Abstract
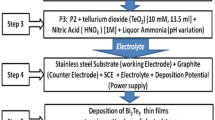
The electrolyses of solutions of bismuth oxide and tellurium oxide in nitric acid with molar ratios of Bi:Te=3:3–4:3 lead to cathodic deposits of films of bismuth telluride (Bi2Te3), an n-type semiconductor. Current densities of 2–5 mA/cm2 were applied. Voltammetric investigations showed that Bi2Te3 deposition occurred at potentials more negative than −0.125 V (Ag/AgCl, 3 M KCl). The deposit was identified as bismuth telluride (γ-phase) by X-ray analysis. Hall-effect measurements verified the n-type semiconducting behaviour. The films can be deposited in microstructures for thermoelectric microdevices like thermoelectric batteries or thermoelectric sensors.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Plötner M (1998) Thermobatterie mit galvanisch abgeschiedenen Schenkeln. Abschlussbericht, TU Dresden
Qu W, Plötner M, Fischer W-J (2001) J Micromech Microeng 11:146
Okamoto H, Tanner LE (1986) In: Massalski TB (ed) Bi-Te (bismuth-tellurium) binary alloy phase diagrams. American Society for Metals, Metals Park, Ohio
Gmelin (1964) Handbuch der anorganischen Chemie. Bismut Ergänzungsband. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, p 800
Magri P, Boulanger C (1995) AIP Conf Proc 316:277
Magri P, Boulanger C, Lecuire JM (1996) J Mater Chem 6:773
Fleurial J-P, Herman J-A, Snyder G-J, Ryan MA, Borshchevsky A, Huang C-K (2000) Mater Res Soc Symp 626:Z11.3.1
Montiel-Santillán T, Solorza O, Sánches H (2002) J Solid State Electrochem 6:433
Cheaouni H, Bessieres J, Modaressi A, Heizmann JJ (2000) J Appl Electrochem 30:419
Lenher V, Wakefield HF (1923) J Am Chem Soc 45:1423
Lang R, Faude E (1937) Z Anal Chem 108:260
Maclachlan JM, Kruesi WH, Fray DJ (1992) J Mater Sci 00:000
Fischer H (1954) Elektrolytische Abscheidung und Elektrokristallisation von Metallen. Springer, Berlin Göttingen Heidelberg, p 485
Budevski E, Staikov G, Lorenz WJ (1996) Electrochemical phase formation and growth. VCH, Weinheim, p 71
Mamantov G, Manning DL, Dale JM (1965) J Electroanal Chem 9:253
Berzins T, Delahay P (1953) J Am Chem Soc 75:555
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the BMWi (Bundesministerium für Wirtschaft) and the AiF (Arbeitsgemeinschaft industrieller Forschungsvereinigungen "Otto von Guericke" e.V.), research no. 12118 BR. The authors are grateful to Dr. B. Hahne (Institute of Chemical Technology and Polymer Chemistry of the Martin-Luther-University Halle, Germany) and Dr. O. Rademacher (Institut of Inorganic Chemistry of the Technical University Dresden, Germany) for performing the X-ray diffraction measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tittes, K., Bund, A., Plieth, W. et al. Electrochemical deposition of Bi2Te3 for thermoelectric microdevices. J Solid State Electrochem 7, 714–723 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-003-0378-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-003-0378-8