Abstract
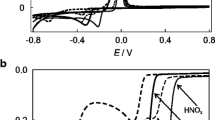
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and voltammetry of immobilized particles (VIMP) measurements using air-saturated mineral water and 0.10 M NaClO4 aqueous solution as electrolytes were applied to eurocent coins and a set of copper/bronze coins from the late nineteenth century exhibiting significant heterogeneity in their degree and type of corrosion. The obtained data presented satisfactory repeatability being fitted to relatively simple equivalent circuits which were dependent on the electrolyte and bias potential, the more satisfactory conditions being obtained using the reduction of dissolved oxygen as a redox probe. Consistent data were obtained using VIMP and EIS characterizing different corrosion patterns, and establishing the possibility of discriminating different monetary emissions in favorable cases of high level of corrosion.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scott DA (1991) Metallography and microstructure of ancient and historic metals. Getty Conservation Institute in association with Archetype Books, Marina del Rey, p 155
Ingo GM, Balbi S, De Caro T et al (2006) Microchemical investigation of Greek and Roman silver and gold plated coins: coating techniques and corrosion mechanisms. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 83(4):623–629
FitzGerald KP, Nairn J, Skennerton G, Atrens A (2006) Atmospheric corrosion of copper and the colour, structure and composition of natural patinas on copper. Corros Sci 48(9):2480–2509
Robbiola L, Blengino JM, Fiaud C (1998) Morphology and mechanisms of formation of natural patinas on archaeological Cu-Sn alloys. Corros Sci 40(12):2083–2111
Chiavari C, Rahmouni K, Takenouti H, Joiret S, Vermaut P, Robbiola L (2007) Composition and electrochemical properties of natural patinas of outdoor bronze monuments. Electrochim Acta 52(27):7760–7769
Robbiola L, Hurtel L (1997) Standard nature of the passive layers of buried archaeological bronze - the example of two Roman half-length portraits. In: METAL 95: international conference on metals conservation. James and James science Publisher, Semuren-Auxois, pp 109–117
Serghini-Idrissi M, Bernard MC, Harrif FZ, Joiret S, Rahmouni K, Srhiri A, Takenouti H, Vivier V, Ziani M (2005) Electrochemical and spectroscopic characterizations of patinas formed on an archaeological bronze coin. Electrochim Acta 50(24):4699–4709
Di Turo F, Montoya N, Piquero-Cilla J et al (2017) Archaeometric analysis of Roman bronze coins from the Magna Mater temple using solid-state voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Anal Chim Acta 955:36–47
Di Turo F, De Vito C, Coletti F et al (2017) A multi-analytical approach for the validation of a jellified electrolyte: application to the study of ancient bronze patina. Microchem J 134:154–163
Aucouturier M, Darque-Ceretti E (2007) The surface of cultural heritage artefacts: physicochemical investigations for their knowledge and their conservation. Chem Soc Rev 36(10):1605
Ingo GM, Riccucci C, Faraldi F, Pascucci M, Messina E, Fierro G, di Carlo G (2017) Roman sophisticated surface modification methods to manufacture silver counterfeited coins. Appl Surf Sci 421:109–119
Griesser M, Kockelmann W, Hradil K, Traum R (2016) New insights into the manufacturing technique and corrosion of high leaded antique bronze coins. Microchem J 126:181–193
Ingo GM, Balbi S, De Caro T et al (2006) Combined use of SEM-EDS, OM and XRD for the characterization of corrosion products grown on silver roman coins. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 83(4):493–497
Bernard MC, Joiret S (2009) Understanding corrosion of ancient metals for the conservation of cultural heritage. Electrochim Acta 54(22):5199–5205
Matthiesen H, Hilbert LR, Gregory D, Sørensen B (2004) Corrosion of archaeological iron artefacts compared to modern iron at the waterlogged site Nydam, Denmark. Eurocorr 2004:1–12
Doménech-Carbó A, Doménech-Carbó MT, Montagna E, Álvarez-Romero C, Lee Y (2017) Electrochemical discrimination of mints: the last Chinese emperors Kuang Hsü and Hsüan T’ung monetary unification. Talanta 169:50–56
Doménech-Carbó A, Doménech-Carbó MT, Capelo S, Pasíes T, Martínez-Lázaro I (2014) Dating archaeological copper/bronze artifacts by using the voltammetry of microparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed 53(35):9262–9266
Doménech-Carbo A (2017) Electrochemical dating: a review. J Solid State Electrochem 21(7):1987–1998
Doménech-Carbó A, Doménech-Carbó M, Martínez-Lázaro I (2008) Electrochemical identification of bronze corrosion products in archaeological artefacts. A case study. Microchim Acta 162(3-4):351–359
Di Turo F, Montoya N, Piquero-Cilla J et al (2018) Dating archaeological strata in the magna mater temple using solid-state voltammetric analysis of leaded bronze coins. Electroanalysis 30(2):361–370
Ramírez Barat B, Cano E (2018) In situ electrochemical impedance spectroscopy measurements and their interpretation for the diagnostic of metallic cultural heritage: a review. ChemElectroChem 5:2698–2716
Sharer Sahir Z, Sykes JM (2014) Effect of temperature on the impedance response of coated metals. Prog Org Coat 77(12):2039–2044
Amirudin A, DT AA, Thierry D (1995) Application of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy to study the degradation of polymer-coated metals. Prog Org Coat 26(1):1–28
Láng GG, Ujvári M, Bazsó F, Vesztergom S, Ujhelyi F (2012) In situ monitoring of the electrochemical degradation of polymer films on metals using the bending beam method and impedance spectroscopy. Electrochim Acta 73:59–69
Fatkullin AR, Parfenov EV, Yerokhin A, Lazarev DM, Matthews A (2015) Effect of positive and negative pulse voltages on surface properties and equivalent circuit of the plasma electrolytic oxidation process. Surf Coat Technol 284:427–437
Bonora PL, Deflorian F, Fedrizzi L (1996) Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy as a tool for investigating underpaint corrosion. Electrochim Acta 41(7-8):1073–1082
Mora N, Cano E, Polo JL, Puente JM, Bastidas JM (2004) Corrosion protection properties of cerium layers formed on tinplate. Corros Sci 46(3):563–578
Doménech-Carbó A, Doménech-Carbó MT, Peiró-Ronda MA, Martínez-Lázaro I, Barrio-Martín J (2012) Application of the voltammetry of microparticles for dating archaeological lead using polarization curves and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. J Solid State Electrochem 16(7):2349–2356
Doménech-Carbò A, Capelo S, Piquero J et al (2016) Dating archaeological copper using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Comparison with voltammetry of microparticles dating. Mater Corros 67(2):120–129
Doménech-Carbò A, Domènech-Carbò MT, Martìnez-Làzaro I (2010) Layer-by-layer identification of copper alteration products in metallic works of art using the voltammetry of microparticles. Anal Chim Acta 680(1-2):1–9
Doménech-Carbó A, Lastras M, Rodríguez F, Cano E, Piquero-Cilla J, Osete-Cortina L (2014) Monitoring stabilizing procedures of archaeological iron using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. J Solid State Electrochem 18(2):399–409
Dermaj A, Hajjaji N, Joiret S, Rahmouni K, Srhiri A, Takenouti H, Vivier V (2007) Electrochemical and spectroscopic evidences of corrosion inhibition of bronze by a triazole derivative. Electrochim Acta 52(14):4654–4662
Hassairi H, Bousselmi L, Khosrof S (2013) Evaluation of the inhibitive effect of benzotriazole on archeological bronze in acidic medium. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 113(4):923–931
Adriaens A, Dowsett M (2008) Time resolved spectroelectrochemistry studies for protection of heritage metals. Surf Eng 24(2):84–89
Di Turo F, Matricardi P, Di Meo C, Mazzei F, Favero G, Zane D (2018) PVA hydrogel as polymer electrolyte for electrochemical impedance analysis on archaeological metals. J Cult Herit. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.culher.2018.09.017
Di Fazio M, Di Turo F, Medeghini L et al (2019) New insights on medieval Provisini silver coins by a combination of non-destructive and micro-invasive techniques. Microchem J 144:309–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2018.09.016
Sluyters-Rehbach M, Sluyters JH (1979) On the meaning of the impedance concept in the case of an object that varies with time and in the case of a swept F frequency. J Electroanal Chem 102(3):415–419
Popkirov GS, Schindler RN (1993) Validation of experimental data in electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Electrochim Acta 38(7):861–867
Macdonald DD, Sikora E, Engelhardt G (1998) Characterizing electrochemical systems in the frequency domain. Electrochim Acta 43(1-2):87–107
Bastidas JM, Polo JL, Torres CL, Cano E (2001) Study on the stability of AISI 316L stainless steel pitting corrosion through its transfer function. Corros Sci 43(2):269–281
Degrigny C, Guibert G, Ramseyer S, Rapp G, Tarchini A (2010) Use of E corr vs time plots for the qualitative analysis of metallic elements from scientific and technical objects: the SPAMT test project. J Solid State Electrochem 14(3):425–435
Vázquez-Huerta G, Ramos-Sánchez G, Rodríguez-Castellanos A, Meza-Calderón D, Antaño-López R, Solorza-Feria O (2010) Electrochemical analysis of the kinetics and mechanism of the oxygen reduction reaction on Au nanoparticles. J Electroanal Chem 645(1):35–40
Çirmi D, Aydin R, Köleli F (2015) The electrochemical reduction of nitrate ion on polypyrrole coated copper electrode. J Electroanal Chem 736:101–106
Scholz F, Meyer B (1996) Voltammetry of solid microparticles immobilized on electrode surfaces. Electroanal Chem 20:1–82
Scholz F, Schröder U, Gulaboski R, Doménech-Carbó A (2015) Electrochemistry of immobilized particles and droplets, 2nd edn. Springer International Publishing, Berlin-Heidelberg
Doménech-Carbó A, Labuda J, Scholz F (2013) Electroanalytical chemistry for the analysis of solids: characterization and classification (IUPAC technical report)*. Pure Appl Chem 85:609–631
Doménech-Carbó A, Doménech-Carbó MTM, Costa V (2009) Electrochemical methods in archaeometry, conservation and restoration, I. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin
Doménech-Carbó A, Doménech-Carbó MT, Álvarez-Romero C, Montoya N, Pasíes-Oviedo T, Buendía M (2017) Electrochemical characterization of coinage techniques the 17thCentury: the maravedís case. Electroanalysis 29(9):2008–2018
Redondo-Marugán J, Piquero-Cilla J, Doménech-Carbó MT, Ramírez-Barat B, Sekhaneh WA, Capelo S, Doménech-Carbó A (2017) Characterizing archaeological bronze corrosion products intersecting electrochemical impedance measurements with voltammetry of immobilized particles. Electrochim Acta 246:269–279
Rahal C, Masmoudi M, Abdelhedi R, Sabot R, Jeannin M, Bouaziz M, Refait P (2016) Olive leaf extract as natural corrosion inhibitor for pure copper in 0.5 M NaCl solution: a study by voltammetry around OCP. J Electroanal Chem 769:53–61
Grdeń M (2014) Interfacial capacitance of an oxidised copper electrode. J Electroanal Chem 713:47–57
Yi P, Dong C, Xiao K, Man C, Li X (2018) In-situ investigation of the semiconductive properties and protective role of Cu2O layer formed on copper in a borate buffer solution. J Electroanal Chem 809:52–58
Caprioli F, Martinelli A, Di Castro V, Decker F (2013) Effect of various terminal groups on long-term protective properties of aromatic SAMs on copper in acidic environment. J Electroanal Chem 693:86–94
Ribotta SB, La orgia LF, Gassa LM, Folquer ME (2008) Characterization of anodic films formed on copper in 0.1 M borax solution. J Electroanal Chem 624(1-2):262–268
Poljacek SM, Risovic D, Cigula T, Gojo M (2012) Application of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy in characterization of structural changes of printing plates. J Solid State Electrochem 16(3):1077–1089
Xu J, Huang W, McCreery R (1996) NewsReader project. J Electroanal Chem 410(2):235–242
Jang JH, Oh SM (2004) Complex capacitance analysis of porous carbon electrodes for electric double-layer capacitors. J Electrochem Soc 151(4):A571
Chen G, Waraksa C, Cho H et al (2003) EIS studies of porous oxygen electrodes with discrete particles-I. Impedance of oxide catalyst supports. J Electrochem Soc 150:E423–E428
Survila A, Surviliene A, Kanapeckaite S et al (2005) Oxide layers developed on copper electrodes in Cu (II) solutions containing ligands. J Electroanal Chem 582(1-2):221–229
Funding
Project CTQ2017-85317-C2-1-P, which is supported with Ministerio de Economía, Industria y Competitividad (MINECO) and Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional (ERDF) funds, and Agencia Estatal de Investigación (AEI) and PhD grants of the Department of Earth Sciences, Sapienza University of Rome, are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 297 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Di Turo, F., Parra, R., Piquero-Cilla, J. et al. Crossing VIMP and EIS for studying heterogeneous sets of copper/bronze coins. J Solid State Electrochem 23, 771–781 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-018-04182-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-018-04182-5