Abstract
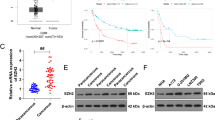
Enhancer of Zeste homologue2 (EZH2) is an epigenetic regulator that functions as oncogene in astrocytic tumors, however, EZH2 regulation remains little studied. In this study, we measured EZH2 levels in low (Gr-II,DA) and high grade (Gr-IV,GBM) astrocytic tumors and found significant increased EZH2 transcript level with grade(median DA-8.5, GBM-28.9).However, a different trend was reflected in protein levels, with GBMs showing high EZH2 LI(median-26.5) compared to DA (median 0.3). This difference in correlation of EZH2 protein and RNA levels suggested post-transcriptional regulation of EZH2, likely mediated by miRNAs. We selected eleven miRNAs that strongly predicted to target EZH2 and measured their expression. Three miRNAs (miR-26a-5p,miR27a-3p and miR-498) showed significant correlation with EZH2 protein, suggesting them as regulators of EZH2, however miR-26a-5p levels decreased with grade. ChIP analyses revealed H3K27me3 modifications in miR-26a promoter suggesting feedback loop between EZH2 and miR26a. We further measured six downstream miRNA targets of EZH2 and found significant downregulation of four (miR-181a/b and 200b/c) in GBM. Interestingly, EZH2 associated miRNAs were predicted to target 25 genes in glioma-pathway, suggesting their role in tumor formation or progression. Collectively, our work suggests EZH2 and its miRNA interactors may serve as promising biomarkers for progression of astrocytic tumors and may offer novel therapeutic strategies.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
McNamara M, Sahebjam S, Mason W (2013) Emerging biomarkers in glioblastoma. Cancer (Basel) 5:1103–1119
Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP et al (2009) Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol 10:459–466
Bracken AP, Helin K (2009) Polycomb group proteins: navigators of lineage pathways led astray in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 9:773–784
Purkait S, Sharma V, Jha P et al (2015) EZH2 expression in gliomas: correlation with CDKN2A gene deletion/p16 loss and MIB-1 proliferation index. Neuropathology 35:421–431
Suvà M-L, Riggi N, Janiszewska M et al (2009) EZH2 is essential for glioblastoma cancer stem cell maintenance. Cancer Res 69:9211–9218
Orzan F, Pellegatta S, Poliani PL et al (2011) Enhancer of Zeste 2 (EZH2) is up-regulated in malignant gliomas and in glioma stem-like cells. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 37:381–394
Li G, Warden C, Zou Z et al (2013) Altered expression of polycomb group genes in glioblastoma multiforme. PLoS One 8:e80970
Chan JA, Krichevsky AM, Kosik KS (2005) MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells microRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human. Cancer Res 65:6029–6033
Ciafrè SA, Galardi S, Mangiola A et al (2005) Extensive modulation of a set of microRNAs in primary glioblastoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 334:1351–1358
Silber J, Lim DA, Petritsch C et al (2008) miR-124 and miR-137 inhibit proliferation of glioblastoma multiforme cells and induce differentiation of brain tumor stem cells. BMC Med 6:14. doi:10.1186/1741-7015-6-14
Godlewski J, Nowicki MO, Bronisz A et al (2008) Targeting of the Bmi-1 oncogene/stem cell renewal factor by MicroRNA-128 inhibits glioma proliferation and self-renewal. Cancer Res 68:9125–9130
Malzkorn B, Wolter M, Liesenberg F et al (2010) Identification and functional characterization of microRNAs involved in the malignant progression of gliomas. Brain Pathol 20:539–550
Li Mengfeng, Li Jun, Liu Lei et al (2013) MicroRNA in human glioma. Cancers 5(4):1306–1331
Rao SAM, Santosh V, Somasundaram K (2010) Genome-wide expression profiling identifies deregulated miRNAs in malignant astrocytoma. Mod Pathol Off J United States Can Acad Pathol Inc Pathol 23:1404–1417
Varambally S, Cao Q, Mani R-S et al (2008) Genomic loss of microRNA-101 leads to overexpression of histone methyltransferase EZH2 in cancer. Sci 322:1695–1699
Gandellini P, Folini M, Longoni N et al (2009) miR-205 exerts tumor-suppressive functions in human prostate through down-regulation of protein kinase Cε. Cancer Res 69:2287–2295
Cao P, Deng Z, Wan M et al (2010) MicroRNA-101 negatively regulates Ezh2 and its expression is modulated by androgen receptor and HIF-1alpha/HIF-1beta. Mol Cancer 9:108
Tzatsos A, Paskaleva P, Lymperi S et al (2011) Lysine-specific demethylase 2B (KDM2B)-let-7-enhancer of zester homolog 2 (EZH2) pathway regulates cell cycle progression and senescence in primary cells. J Biol Chem 286:33061–33069
Kottakis F, Polytarchou C, Foltopoulou P et al (2011) FGF-2 regulates cell proliferation, migration and angiogenesis through an NDY1/KDM2B-miR-101-EZH2 pathway. Mol Cell 43:285–298
Cao Q, Mani R-S, Ateeq B et al (2011) Coordinated regulation of polycomb group complexes through microRNAs in cancer. Cancer Cell 20:187–199
Valente V, Teixeira SA, Neder L et al (2009) Selection of suitable housekeeping genes for expression analysis in glioblastoma using quantitative RT-PCR. BMC Mol Biol 10:17
Kleer CG, Cao Q, Varambally S et al (2003) EZH2 is a marker of aggressive breast cancer and promotes neoplastic transformation of breast epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100:11606–11611
Batlle E, Sancho E, Franci C et al (2000) The transcription factor Snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in epithelial tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol 2:84–89
Zhang J, Chen L, Han L et al (2015) EZH2 is a negative prognostic factor and exhibits pro-oncogenic activity in glioblastoma. Cancer Lett 356:929–936
Suh S-S, Yoo JY, Nuovo GJ et al (2012) MicroRNAs/TP53 feedback circuitry in glioblastoma multiforme. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109:5316–5321
Xu W, Liu M, Peng X et al (2013) MiR-24-3p and miR-27a-3p promote cell proliferation in glioma cells via cooperative regulation of MXI1. Int J Oncol 42:757–766
Ge YF, Sun J, Jin CJ et al (2013) AntagomiR-27a targets FOXO3a in glioblastoma and suppresses U87 cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Asian Pacific J Cancer Prev 14:963–968
Guo P, Nie Q, Lan J et al (2013) C-Myc negatively controls the tumor suppressor PTEN by upregulating miR-26a in glioblastoma multiforme cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 441:186–190
Guo P, Lan J, Ge J et al (2014) MiR-26a enhances the radiosensitivity of glioblastoma multiforme cells through targeting of ataxia–telangiectasia mutated. Exp Cell Res 320:200–208
Smits M, Nilsson J, Mir SE et al (2010) miR-101 is down-regulated in glioblastoma resulting in EZH2-induced proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis. Oncotarget 1:710–720
Yao Y-L, Ma J, Wang P et al (2015) miR-101 acts as a tumor suppressor by targeting Kruppel-like factor 6 in glioblastoma stem cells. CNS Neurosci Ther 21:40–51
Lv Z, Yang L (2013) MiR-124 inhibits the growth of glioblastoma through the downregulation of SOS1. Mol Med Rep 8:345–349
Chen Q, Lu G, Cai Y et al (2014) MiR-124-5p inhibits the growth of high-grade gliomas through posttranscriptional regulation of LAMB1. Neuro-Oncology 16:637–651
Bier A, Giladi N, Kronfeld N et al (2013) MicroRNA-137 is downregulated in glioblastoma and inhibits the stemness of glioma stem cells by targeting RTVP-1. Oncotarget 4:665–676
Qiu S, Huang D, Yin D et al (2013) Suppression of tumorigenicity by MicroRNA-138 through inhibition of EZH2-CDK4/6-pRb-E2F1 signal loop in glioblastoma multiforme. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1832:1697–1707
Hausser J, Zavolan M (2014) Identification and consequences of miRNA-target interactions—beyond repression of gene expression. Nat Rev Genet 15:599–612
Gao J, Liu QG (2011) The role of miR-26 in tumors and normal tissues (Review). Oncol Lett 2:1019–1023
Huse JT, Brennan C, Hambardzumyan D et al (2009) The PTEN-regulating microRNA miR-26a is amplified in high-grade glioma and facilitates gliomagenesis in vivo. Genes Dev 23:1327–1337
Kim H, Huang W, Jiang X et al (2010) Integrative genome analysis reveals an oncomir/oncogene cluster regulating glioblastoma survivorship. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107:2183–2188
Visani M, de Biase D, Marucci G et al (2014) Expression of 19 microRNAs in glioblastoma and comparison with other brain neoplasia of grades I–III. Mol Oncol 8:417–430
Iliopoulos D, Lindahl-Allen M, Polytarchou C et al (2010) Loss of miR-200 inhibition of Suz12 leads to polycomb-mediated repression required for the formation and maintenance of cancer stem cells. Mol Cell 39:761–772
Acknowledgments
We thank Mrs. Kiran Rani and Mr. Pankaj Kumar for their help in immunohistochemistry. We would also like to thank the technical staff of the Neuropathology laboratory, All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), New Delhi, India and all the consultants of the Neurosurgery department. This work was funded by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR). Vikas Sharma thanks Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) for SRF fellowship. Sonam Takkar thanks Department of Science and Technology (DST-Inspire) for fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest for any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10014_2015_245_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplementary material 2 (TIFF 451 kb) EZH2 transcript expression in GBM patient (n=572) and normal brain samples (n=10) based on microarray data from freely available TCGA portal (p-value< 0.0001)
10014_2015_245_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Supplementary material 3 (TIFF 545 kb) Spearman correlation tables for miRNA targeting EZH2 with EZH2 mRNA and protein levels. The samples with significant correlation (p<0.05 ) have been highlighted
10014_2015_245_MOESM4_ESM.tif
Supplementary material 4 (TIFF 264 kb) Spearman correlation tables for EZH2 regulated miRNAs with EZH2mRNA and protein levels. The samples with significant correlation (p<0.05) have been highlighted
10014_2015_245_MOESM5_ESM.tif
Supplementary material 5 (TIFF 1398 kb) A diagrammatic representation of the glioma pathway using KEGG program. The genes in the glioma pathway predicted to be targeted by EZH2 associated miRNAs have been highlighted in red
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, V., Purkait, S., Takkar, S. et al. Analysis of EZH2: micro-RNA network in low and high grade astrocytic tumors. Brain Tumor Pathol 33, 117–128 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10014-015-0245-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10014-015-0245-1