Abstract
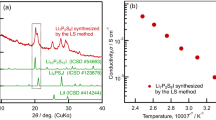
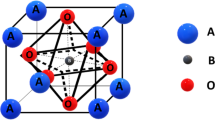
The aim of this work was to study the electrical and electrochemical properties of the (Ba1 − x Ca x )(Zr0.9Y0.1)O3 solid solutions. The powders of different calcium content (x = 0, 0.05, 0.1, and 1) were prepared by a thermal decomposition of organo-metallic precursors containing ethylenediaminetetraacetate acid. X-ray diffraction analysis showed that a small substitution of calcium for barium caused formation of cubic solid solutions with the decreasing cell parameters. Electrical conductivity measurements were performed by the d.c. four-probe method in controlled gas atmospheres containing Ar, air, H2, and/or H2O at temperature from 300 to 800 °C. It was found that the conductivity depended on a chemical composition of the samples and the atmosphere. Overall, the electrical conductivity was higher in wet atmospheres that contained oxygen that was in accordance with the model of a proton transport in perovskite structure which assumed the presence of the oxygen vacancies. The solid solution containing 5 mol% of calcium showed the highest conductivity and the lowest activation energy of conductivity regardless of the atmospheres; this can be attributed to the local changes in the cubic perovskite structure. Test results for CaZr0.9Y0.1O3 used as an electrolyte in solid oxide galvanic cells involving CaCr2O4 as a reference electrode are also reported.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iwahara H, Esaka T, Uchida H, Maeda N (1981) Solid State Ion 3–4:359 doi:10.1016/0167-2738(81)90113-2
Davies RA, Islam MS, Chadwick AV, Rush GE (2000) Solid State Ion 130:115 doi:10.1016/S0167-2738(00)00573-7
Iwahara H, Uchida H, Ono K, Ogaki K (1988) J Electrochem Soc 135:529 doi:10.1149/1.2095649
Kokkofitis C, Ouzounidou M, Skodra A, Stoukides M (2008) Solid State Ion 178:475 doi:10.1016/j.ssi.2007.01.002
Stuart P, Unno T, Kilner JA, Skinner SJ (2008) Solid State Ion 179:1120 doi:10.1016/j.ssi.2008.01.067
Schober T (2003) Solid State Ion 162–163:277 doi:10.1016/S0167-2738(03)00241-8
Shiumura T, Esaka K, Matsumoto H (2002) Solid State Ion 149:237 doi:10.1016/S0167-2738(02)00400-9
Kurita N, Fukatsu N, Miyamoto S, Sato F, Nakai H, Ire K, Ohashi T (1996) Metall Mater Trans 27B:929
Yamija T, Kazeoka H, Yogo T, Iwahara H (1991) Solid State Ion 47:271 doi:10.1016/0167-2738(91)90249-B
Janke D (1982) Metall Trans 13B:227
Dudek M, Bućko MM (2003) Solid State Ion 157:183 doi:10.1016/S0167-2738(02)00207-2
Dudek M, Róg G, Bogusz W, Kozłowska-Róg A, Bućko MM, Zych Z (2006) Mater Sci Pol 24:253
Fergus J (2006) J Power Sources 162:30 doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2006.06.062
Haile S (2003) Mater Today 3:24 doi:10.1016/S1369-7021(03)00331-6
Katahira K, Kokchi Y, Shimura T, Iwahara H (2008) Solid State Ion 138:91 doi:10.1016/S0167-2738(00)00777-3
Ryu K, Haile S (1999) Solid State Ion 125:355 doi:10.1016/S0167-2738(99)00196-4
Bhide SV, Virkar AV (1999) J Electrochem Soc 146:2038 doi:10.1149/1.1391888
Li J, Luo J, Chuang K, Sanger A (2008) Electrochim Acta 53:3701 doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2007.12.020
Fang S, Bi L, Wu X, Gao H, Chen C (2008) J Power Sources 183:126 doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2008.05.015
Fabbri E, Epifanio AD, Bartolomeo ED, Licoccia S, Traversa E (2008) Solid State Ion 179:558 doi:10.1016/j.ssi.2008.04.002
Ding H, Lin B, Liu X, Meng G (2008) Electrochem Commun 10:1388 doi:10.1016/j.elecom.2008.07.016
Norby T (1999) Solid State Ion 125:1 doi:10.1016/S0167-2738(99)00152-6
Matsushita E, Sasaki T (1999) Solid State Ion 125:31 doi:10.1016/S0167-2738(99)00155-1
Kreuer K (1999) Solid State Ion 125:285 doi:10.1016/S0167-2738(99)00188-5
Kobayashi K, Yamaguchi S, Iguchi Y (1998) Solid State Ion 108:355 doi:10.1016/S0167-2738(98)00063-0
Kiukola K, Wagner C (1957) J Electrochem Soc 104:379 doi:10.1149/1.2428586
Weyl A, Wei S, Janke D (1994) Steel Res 65:167
Schober T, Bohn HG (2000) Solid State Ion 127:351 doi:10.1016/S0167-2738(99)00283-0
Kurita N, Fukatsu N, Ito K, Ohashi T (1995) J Electrochem Soc 142:1553 doi:10.1149/1.2048611
Patterson J, Bogern E, Rapp R (1967) J Electrochem Soc 114:752 doi:10.1149/1.2426723
Nowick AS, Du Y, Liang K (1999) Solid State Ion 125:303 doi:10.1016/S0167-2738(99)00189-7
Sata N, Yugami H, Akiyama Y, Sone H, Kitamura N, Hattori T, Ishigame M (1999) Solid State Ion 125:383 doi:10.1016/S0167-2738(99)00199-X
Novick AS (1989) Superionic solids and solid electrolytes. Academic, New York
Janke D (1983) Arch Eissenhuttenwes 54:259
Jacob KT, Kale GM, Abraham KP (1992) J Electrochem Soc 139:517 doi:10.1149/1.2069248
Acknowledgment
This work was carried out under contract no. T08D 051 280 with the Polish Ministry of Science and High Education.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Contribution to the Fifth Baltic Conference on Electrochemistry, 30 April - 3 May 2008, Tartu, Estonia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dudek, M., Bućko, M.M. Ceramic electrolytes based on (Ba1 − x Ca x )(Zr0.9Y0.1)O3 solid solution. J Solid State Electrochem 14, 565–570 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-008-0706-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-008-0706-0