Abstract
Purpose
This systematic review aimed to determine whether differences in the macro-geometry of titanium implants promote changes in osseointegration.
Material and method
SCOPUS, PubMed/Medline, Web of Science, and EMBASE databases were searched in June 2021. In addition, it was performed a manual search of the reference lists of the included articles. Eligibility criteria were in vivo studies that addressed the effect of titanium implant macro-geometry on osseointegration, studies that evaluated periodontally healthy models, and papers indexed in Journal Citation Reports.
Results
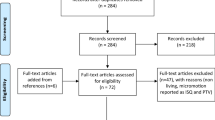
The database search resulted in 1037 articles. Of the 19 articles selected for full reading, 16 remained in this systematic review. These had a high heterogeneity making it hard to perform statistical analysis of the data, so a descriptive analysis was performed.
Conclusions
Based on the studies included in this systematic review, implant macro-geometry provides influences on osseointegration. In this sense, the various isolated characteristics (thread type, thread pitch, thread depth, face angle) should be studied so that the implant geometry can balance the compressive stress and tensile stress and produce a minimum shear force.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Valente ML, de Castro DT, Shimano AC, Lepri CP, dos Reis AC (2016) Analyzing the influence of a new dental implant design on primary stability. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 18:168–173. https://doi.org/10.1111/cid.12324
Valente ML, Castro DT, Shimano AC, Reis AC (2019) Influence of an alternative implant design and surgical protocol on primary stability. Braz Dent J 30:47–51. https://doi.org/10.1590/0103-6440201902324
Silva GA, Faot F, da Rosa Possebon AP, da Silva WJ, Cury AA (2021) Effect of macrogeometry and bone type on insertion torque, primary stability, surface topography damage and titanium release of dental implants during surgical insertion into artificial bone. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 119:104515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2021.104515
Eskan MA, Uzel G, Yilmaz S (2020) A fixed reconstruction of fully edentulous patients with immediate function using an apically tapered implant design: a retrospective clinical study. Int J Implant Dent 6:1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40729-020-00271-1
Herrero-Climent M, Lemos BF, Herrero-Climent F, Falcao C, Oliveira H, Herrera M, Gil FJ, Ríos-Carrasco B, Ríos-Santos JV (2020) Influence of implant design and under-preparation of the implant site on implant primary stability. An in vitro study. International J Environ Public Health 17:4436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124436
Lozano-Carrascal N, Salomó-Coll O, Gilabert-Cerdà M, Farré-Pagés N, Gargallo-Albiol J, Hernández-Alfaro F (2016) Effect of implant macro-design on primary stability: a prospective clinical study. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 21:e214. https://doi.org/10.4317/medoral.21024
Fanali S, Tumedei M, Pignatelli P, Petrini M, Piattelli A, Iezzi G (2021) The effect of threads geometry on insertion torque (IT) and periotest implant primary stability: a high-density polyurethane simulation for the anterior mandible. Curr Comput-Aided Drug Des 11:308. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11030308
Tardelli JD, da Costa Valente ML, Macedo AP, dos Reis AC (2022) Evaluation of biomechanical and stress distribution of different dental implant designs: primary stability and photoelastic analysis. IRBM 43:100–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.irbm.2021.01.003
Cochran D, Stavropoulos A, Obrecht M, Pippenger B, Dard M (2016) A comparison of tapered and nontapered implants in the minipig. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 31:1341–1347. https://doi.org/10.11607/jomi.4712
Tumedei M, Petrini M, Pietropaoli D, Cipollina A, La Torre C, Di Carmine MS, Piattelli A, Iezzi G (2021) The influence of the implant macrogeometry on insertion torque, removal torque, and periotest implant primary stability: A mechanical simulation on high-density artificial bone. Symmetry 13:776. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13050776
Soto-Peñaloza D, Caneva M, Viña-Almunia J, Martin-de-Llano JJ, García-Mira B, Peñarrocha-Oltra D, Botticelli D, Peñarrocha-Diago M (2019) Effect on osseointegration of two implant macro-designs: a histomorphometric analysis of bicortically installed implants in different topographic sites of rabbit’s tibiae. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 24:e502. https://doi.org/10.4317/medoral.22825
Chien SK, Hsue SS, Lin CS, Kuo TF, Wang DJ, Yang JC, Lee SY (2017) Influence of thread design on dental implant osseointegration assayed using the Lan-Yu mini-pig model. J Med Biol Eng 37:627–638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40846-017-0240-6
Vandamme K, Naert I, Geris L, Sloten JV, Puers R, Duyck J (2007) Influence of controlled immediate loading and implant design on peri-implant bone formation. J Clin Periodontol 34:172–181. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-051X.2006.01014.x
Dayan C, Geckili O, Bural C (2019) The influence of implant shape on primary stability of implants with a thread cutting and forming design: an ex vivo study. J Oral Implantol 45:181–185. https://doi.org/10.1563/aaid-joi-D-18-00158
Orsini E, Giavaresi G, Trirè A, Ottani V, Salgarello S (2012) Dental implant thread pitch and its influence on the osseointegration process: an in vivo comparison study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 27:383–392
Cardoso MV, Vandamme K, Chaudhari A, De Rycker J, Van Meerbeek B, Naert I, Duyck J (2015) Dental implant macro-design features can impact the dynamics of osseointegration. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 17:639–645. https://doi.org/10.1111/cid.12178
Almas K, Smith S, Kutkut A (2019) What is the best micro and macro dental implant topography? Dental Clinics 63:447–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cden.2019.02.010
Manikyamba YJ, Sajjan S, AV RR, Rao B, Nair CK (2018) Implant thread designs: an overview. Trends Prosthodont Dent Implantol 8:11–20
Muktadar AK, Gangaiah M, Chrcanovic BR, Chowdhary R (2018) Evaluation of the effect of self-cutting and nonself-cutting thread designed implant with different thread depth on variable insertion torques: an histomorphometric analysis in rabbits. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 20:507–514. https://doi.org/10.1111/cid.12611
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altamann DG (2009) PRISMA Group: methods of systematic reviews and meta-analysis: preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. J Clin Epidemiol 62:1006–1012. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JPA, Clark M, Devereaux PJ, Kleijnen J, Moher D (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. Ann Intern Med 151:W-65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2009.06.006
-Tufanaru C, Munn Z, Aromataris E, Campbell J, Hopp L (2020) Chapter 3: Systematic reviews of effectiveness. In: JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis.
Zonfrillo G, Matteoli S, Ciabattini A, Dolfi M, Lorenzini L, Corvi A (2014) Analysis and comparison of clutch techniques of two dental implants. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 34:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2014.01.017
Hong JY, Ko SY, Lee W, Chang YY, Kim SH, Yun JH (2020) Enhancement of bone ingrowth into a porous titanium structure to improve osseointegration of dental implants: a pilot study in the canine model. Materials 13:3061
Steigenga J, Al-Shammari K, Misch C, Nociti FH Jr, Wang HL (2004) Effects of implant thread geometry on percentage of osseointegration and resistance to reverse torque in the tibia of rabbits. J Periodontol 75:1233–1241. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2004.75.9.1233
Gehrke SA, Marin GW (2015) Biomechanical evaluation of dental implants with three different designs: removal torque and resonance frequency analysis in rabbits. Annals of Anatomy-Anatomischer Anzeiger 199:30–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aanat.2014.07.009
Jimbo R, Tovar N, Anchieta RB, Machado LS, Marin C, Teixeira HS, Coelho PG (2014) The combined effects of undersized drilling and implant macrogeometry on bone healing around dental implants: an experimental study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 43:1269–1275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2014.03.017
Calvo-Guirado JL, Gomez Moreno G, Aguilar-Salvatierra A, Sanchez M, de Val JE, Abboud M, Nemcovsky CE (2015) Bone remodeling at implants with different configurations and placed immediately at different depth into extraction sockets. Experimental study in dogs. Clin Oral Implants Res 26:507–515. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.12433
Trisi P, Berardini M, Falco A, Vulpiani MP (2015) Effect of implant thread geometry on secondary stability, bone density, and bone-to-implant contact: a biomechanical and histological analysis. Implant Dent 24:384–391. https://doi.org/10.1097/ID.0000000000000269
Abrahamsson I, Berglundh T (2006) Tissue characteristics at microthreaded implants: an experimental study in dogs. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 8:107–113. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1708-8208.2006.00016.x
Chowdhary R, Jimbo R, Thomsen C, Carlsson L, Wennerberg A (2013) Biomechanical evaluation of macro and micro designed screw-type implants: an insertion torque and removal torque study in rabbits. Clin Oral Implants Res 24:342–346. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2011.02336.x
Chowdhary R, Jimbo R, Thomsen CS, Carlsson L, Wennerberg A (2013) The osseointegration stimulatory effect of macrogeometry-modified implants: a study in the rabbit. Clin Oral Implants Res 25:1051–1055. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.12212
Patel A, Gil LF, Castellano A, Freitas G, Navarro D, Peredo AP, Tovar N, Coelho P (2016) Effect of simplified one-step drilling protocol on osseointegration. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 36:e82–e87. https://doi.org/10.11607/prd.2755
Jimbo R, Tovar N, Marin C, Teixeira HS, Anchieta RB, Silveira LM, Janal MN, Shibli JA, Coelho PG (2014) The impact of a modified cutting flute implant design on osseointegration. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 43:883–888. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2014.01.016
Gehrke SA, Júnior JA, Treichel TL, do Prado TD, Dedavid BA, de Aza PN (2022) Effects of insertion torque values on the marginal bone loss of dental implants installed in sheep mandibles. Sci Rep 12:1–3. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-04313-5
Rocci A, Calcaterra R, Di Girolamo M, Rocci M, Rocci C, Baggi L (2015) The influence of micro and macro-geometry in term of bone-implant interface in two implant systems an histomorphometrical study. Oral Implantol 8:87. https://doi.org/10.11138/orl/2015.8.4.087
Al-Sabbagh M, Eldomiaty W, Khabbaz Y (2019) Can osseointegration be achieved without primary stability? Dental Clinics 63:461–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cden.2019.02.001
Comuzzi L, Tumedei M, De Angelis F, Lorusso F, Piattelli A, Iezzi G (2021) Influence of the dental implant macrogeometry and threads design on primary stability: an in vitro simulation on artificial bone blocks. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin 24:1242–1250. https://doi.org/10.1080/10255842.2021.1875219
Niroomand MR, Arabbeiki M (2019) Statistical analysis of implant and thread parameters effects on dental implant stability and bone resorption using central composite design method. Proc Inst Mech Eng H 233:1299–1309. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954411919881250
Lemos CA, Verri FR, de Oliveira Neto OB, Cruz RS, Gomes JM, da Silva Casado BG, Pellizzer EP (2021) Clinical effect of the high insertion torque on dental implants: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Prosthet Dent 126:490–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prosdent.2020.06.012
Norton MR (2017) The influence of low insertion torque on primary stability, implant survival, and maintenance of marginal bone levels a closed-cohort prospective study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 32:848–57. https://doi.org/10.11607/jomi.5889
Marconcini S, Giammarinaro E, Toti P, Alfonsi F, Covani U, Barone A (2018) Longitudinal analysis on the effect of insertion torque on delayed single implants: a 3-year randomized clinical study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 20:322–332. https://doi.org/10.1111/cid.12586
Cohen O, Ormianer Z, Tal H, Rothamel D, Weinreb M, Moses O (2016) Differences in crestal bone-to-implant contact following an under-drilling compared to an over-drilling protocol. A study in the rabbit tibia. Clin Oral Investig 20:2475–2480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-016-1765-8
Campos FE, Gomes JB, Marin C, Teixeira HS, Suzuki M, Witek L, Zanetta-Barbosa D, Coelho PG (2012) Effect of drilling dimension on implant placement torque and early osseointegration stages: an experimental study in dogs. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 70:e43-50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2011.08.006
Devi S, Duraisamy R (2021) Evaluation of bone density, implant site, and crestal position of implants and their influence on implant primary stability− a retrospective study. J Long Term Eff Med Implants 31:77–82. https://doi.org/10.1615/JLongTermEffMedImplants.2021035937
Anitua E, Alkhraisat MH (2019) Fifteen-year follow-up of short dental implants in the completely edentulous jaw: submerged versus nonsubmerged healing. Implant Dent 28:551–555. https://doi.org/10.1097/ID.0000000000000935
Chrcanovic BR, Albrektsson T, Wennerberg A (2015) Immediately loaded non-submerged versus delayed loaded submerged dental implants: a meta-analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 44:493–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2014.11.011
Sánchez-Siles M, Muñoz-Cámara D, Salazar-Sánchez N, Camacho-Alonso F, Calvo-Guirado JL (2018) Crestal bone loss around submerged and non-submerged implants during the osseointegration phase with different healing abutment designs: a randomized prospective clinical study. Clin Oral Implants Res 29:808–812. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.12981
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S. K. and I. F. designed the study, conducted the literature survey, and wrote the draft. M. L. C. V and A. C. R. designed the study and revised the manuscript critically. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This is an observational study. The University of Sao Paulo Research Ethics Committee has confirmed that no ethical approval is required.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kreve, S., Ferreira, I., da Costa Valente, M.L. et al. Relationship between dental implant macro-design and osseointegration: a systematic review. Oral Maxillofac Surg 28, 1–14 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10006-022-01116-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10006-022-01116-4