaran et al. (1999) ArticleTitleCoeliac artery aneurysm: aortohepatic artery reconstruction Vasa 28 127–129
M Grosso E Zanon A Mancini et al. (1998) ArticleTitlePercutaneous transcatheter therapy of visceral pseudoaneurysms Minerva Chir. 53 363–368
TP McIntyre ST Simone KR Stahlfeld (2002) ArticleTitleIntraoperative thrombin occlusion of a visceral artery aneurysm J. Vasc. Surg. 36 393–395
A Gabelmann J Gorich EM Merkle (2002) ArticleTitleEndovascular treatment of visceral artery aneurysms J. Endovasc. Ther. 9 38–47
TA Salam AB Lumsden LG Martin RB Smith (1992) ArticleTitle3rd. Nonoperative management of visceral aneurysms and pseudoaneurysms Am. J. Surg. 164 215–219
M Grosso F Spalluto GC Anselmetti et al. (1992) ArticleTitlePercutaneous transcatheter embolization of deep visceral pseudoaneurysms Radiol. Med. 83 795–799
K Kasirajan RK Greenberg D Clair K Ouriel (2001) ArticleTitleEndovascular management of visceral artery aneurysm J. Endovasc. Ther. 8 150–155
PA Araoz JC Andrews (2000) ArticleTitleDirect percutaneous embolization of visceral artery aneurysms: techniques and pitfalls J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 11 1195–1200
GW Stambo MJ Hallisey JJ Gallagher SuffixJr (1996) ArticleTitleArteriographic embolization of visceral artery pseudoaneurysms Ann. Chir. Vasc. 10 476–480
MM Herskowitz MA Flyer SJ Sclafani (1993) ArticleTitlePercutaneous transhepatic coil embolization of a ruptured intrahepatic aneurysm in polyarteritis nodosa Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 16 254–256
PU Reber HU Baer AG Patel et al. (1998) ArticleTitleSuperselective microcoil embolization: treatment of choice in high-risk patients with extrahepatic pseudoaneurysms of the hepatic arteries J. Am. Coll. Surg. 186 325–330
AF Little WK Lee (2002) ArticleTitlePercutaneous and endovascular embolization of ruptured hepatic artery aneurysm Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 25 208–211
JH Rapp R Kerlan EJ Ring RJ Stoney (1988) ArticleTitlePreoperative balloon-tipped catheter placement for proximal control in visceral artery aneurysm surgery Surgery 104 112–113
M Venturini E Angeli M Salvioni et al. (2002) ArticleTitleHemorrhage from a right hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm: endovascular treatment with a coronary stent-graft J. Endovasc. Ther. 9 221–224
RA Larson J Solomon JP Carpenter (2002) ArticleTitleStent graft repair of visceral artery aneurysms J. Vasc. Surg. 36 1260–1263
M Hashizume M Ohata K Ueno et al. (1993) ArticleTitleLaparoscopic ligation of splenic artery aneurysm Surgery 113 352–354
G Melissano R Chiesa (1998) ArticleTitleSuccessful surgical treatment of visceral artery aneurysms: after failure of percutaneous treatment Tex. Heart Inst. J. 25 75–78
F Pilleul F Dugougeat (2002) ArticleTitleTranscatheter embolization of splanchnic aneurysms/pseudoaneurysms: early imaging allows detection of incomplete procedure J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 26 107–112
PG Tarazov VK Ryzhkov VN Polysalov et al. (1998) ArticleTitleExtraorganic hepatic artery aneurysm: failure of transcatheter embolization H.P.B. Surg. 11 55–59
KB Garby TS King FY Tsai (1997) ArticleTitleRecurrence of pseudoaneurysm after successful embolization J. Endovasc. Surg. 4 385–388
AB Lumsden SG Mattar RC Allen EA Bacha (1996) ArticleTitleHepatic artery aneurysms: the management of 22 patients J. Surg. Res. 60 345–350
Acknowledgment
We express our gratitude to Dr. Chaix for his contribution to imaging.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Sessa, C., Tinelli, G., Porcu, P. et al. Treatment of Visceral Artery Aneurysms: Description of a Retrospective Series of 42 Aneurysms in 34 Patients. Ann Vasc Surg 18, 695–703 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10016-004-0112-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10016-004-0112-8