Abstract
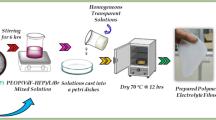
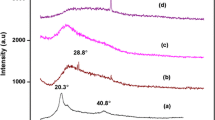
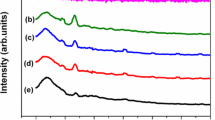
An attempt has been made to prepare a new blend polymer electrolytes (BPEs) based on PVdF-co-HFP and PVAc doped with Mg (ClO4)2 by using the solvent-casting technique. The physicochemical properties of the as prepared polymer electrolytes were characterized by XRD, FTIR, SEM, TG/DTA, linear sweep voltammetry (LSV), and cyclic voltammetry (CV). The maximum ionic conductivity value 3.85 × 10−5 S cm−1 has been observed for PVdF-co-HFP (69)-PVAc (23)-Mg (ClO4)2 (8 wt%) system at 30 °C using AC impedance spectroscopic technique. The FTIR analysis confirms the complex formation between the polymers and salts. The TG/DTA studies showed the thermal stability of the film. The polymer electrolyte membrane shows a wide electrochemical stability window, and the temperature dependence of ionic conductivity obeys the Arrhenius rule.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PVdF-HFP:
-
poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexaflouropropylene)
- PVAc:
-
poly(vinyl acetate)
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction,
- FTIR:
-
Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy
- SEM:
-
scanning electron microscope,
- TG/DTA:
-
Thermogravimetric/differential thermal analysis
- PMMA:
-
poly(methyl methacrylate)
- PEG:
-
polyethylene glycol
References
Mohtadi R, Mizuno F (2014) Magnesium batteries: current state of the art, issues and future perspectives. Beilstein J Nanotechnology 5:1291–1311
Liu C, Zachary GN, Cao G (2016) Mater Today. 19(2):109–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2015.10.009
Ha CJ, HyukYoon J, IlCho W, HoJang (2004) Electrochemical properties of LiNi0.8Co0.2 − xAlxO2 prepared by a sol–gel method. J Power Sources 136:132–138
Deng H, Nie P, Luo H, Zhang Y, Wang J, Zhang X (2014) Highly enhanced lithium storage capability of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 by coating with Li2TiO3 for Li-ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 2(43):18256–18262
Aurbach D, Lu Z, Schechter A, Gofer Y, Gizbar H, Turgeman R, Cohen geman R, Cohen Y, Moshkovich M, Levi E (2000) Prototype systems for rechargeable magnesium batteries. Nature 407(6805):724–727
Pandey GP, Hashmi SA (2009) Experimental investigations of an ionic-liquid-based, magnesium ion conducting, polymer gel electrolyte. J Power Sources 187(2):627–634
Novak P, Imdhof R, Haas O (1999) Magnesium insertion electrodes for rechargeable nonaqueous batteries—a competitive alternative to lithium. Electrochim Acta 45(1-2):351–367
Wu N, Yang ZZ, Yao HR, Yin YX, Gu L, Guo YG (2015) Improving the electrochemical performance of Li4Ti5O12 electrode in a rechargeable Mg battery by lithium magnesium co-intercalation. J Angew Chem Int Ed 54(19):5757–5761
Tao ZL, Xu LN, Gou XL, Chen J, Yuan HI (2004) TiS2 nanotubes as the cathode materials of Mg ion batteries. J Chem Comm 18:2080–2081
Kim J, Lee J, You J, Park MS, Hossain MSA, Yamauchi Y, Kim JH (2016) Conductive polymers for next generation energy storage systems, recent progress and new function. MaterHoriz 3:517–535
Gregory TD, Hoffman RJ, Winterton RC (1990) Nonaqueous electrochemistry of magnesium applications to energy storage. J Electrochem Soc 137(3):775–780
Kumar GG, Munichandriah N (2002) Poly(methylmethacrylate) magnesium triflate gel polymer electrolyte for solid state magnesium battery application. J Electrochim Acta 47(7):1013–1022
Yoshimoto N, Yakushiji S, Ishikawa M, Morita M (2003) Rechargeable magnesium batteries with polymeric gel electrolytes containing magnesium salts. J. Electrochim Acta 48(14-16):2317–2322
Polu AR, Kumar R (2012) Ionic conductivity and discharge characteristic studies of PVA-Mg (CH3COO)2 solid polymer electrolytes. Int J Polymer Mater 62:76–80
Polu AR, Kumar R (2014) Mg2+-ion conducting poly(ethylene glycol)-TiO2composite polymer electrolytes for solid-state batteries. Materials Express 4:79–84
Ulaganathan M, Rajendran S (2010) Preparation and characterization of PVAc/P(VdF-HFP)-based polymer blend electrolytes. Ionics 16:515–521
Pandey GP, Agrawal RC, Hashmi SA (2011) Magnesium ion-conducting gel polymer electrolytes dispersed with fumed silica for rechargeable magnesium battery application. J Solid State Electrochem 15(10):2253–2264
Oh JS, Ko JM, Kim DW (2004) Preparation and characterization of gel polymer electrolytes for solid state magnesium batteries. J Electrochim Acta 50(2-3):903–906
Shakur MF, Ithnin R, Illias HA, Kadir MFZ (2013) Proton conducting polymer electrolyte based on plasticized chotosan-PEO and application in electrochemical devices. Opt Mater 35(10):1834–1841
Kalyanasundaram NT, Subramanian A, Lokesh KS, Muhammed Musthafa OT (2008) Effect of porosity on PVdF-HFP/PMMA based electrolyte. J Materials Chem and Phy 110:11–16
Basri NH, Mohamed NS (2009) Conductivity studies and dielectric behavior of PVdF-HFP/PVC LiClO4 solid polymer electrolyte. Solid State Sci Technol 17:63–72
Rajendran S, Shanthi Bama V, Ramesh Prabhu M (2010) Effect of lithium salt concentration in PVAc/PMMA-based gel polymer electrolytes. Ionics 16(1):27–32
Lee H, Yanilmaz M, Toprakci O, Fu K, Zhang X (2014) PVdF-HFP/PVAc: a review of recent developments in membrane separators for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. J Energy Environ Sci 7(12):3857–3886
JuHwangSoo Y, KyungJeong KSN, Manuel Stephan A (2007) Electrochemical studies on poly(vinylidene fluoride–hexafluoropropylene) membranes prepared by phase inversion method. Eur Polym J 43:65–71
Ulaganathan M, Rajendran S (2010) Effect of different salts on PVAc/PVdF-co-HFP based polymer blend electrolytes. J Appl Polym Sci 118:646–651
Kirankumar K, Ravi M, Pavani Y, Bhavani S, Sharma AK, VVR NR (2014) Investigations on PEO/PVP/NaBr complexed polymer blend electrolytes for electrochemical cell applications. J Membr Sci 454:200–211
Kim DW, Park JK, Rhee HW (1996) Conducting and thermal studies of solid polymer electrolytes prepared by poly(ethyleneoxide), poly(oligo[oxyethylene]oxysebacoyl) and lithium perchlorate. Solid State Ionics 83(1-2):49–56
Kim CH, Kim HT, Park JK, Moon SI, Yoon MS (1996) Preparation and ionic conductivities of the plasticized polymer electrolytes based on poly(methyl methacrylate-co-alkali metal methacrylate). J polymer Sci: part B:Polymer Phys 34(16):2709–2714
Sung HY, Wang YY, Wan CC (1998) Preparation and characterization of poly(vinyl chloride-co-vinyl acetate)-based gel electrolytes for Li-ion batteries. J Electrochem Soc 145(4):1207–1211
Rhoo HJ, Kim HT, Park JK, Hwang TS (1997) Ionic conduction in plasticized PVCPMMA blend polymer electrolytes. Electrochimca Acta 42(10):1571–1579
Jian-HuaCao, Bao-KuZhu, You-YiXu (2006) Structure and ionic conductivity of porous polymer electrolytes based on PVDF-HFP copolymer membranes. J Membr Sci 281:446–453
Wieczorek W, Florjancy Z, Stevens JR (1995) Proton conducting polymer gels based on a poly acrylamide matrix. Electrochim Acta J 40:2327–2330
Shanmukaraj D, Wang GX, Murugan R, Liu HK (2008) Ionic conductivity and electrochemical stability of PMMA-PEO blend ceramic filler composites. J Phys Chem Solids 69(1):243–248
Prajapathi GK, Roshan R, Gupta PN (2010) Effect of plasticizer on ionic transport and dielectric properties of PVA:H3PO4 proton conducting polymeric electric electrolyte. J Phys and Chem of Solids 71(12):1717–1723
Ulaganathan M, Rajendran S (2011) Novel Li-ion conduction on poly(vinyl acetate)-based hybrid polymer electrolytes with double plasticizers. J Appl Electrochem 41(1):83–88
Gebreyesus MA, Purushotham Y, Sivakumar J (2016) Preparation and characterization of lithium ion conducting polymer electrolytes based on a blend of poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) and poly(methyl methacrylate). Heliyon 2(7):e00134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2016.e00134
Abbrent S, Plestil J, Hlavata D, Lindgren J, Tegenfeldt J, Wendsjo A (2001) Crystallinity and morphology of PVdF-HFP-based gel electrolytes. Polymer 42(4):1407–1416
Ataollahi N, Ahmad A, Hamzah H, Rahman MYA, Mohamed NS (2012) Preparation and characterization of PVDF-HFP/MG49 based polymer blend electrolyte. Int J Electrochem Sci 7:6693–6703
Tafur JP, Santos F, Fernández Romero AJ (2015) Influence of the ionic liquid on the gel polymer electrolytes properties. Membranes 5(4):752–771
Baskaran R, Selvasekarapandian S, Hirankumar G, Bhuvaneswari MS (2004) Vibrational ac impedance and dielectric spectroscopic studies of poly(vinylacetate)-N,N-dimethylformamide-LiClO4 polymer gel electrolytes. J Power Sources 134(2):235–240
Baskaran R, Selvasekarapandian S, Kuwata N, Kawamura J, Hattori T (2007) Structure, thermal and transport properties of PVAc–LiClO4 solid polymer electrolytes. J Phys and Chem Solids 68(3):407–412
Arunkumar D, Selvasekarapandian S, Baskaran R, Savitha T, Nithya H (2012) Thermal vibrational and AC impedence studies on proton conducting polymer electrolytes based on poly(vinylacetate). J Non crystal solids 358:531–536
Ulaganathan M, Nithya R, Rajendran S, Raghu S (2012) Li-ion conduction on nanofiller incorporated PVdF-co-HFP based composite polymer blend electrolytes for flexible battery applications. Solid State Ionics 218:7–12
Michael MS, Jacob MME, Prabaharan SRS, Radhakrishna S (1997) Enhanced lithium ion transport in PEO-based solid polymer electrolytes employing a novel class of plasticizers. Solid State Ionics 98(3-4):167–174
Ulaganathan M, Chithra MM, Rajendran S (2013) Highly porous lithium ion conducting solvent free poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene)/poly( ethyl methacrylate) based polymer blend electrolytes for Li battery applications. J. Electrochim Acta 93:230–235
Selvasekarapandian S, Baskaran R, Kamishima O, Kawamura J, Hattori T (2006) Laser Raman and FTIR studies on Li+ interaction in PVAc-LiClO4 polymer electrolytes. J Spectrochim Acta part A 65(5):1234–1240
Ulaganathan M, Sundar Pethaiah S, Rajendran S (2011) Li-ion conduction in PVAc based blend electrolytes for lithium battery applications. J Mater Chem Phys 129(1-2):471–476
Tsunemi K, Ohno H, Tsuchida A (1983) A mechanism of ionic conduction of poly(vinylidene fluoride)-lithium perchlorate hybrid films. J. Electrochim Acta 28(6):833–837
Park US, Hong YJ, Oh SM (1996) Fluorescence spectroscopy for local viscosity measurements in polyacrylonitrile (pan)-based polymer gel electrolytes. J Electrochim Acta 41(6):849–855
Missan HPS, Chu PP, Sekhon SS (2006) Ion conduction mechanism in non-aqueous polymer electrolytes based on oxalic acid: effect of plasticizer and polymer. J Power Sources 158(2):1472–1479
Polu AR, Kumar R (2013) Preparation and characterization of PVA based polymer electrolytes for electrochemical cell application. Chinese J Polym Sci 31(4):641–648
Tripathi SK, Jain A, Gupita A, Mishra M (2012) Electrical and electrochemical studies on magnesium ion-based polymer gel electrolytes. J Solid State Electrochem 16(5):1799–1806
Manjuladevi R, Thamilselvan M, Selvasekarapandian S, Mangalam R, Premalatha M, Monisha S (2017) Mg-ion conducting blend polymer electrolyte based on poly(vinyl alcohol)-poly(acrylonitrile) with magnesium perchlorate. Solid State Ionics 308:90–100
Pandey GP, Hashmi SA (2009) Experimental investigations of an ionic-liquid-based magnesium ion conducting polymer gel electrolytes. J Power Sources 187(2):627–634
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 38 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ponmani, S., Kalaiselvimary, J. & Ramesh Prabhu, M. Structural, electrical, and electrochemical properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexaflouropropylene)/poly(vinyl acetate)-based polymer blend electrolytes for rechargeable magnesium ion batteries. J Solid State Electrochem 22, 2605–2615 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-018-3971-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-018-3971-6