Abstract
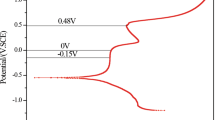
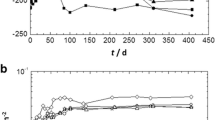
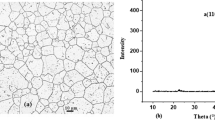
The passivation of two high strength duplex stainless steels (HSSS) was investigated in alkaline solutions simulating the pore solution of concrete by the growth of natural and induced passive films. Induced passive films were generated both by cyclic voltammetry and by chronoamperometry. Natural passive films were spontaneously grown by the immersion of the steel in the alkaline electrolyte. These passive layers were characterised by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, corrosion current density (i corr) and corrosion potential (E corr) monitoring. The effect of significant parameters, such as the pH in the HSSS/alkaline solution interface, the composition of the duplex stainless steels and the ageing of the passive layer, on the electrochemical performance of both induced and spontaneously grown passive films has been analysed. The increase of alkalinity highly influences the electrochemical performance of the passive film by promoting the formation of a passive layer with a less resistant electrochemical response. The electrochemical behaviour of the passive layer is also affected by the alloying elements like Mo or Ni. Both natural and induced passive films show similar electrochemical trend with respect to significant parameters such as the pH and the composition of the steel. The ageing of the spontaneously grown passive layer promotes a higher resistive electrochemical response which might be related to the enrichment of the passive layer in non-conducting (or semi-conducting) oxides.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Elsener B, DeFilippo D, Rossi A (1994) Modifications of passive films. In: Marcus P, Baroux B, Keddam M (eds.) EFC publ. No 12, The Institute of Materials, London, pp 6–11
Elsener B, Rossi A (1995) Mater Sci Forum 192–194:225–236
Freire L, Carmezim MJ, Ferreira MGS, Montemor MF (2010) Electrochim Acta 55:6174–6181
Bastidas JM, Torres CL, Cano E, Polo JL (2002) Corros Sci 44:625–633
Montemor MF, Simoes AM, Ferreira MGS, Da Cunha Belo M (1999) Corros Sci 41:17–34
Lee JB, Kim SW (2007) Mater Chem Phys 104:98–104
Kocijan A, Donik C, Jenko M (2007) Corros Sci 49:2083–2098
Lu YC, Clayton CR, Brooks R (1989) Corros Sci 29:863–880
Clayton CR, Lu YC (1986) J Electrochem Soc 133:2465–2473
Brooks AR, Clayton CR, Doss K, Lu YC (1986) J Electrochem Soc 133:2459–2464
Schmuki P, Böhni H (1992) J Electrochem Soc 139:1908–1913
Szklarska-Smialowska Z (2002) Corros Sci 44:1143–1149
Ameer MA, Fekry AM, El-Taib Heakal F (2004) Electrochim Acta 50:43–49
Boucherit N, Hugot-le Goff A, Joiret S (1992) Corrosion 48:569–579
Vignal V, Olive JM, Desjardins D (1999) Corros Sci 41:869–884
Tobler WJ, Virtanen S (2006) Corros Sci 48:1585–1607
Pardo A, Merino MC, Coy AE, Viejo F, Arrabal R, Matykina E (2008) Corros Sci 50:780–794
Ilevbare GO, Burstein GT (2001) Corros Sci 43:485–513
Castro-Borges P, de Rincón OT, Moreno EI, Torres-Acosta AA, Martínez-Madrid M, Knudsen A (2002) Mater Perform 41:50–55
Knudsen A, Jensen FM, Klinghoffer O, Skovsgaard T (1998) Cost-effective enhancement of durability of concrete structures by intelligent use of stainless steel reinforcement. In: Conference on Corrosion and rehabilitation of reinforced concrete structures, Florida, December 8–11
Klingghoffer O, Forlung T, Kofoad B, Knudsen A, Jensen FM, Skovsgaard T (2000) Practical and economical aspects of application of austenitic stainless steel , AISI 316, as reinforcement in concrete. In: Mietz J, Polder R, Elsener B (eds.) Corrosion of reinforcement in concrete, European Federation of corrosion, IOM Communications , London, pp 121–133
Abreu CM, Cristóbal MJ, Losada R, Nóvoa XR, Pena G, Pérez MC (2004) Electrochim Acta 49:3049–3056
Abreu CM, Cristóbal MJ, Losada R, Nóvoa XR, Pena G, Pérez MC (2006) Electrochim Acta 51:1881–1890
Abreu CM, Cristóbal MJ, Losada R, Nóvoa XR, Pena G, Pérez MC (2004) J Electroanal Chem 572:335–345
Bautista A, Blanco G, Velasco F, Gutiérrez A, Soriano L, Palomares FJ, Takenouti H (2009) Corros Sci 51:785–792
Addari D, Elsener B, Rossi A (2008) Electrochim Acta 53:8078–8086
Freire L, Carmezim MJ, Ferreira MGS, Montemor MF (2011) Electrochim Acta. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2011.02.094
Sánchez M, Gregori J, Alonso C, García-Jareño JJ, Takenouti H, Vicente F (2007) Electrochim Acta 52:7634–7641
Nürnberger U, Wu Y (2008) Mater Corros 59:144–158
Wu Y, Nürnberger U (2009) Mater Corros 60:1–10
Rajan TV, Sharma CP, Sharma A (2006) Heat treatment-Principales and techniques Revised Edition, ISBE-81-203-0716-X. Prentice-Hall of Indian Private Limited, New Delhi, pp 48–51
Stern M, Geary AL (1957) J Electrochem Soc 104:56–63
Poorqasemi E, Abootalebi O, Peikari M, Haqdar F (2009) Corros Sci 51:1043–1054
Pourbaix M (1968) Atlas of Electrochemical Equilibrium in Aqueous Solution. Pergamon Press, Oxford
Kim JD, Pyun SI (1995) Electrochim Acta 40:1863–1869
Abreu CM, Cristóbal MJ, Losada R, Nóvoa XR, Pena G, Pérez MC (2008) Electrochim Acta 53:6000–6007
Abreu CM, Cristóbal MJ, Nóvoa XR, Pena G, Pérez MC, Rodriguez RJ (2002) Surf Coatings Tech 158–159:582–587
Kim JD, Pyun SI (1996) Corros Sci 38:1093–1102
Acknowledgements
Authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from Spanish MICINN for the financial support given to this research in BIA2007-65394 project and also for the FPI given to H. Mahmoud. M. Sánchez acknowledges to Spanish Ministry of Education her post-doctoral position. The authors also acknowledge to INOXFIL for supplying of the HSSS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sánchez, M., Mahmoud, H. & Alonso, M.C. Electrochemical response of natural and induced passivation of high strength duplex stainless steels in alkaline media. J Solid State Electrochem 16, 1193–1202 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-011-1498-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-011-1498-1