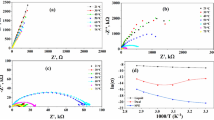
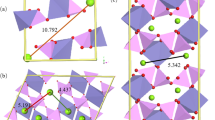
Abstract
Realizing practical Mg batteries still confronts crucial obstacles like the absence of a novel cathode with sufficient fast kinetic and the rapid passivation of the Mg anode. The paper aims to probe the effect of NaF electrolyte additive to halogen-free electrolyte HFE (0.69 M Mg(NO3)2·6H2O in ACN:G4(∼2:1) on changing the interfacial structure at the Mg anode surface, suppressing side reactions, mitigating Mg passivation, and facilitating Mg2+ transport. Electrochemical and spectroscopic approaches are applied to investigate the interaction of the anode–electrolyte interface. The modified Mg electrode in HFE@NaF electrolyte displays lower overpotential and interfacial impedance than the bare Mg electrode in HFE electrolyte. The assembled MgS cell with bare and modified Mg electrodes delivers a high initial capacity (> 1200 mAhg−1 at a current density of 0.02 mA cm−1) with short cycle life. Post-mortem analysis techniques confirm the results, and the current study provides fundamental insights into the interfacial phenomena in Mg and emphasizes the great promise of overcoming Mg battery challenges.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Y, Atwi R, Han KS, Ryu J, Washton NM, Hu JZ et al (2021) Role of a multivalent ion–solvent interaction on restricted Mg2+ diffusion in dimethoxyethane electrolytes. J Phys Chem B
Xiu Y, Li Z, Bhaghavathi Parambath V, Ding Z, Wang L, Reupert A et al (2021) Combining quinone‐based cathode with an efficient borate electrolyte for high‐performance magnesium batteries. Batter Supercaps
Hou S, Ji X, Gaskell K, Wang P-f, Wang L, Xu J et al (2021) Solvation sheath reorganization enables divalent metal batteries with fast interfacial charge transfer kinetics. Science 374(6564):172–8
Li Y, Zuo P, Li R, Huo H, Ma Y, Du C et al (2021) Formation of an artificial Mg2+-permeable interphase on Mg anodes compatible with ether and carbonate electrolytes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13(21):24565–24574
Son S-B, Gao T, Harvey SP, Steirer KX, Stokes A, Norman A et al (2018) An artificial interphase enables reversible magnesium chemistry in carbonate electrolytes. Nat Chem 10(5):532–539
Nguyen QH, Luu VT, Lim SN, Lee Y-W, Cho Y, Jun Y-S et al (2021) Metal–organic frameworks reinforce the carbon nanotube sponge-derived robust three-dimensional sulfur host for lithium–sulfur batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13(24):28036–28048
Sun Y, Zou Q, Wang W, Lu Y-C (2021) Non-passivating anion adsorption enables reversible magnesium redox in simple non-nucleophilic electrolytes. ACS Energy Lett 6(10):3607–3613
Wally N, Sheha E, Kamal B, Hannora A, El-Desoky M (2021) Exploring the electrochemical properties of Na2S–V2O5–P2O5 glass-ceramic nanocomposites as a cathode for magnesium-ion batteries. J Alloy Compd 162644
Forero‐Saboya JD, Tchitchekova DS, Johansson P, Palacín MR, Ponrouch A (2021) Interfaces and interphases in ca and mg batteries. Adv Mater Interf 2101578
Li Z, Diemant T, Meng Z, Xiu Y, Reupert A, Wang L et al (2021) Establishing a stable anode–electrolyte interface in Mg batteries by electrolyte additive. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13(28):33123–33132
Xu M, Li Y, Ihsan-Ul-Haq M, Mubarak N, Liu Z, Wu J et al (2022) NaF-rich solid electrolyte interphase for dendrite-free sodium metal batteries. Energy Storage Mater 44:477–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2021.10.038
Ye M, You S, Xiong J, Yang Y, Zhang Y, Li CC (2022) In-situ construction of a NaF-rich cathode–electrolyte interface on Prussian blue toward a 3000-cycle-life sodium-ion battery. Mater Today Energy 23:100898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtener.2021.100898
Wen X, Yu Z, Zhao Y, Zhang J, Qiao R, Cheng L et al (2021) Enabling magnesium anodes by tuning the electrode/electrolyte interfacial structure. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13(44):52461–52468
Sheha E, Farrag M, Fan S, Kamar E, Sa N (2022) A Simple Cl–-free electrolyte based on magnesium nitrate for magnesium–sulfur battery applications. ACS Appl Energy Mater 5(2):2260–2269
Cao J, Zhang D, Yue Y, Chanajaree R, Wang S, Han J et al (2022) Regulating solvation structure to stabilize zinc anode by fastening the free water molecules with an inorganic colloidal electrolyte. Nano Energy 93:106839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2021.106839
Zhang X, Luo Y, Lu K, Lu Q, Gong J, Liu R (2020) Tuning band gaps and photoelectrochemical properties of electrodeposited CuO films by annealing in different atmospheres. J Electrochem Soc 167(2):026504
Shetty SK, Ismayil, Shetty G (2020) Enhancement of electrical and optical properties of sodium bromide doped carboxymethyl cellulose biopolymer electrolyte films. J Macromole Sci Part B 59(4):235–47
de Oliveira Silva J, Rodrigues Filho G, da Silva Meireles C, Ribeiro SD, Vieira JG, da Silva CV et al (2012) Thermal analysis and FTIR studies of sewage sludge produced in treatment plants. The case of sludge in the city of Uberlândia-MG, Brazil. Thermochimica Acta 528:72–5
Reddy V, Ramulu TS, Sinha B, Lim J, Hoque MR, Lee J-H et al (2012) Electrochemical detection of single nucleotide polymorphism in short DNA sequences related to cattle Fatty acid binding protein 4 gene. Int J Electrochem Sci 7:11058–11067
Huuhtanen M, Rahkamaa-Tolonen K, Maunula T, Keiski RL (2005) Pt-loaded zeolites for reducing exhaust gas emissions at low temperatures and in lean conditions. Catal Today 100(3–4):321–325
Addison C, Walker A (1963) Study of the structure of complex compounds of beryllium, aluminum, and magnesium with mixed ligands (ammino chlorides and ammino nitrates) by IR spectroscopy. J Chem Soc 1:1120
Nassar MY, Ahmed IS, Samir I (2014) A novel synthetic route for magnesium aluminate (MgAl2O4) nanoparticles using sol–gel auto combustion method and their photocatalytic properties. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 131:329–334
Bekiaris G, Bruun S, Peltre C, Houot S, Jensen LS (2015) FTIR–PAS: a powerful tool for characterising the chemical composition and predicting the labile C fraction of various organic waste products. Waste Manage 39:45–56
Tavares TS, da Rocha EP, Esteves Nogueira FG, Torres JA, Silva MC, Kuca K et al (2020) Δ-FeOOH as support for immobilization peroxidase: optimization via a chemometric approach. Molecules 25(2):259
Han Y, Li G, Hu Z, Wang F, Chu J, Huang L et al (2022) High-performance Mg–organic batteries based on hybrid MgCl2–LiCl/THF electrolytes. Energy Storage Mater
Fan S, Asselin GM, Pan B, Wang H, Ren Y, Vaughey JT et al (2020) A simple halogen-free magnesium electrolyte for reversible magnesium deposition through cosolvent assistance. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12(9):10252–10260
Saroha R, Heo J, Liu Y, Angulakshmi N, Lee Y, Cho K-K et al (2022) V2O3-decorated carbon nanofibers as a robust interlayer for long-lived, high-performance, room-temperature sodium–sulfur batteries. Chem Eng J 431:134205
Zhang R, Cui C, Xiao R, Li R, Mu T, Huo H et al (2022) Interface regulation of Mg anode and redox couple conversion in cathode by copper for high-performance Mg-S battery. Chem Eng J 138663
Bhauriyal P, Pathak B (2020) Superior anchoring effect of a Cu-benzenehexathial MOF as an aluminium–sulfur battery cathode host. Mater Adv 1(9):3572–3581
Wohlgemuth S-A, White RJ, Willinger M-G, Titirici M-M, Antonietti M (2012) A one-pot hydrothermal synthesis of sulfur and nitrogen doped carbon aerogels with enhanced electrocatalytic activity in the oxygen reduction reaction. Green Chem 14(5):1515–1523
Lee JH, Kang J, Kim S-W, Halim W, Frey MW, Joo YL (2018) Effective suppression of the polysulfide shuttle effect in lithium–sulfur batteries by implementing rGO–PEDOT: PSS-coated separators via air-controlled electrospray. ACS Omega 3(12):16465–16471
Kim HS, Arthur TS, Allred GD, Zajicek J, Newman JG, Rodnyansky AE et al (2011) Structure and compatibility of a magnesium electrolyte with a sulphur cathode. Nat Commun 2(1):1–6
Zhao T, Ye Y, Lao CY, Divitini G, Coxon PR, Peng X et al (2017) A praline-like flexible interlayer with highly mounted polysulfide anchors for lithium–sulfur batteries. Small 13(40):1700357
Lu Y, Gu S, Guo J, Rui K, Chen C, Zhang S et al (2017) Sulfonic groups originated dual-functional interlayer for high performance lithium–sulfur battery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(17):14878–14888
Gao T, Hou S, Wang F, Ma Z, Li X, Xu K et al (2017) Reversible S0/MgSx redox chemistry in a MgTFSI2/MgCl2/DME electrolyte for rechargeable Mg/S batteries. Angew Chem 129(43):13711–13715
Huang D, Tan S, Li M, Wang D, Han C, An Q et al (2020) Highly efficient non-nucleophilic Mg (CF3SO3) 2-based electrolyte for high-power Mg/S battery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12(15):17474–17480
Funding
This work is financially supported by the Academy of Scientific Research Technology/Bibliotheca Alexandrina (ASRT/BA) (Grant No. 1530) and the Science Technology Development Fund, Egypt, (Grant No. 30340).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Farrag, M., Refai, H.S. & Sheha, E. The role of adding NaF to the electrolyte in constructing a stable anode/electrolyte interphase for magnesium battery applications. J Solid State Electrochem 27, 379–389 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-022-05329-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-022-05329-1