Abstract
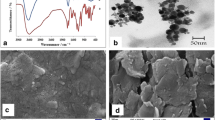
In this paper, we developed an amperometric hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) sensor based on cobalt-containing calcined layered double hydroxide (Co CLDH). The electrocatalytic activity of the Co CLDH towards the determination of H2O2 showed a fast response and high sensitivity. Moreover, the sensor exhibited good reproducibility and long-term stability. The superior electrocatalytic response to H2O2 is mainly attributed to the large surface area, minimized diffusion resistance, and enhanced electron transfer of the synthesized Co CLDH. This method with good analytical performance, low cost, and straightforward preparation made this novel electrode material promising for the determination of trace H2O2 in beverages with high accuracy, demonstrating its potential for practical application.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thome-Duret V, Reach G, Gangnerau MN, Lemonnier F, Klein JC, Zhang Y, Hu Y, Wilson GS (1996) Use of a subcutaneous glucose sensor to detect decreases in glucose concentration prior to observation in blood. Anal Chem 68:3822–3826
You T, Niwa O, Tomita M, Hirono S (2003) Characterization of platinum nanoparticle-embedded carbon film electrode and its detection of hydrogen peroxide. Anal Chem 75:2080–2085
Wang J, Lin Y, Chen L (1993) Organic-phase biosensors for monitoring phenol and hydrogen peroxide in pharmaceutical antibacterial products. Analyst 118:277–280
Ferapontova E, Schmengler K, Börchers T, Ruzgas T, Gorton L (2002) Effect of cysteine mutations on direct electron transfer of horseradish peroxidase on gold. Biosens Bioelectron 17:953–963
Kaushik A, Khan R, Solanki PR, Pandey P, Alam J, Ahmad S, Malhotra BD (2008) Iron oxide nanoparticles—chitosan composite based glucose biosensor. Biosens Bioelectro 24:676–683
Yuan JH, Wang K, Xia XH (2005) Highly ordered platinum-nanotubule arrays for amperometric glucose sensing. Adv Funct Mater 15:803–809
Davis J, Moorcroft MJ, Wilkins SJ, Compton RG, Cardosi MF (2000) Electrochemical detection of nitrate and nitrite at a copper modified electrode. Analyst 125:737–741
Sljukic B, Banks CE, Compton RG (2006) Iron oxide particles are the active sites for hydrogen peroxide sensing at multiwalled carbon nanotube modified electrodes. Nano Lett 6:1556–1558
Dai ZH, Liu SH, Bao JC, Ju HX (2009) Nanostructured FeS as a mimic peroxidase for biocatalysis and biosensing. Chem Eur J 15:4321–4326
Li CL, Su Y, Zhang SW, Lv XY, Xia HL, Wang YJ (2010) An improved sensitivity nonenzymatic glucose biosensor based on a Cu x O modified electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 26:903–907
Shan D, Cosnier S, Mousty C (2003) Layered double hydroxides: an attractive material for electrochemical biosensor design. Anal Chem 75:3872–3879
Carpani I, Berrettoni M, Ballarin B, Giorgetti M, Scavetta E, Tonelli D (2004) Study on the intercalation of hexacyanoferrate(II) in a Ni, Al based hydrotalcite. Solid State Ionics 168:167–175
Terry PA (2004) Characterization of Cr ion exchange with hydrotalcite. Chemosphere 57:541–546
Scavetta E, Ballarin B, Gazzano M, Tonelli D, Duan X (2009) Electrochemical behaviour of thin films of Co/Al layered double hydroxide prepared by electrodeposition. Electrochim Acta 54:1027–1033
Shao MF, Han JB, Shi WY, Wei M (2010) Layer-by-layer assembly of porphyrin/layered double hydroxide ultrathin film and its electrocatalytic behavior for H2O2. Electrochem Commun 12:1077–1080
Kong XG, Zhao JW, Han JB, Zhang DY, Wei M, Duan X (2011) Fabrication of Naphthol green B/layered double hydroxide nanosheets ultrathin film and its application in electrocatalysis. Electrochim Acta 26:1123–1129
Cavani F, Trifiro F, Vaccari A (1991) Hydrotalcite-type anionic clays: preparation, properties and applications. Catal Today 11:173–301
Vaccari A (1998) Preparation and catalytic properties of cationic and anionic clays. Catal Today 41:53–71
Bellotto M, Rebours B, Clause O, Lynch J, Bazin D, Elkaïm E (1996) A Reexamination of Hydrotalcite Crystal Chemistry. J Phys Chem 100:8527–8534
Bellotto M, Rebours B, Clause O, Lynch J, Bazin D, Elkaïm E (1996) Hydrotalcite Decomposition Mechanism: A Clue to the Structure and Reactivity of Spinel-like Mixed Oxides. J Phys Chem 100:8535–8542
Cantú M, López-Salinas E, Valente JS, Montiel R (2005) SO x removal by calcined MgAlFe hydrotalcite-like materials: effect of the chemical composition and the cerium incorporation method. Environ Sci Technol 39:9715–9720
Cui L, Yin HS, Dong J, Fan H, Liu T, Ju P, Ai SY (2010) A mimic peroxidase biosensor based on calcined layered double hydroxide for detection of H2O2. Biosens Bioelectron 26:3278–3283
Kannan S, Swamy CS (1999) Catalytic decomposition of nitrous oxide over calcined cobalt aluminum hydrotalcites. Catal Today 53:725–737
Pérez-Ramírez J, Kapteijn F, Moulijn JA (1999) High activity and stability of the Rh-free Co-based ex-hydrotalcite containing Pd in the catalytic decomposition of N2O. Catal Lett 60:133–138
Chmielarz L, Kuśtrowski P, Rafalska-Łasocha A, Majda D, Dziembaj R (2002) Catalytic activity of Co–Mg–Al, Cu–Mg–Al and Cu–Co–Mg–Al mixed oxides derived from hydrotalcites in SCR of NO with ammonia. Appl Catal B: Environmental 35:195–210
Gennequin C, Kouassi S, Tidahy L, Cousin R, Lamonier JF, Garcon G, Shirali P, Cazier F, Aboukaïs A, Siffert S (2010) Co–Mg–Al oxides issued of hydrotalcite precursors for total oxidation of volatile organic compounds. Identification and toxicological impact of the by-products. C R Chimie 13:494–501
Tichit D, Bennani MN, Figueras F, Ruiz JR (1998) Decomposition processes and characterization of the surface basicity of Cl− and CO 2−3 hydrotalcites. Langmuir 14:2086–2091
Zhang L, Dong SJ (2004) The electrocatalytic oxidation of ascorbic acid on polyaniline film synthesized in the presence of camphorsulfonic acid. J Electroanal Chem 568:189–194
Andriex CP, Saveant JM (1978) Heterogeneous (chemically modified electrodes, polymer electrodes) vs. homogeneous catalysis of electrochemical reactions. J Electroanal Chem 93:163–168
Laviron E (1974) Adsorption, autoinhibition and autocatalysis in polarography and in linear potential sweep voltammetry. J Electroanal Chem 52:355–393
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 201075078) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (ZR2010BM05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jun Wang and Lin Cui equally contributed to this work.
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10008-011-1599-x.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Cui, L., Yin, H. et al. Determination of hydrogen peroxide based on calcined layered double hydroxide-modified glassy carbon electrode in flavored beverages. J Solid State Electrochem 16, 1545–1550 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-011-1551-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-011-1551-0