Abstract
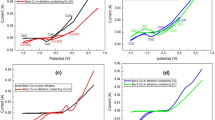
Zinc–cobalt (Zn–Co) and zinc–nickel (Zn–Ni) alloy electrodeposits each prepared from acid and alkaline formulations were compared for their properties. Compared to alkaline baths, acid baths offer higher metal percent of the alloying element and higher current efficiency. In alkaline baths, the variation of metal percent in deposit with current density is less significant, but that of current efficiency with current density is more. Electrolyte pH does not change significantly in alkaline solutions compared to acid solutions. X-ray diffraction evaluation of Zn–Co deposits from both electrolytes indicated their presence in the η-phase, while Zn–Ni shows pure γ-phase for deposits obtained from alkaline solutions and the existence of γ-phase with traces of η-phase of zinc for deposits obtained from the acid electrolytes. Scanning electron microscope examination shows finer grain structure for deposits obtained from alkaline solutions, and atomic force microscope studies confirm their nanostructure with reduced surface roughness. Deposits obtained from the alkaline baths exhibited higher corrosion resistance probably due to their nanostructure.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carpenter EOS, Farr JPG (1998) Trans Inst Met Finish 76:135
Tsuru T, Kobayshi S, Akiyama T, Fukushima H, Gogia SK, Kammel RJ (1997) J Appl Electrochem 27:209
Brenner A (1963) Electrodeposition of alloys—principles and practice, vol 1. Academic, New York
Short NR, Dennis JK, Zhou S (1996) Surf Coat Technol 79:218
Gabe DR, Green WA (1998) Surf Coat Technol 105:195
Kalantary MR (1994) Plat Surf Finish 81:80
Wilcox GD, Gabe DR (1994) Proceedings of Asian-Pacific Interfinish, Melbourne-2, Australian IMF, 50.1
Crotty D, Griffin R (1997) Plat Surf Finish 84:57
Short NR, Dennis JK (1997) Trans Inst Met Finish 75:47
Roper ME, O’ Grady J (1996) Trans Inst Met Finish 74:3
Verberne WMJC (1986) Trans Inst Met Finish 64:30
Tu ZM, Yang ZL, An MZ, Li WL, Zhang JS (1999) Trans Inst Met Finish 77:246
Loar GW (1991) Plat Surf Finish 78:74
Fratesi R, Roventi G, Giuliani G, Tomachuck CR (1997) J Appl Electrochem 27:1088
Gomez E, Valles E (1997) J Electroanal Chem 421:157
Kalantary MR, Wilcox GD, Gabe DR (1995) Electrochim Acta 40:1609
Nabil Z (1999) Product Finish 6:53
Baldwin KR, Smith CJE (1996) Trans Inst Metal Finish 74:202
Rajendran S, Bharathi S, Krishna C, Vasudevan T (1997) Plat Surf Finish 84:53
Carpenter DEOS, Farr JPG (2005) Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Advanced Materials. Kahuta Research Laboratory, Lahore, Abstracts 101
Yan H, Downes J, Boden PJ, Harris SJ (1996) J Electrochem Soc 143:1577
Carpenter DEOS, Carpenter SD, Farr JPG (2000) Trans Inst Metal Finish 78:152
Wilcox GD, Mitchell PJ (1987) Trans Inst Metal Finish 65:75
Gircine O, Ramanauskas P, Castro P, Bertolo-Perez P (2001) Trans Inst Metal Finish 79:199
Roland P, Gernot S (1996) Trans Inst Metal Finish 74:158
Pech-Canul MA, Ramanauskas R, Maldonado L (1997) Electrochim Acta 42:255
Tu ZM, Zhang JS, Li WL, Yang ZL, An MZ (1995) Trans Inst Metal Finish 73:48
Michael M (1996) PhD thesis, Madurai Kamaraj University, Tamil Nadu, India
Pushpavanam M, Natarajan SR, Balakrishnan K, Sharma LR (1991) J Appl Electrochem 19:642
Pushpavanam M, Raman V, Jayakrishnan S, Shenoy BA (1983) Metal Finish 81:85
Pushpavanam M, Balakrishnan K (1995) J Appl Electrochem 25:283
Pushpavanam M, Balakrishnan K (1996) J Appl Electrochem 26:1065
Pushpavanam M, Balakrishnan K (1996) Trans Inst Metal Finish 74:33
Siluvai MM, Pushpavanam M, Balakrishnan K (1995) Br Corros J 30:317
Siluvai MM, Pushpavanam M (2004) Trans Inst Metal Finish 82:57
Shanmugasigamani, Pushpavanam M (2006) Trans Inst Metal Finish 84:326
Shanmugasigamani, Pushpavanam M (2008) Trans Inst Metal Finish 86:122
Dahms H, Croll J (1965) J Electrochem Soc 112:771
Shanmugasigamani, Pushpavanam M (2005) J Appl Electrochem 36:315
Beltowska-Lehman E, Ozga P, Swiatek Z, Lupi C (2002) Cryst Eng 5:335
Gavrila M, Millet JP, Mazille H, Marchandise D, Cuntz JM (2000) Surf Coat Technol 123:164
Muller C, Sarret M, Benballa M (2002) J Electroanal Chem 519:85
Ramanauskas R, Gudaviciute L, Kalinicenko A, Juskenas R (2005) J Solid State Electrochem 9:900
Lee HY, Kim SG (2000) Surf Coat Technol 135:69
Hall DE (1983) Plat Surf Finish 70:59
Ramanauskas R (1999) Appl Surf Sci 153:53
Acknowledgment
The authors wish to express their sincere thanks to the Director, CECRI for the encouragement given and permission to publish this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
M. S., C., Srinivasan, S. & Pushpavanam, M. Properties of Zinc alloy electrodeposits produced from acid and alkaline electrolytes. J Solid State Electrochem 13, 781–789 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-008-0607-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-008-0607-2