Abstract
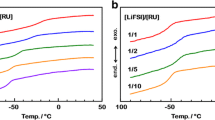
Poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) oligomers having alkali metal thiolate groups on the chain ends (PEO m -S−M+) were prepared as an ion conductive matrix. The molecular weight of the PEO part (m) and the content of the thiolate groups in the molecule were changed to analyze the effect of carrier ion concentration in the bulk. In a series of potassium salt derivatives, PEO350-SK showed the highest ionic conductivity of 6.42 × 10−5 S/cm at 50 °C. In spite of a poor degree of dissociation which was derived from the acidity of the thiolate groups, PEO m -SM showed quite high ionic conductivity among other PEO/salt hybrids. PEO m -SM had glass transition temperatures (T g) 20 °C lower than other PEO/salt hybrids. Lowering the T g was concluded to be effective in providing higher ionic conductivity for PEO-based polymer electrolytes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 30 April 1999 / Accepted: 20 June 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kato, Ki., Ito-Akita, K. & Ohno, H. Preparation and ionic conductivity of poly(ethylene oxide) oligomers having thiolate groups on the chain ends. J Solid State Electrochem 4, 141–145 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100080050011
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100080050011