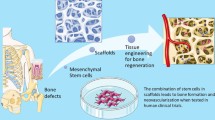
Abstract
Purpose
The current systematic review investigated the results of application of some of the most commonly used scaffolds in conjugation with stem cells and growth factors in animal and clinical studies.
Methods
A comprehensive electronic search was conducted according to the PRISMA guidelines in NCBI PMC and PubMed from January 1970 to December 2015 limited to English language publications with available full texts. In vivo studies in relation to “bone healing,” “bone regeneration,” and at least one of the following items were investigated: allograft, β-tricalcium phosphate, deproteinized bovine bone mineral, hydroxyapetite/tricalcium phosphate, nanohydroxyapatite, and composite scaffolds.
Results
A total of 1252 articles were reviewed, and 46 articles completely fulfilled the inclusion criteria of this study. The highest bone regeneration has been achieved when combination of all three elements, given scaffolds, mesenchymal stem cells, and growth factors, were used. Among studies being reported in this review, bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells are the most studied mesenchymal stem cells, β-tricalcium phosphate is the most frequently used scaffold, and platelet-rich plasma is the most commonly used growth factor.
Conclusion
The current review aimed to inform reconstructive surgeons of how combinations of various mesenchymal stem cells, scaffolds, and growth factors enhance bone regeneration. The highest bone regeneration has been achieved when combination of all three elements, given scaffolds, mesenchymal stem cells, and growth factors, were used.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Behnia H, Khojasteh A, Esmaeelinejad M, Naghdi N (2012) Growth factor carriers in bone formation: a systematic review. Journal of Islamic Dental Association of Iran 24:150–167
Hassani A, Khojasteh A, Alikhasi M (2008) Anterior palate of the maxilla as a donor site for oral and maxillofacial reconstructive procedures. Asian Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 20:135–138
Hassani A, Khojasteh A, Alikhasi M, Vaziri H (2009) Measurement of volume changes of sinus floor augmentation covered with buccal fat pad: a case series study. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology, and Endodontology 107:369–374
Hassani A, Khojasteh A, Shamsabad AN (2005) The anterior palate as a donor site in maxillofacial bone grafting: a quantitative anatomic study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 63:1196–1200
Khojasteh A, Behnia H, Dashti SG, Stevens M (2012) Current trends in mesenchymal stem cell application in bone augmentation: a review of the literature. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 70:972–982
Khojasteh A, Behnia H, Shayesteh YS, Morad G, Alikhasi M (2011) Localized bone augmentation with cortical bone blocks tented over different particulate bone substitutes: a retrospective study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 27:1481–1493
Morad G, Kheiri L, Khojasteh A (2013) Dental pulp stem cells for in vivo bone regeneration: a systematic review of literature. Arch Oral Biol 58:1818–1827
Amini AR, Laurencin CT, Nukavarapu SP (2012) Bone tissue engineering: recent advances and challenges. Critical Reviews™ in. Biomed Eng 40
Behnia H, Khojasteh A, Kiani MT, Khoshzaban A, Abbas FM, Bashtar M et al (2013) Bone regeneration with a combination of nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite silica gel, platelet-rich growth factor, and mesenchymal stem cells: a histologic study in rabbit calvaria. Oral surgery, oral medicine, oral pathology and oral radiology 115:e7–e15
Khojasteh A, Soheilifar S, Mohajerani H, Nowzari H (2012) The effectiveness of barrier membranes on bone regeneration in localized bony defects: a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 28:1076–1089
Mortazavi SH, Khojasteh A, Vaziri H, Khoshzaban A, Roudsari MV, Razavi SHE (2009) The effect of fluoxetine on bone regeneration in rat calvarial bone defects. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology, and Endodontology 108:22–27
Phinney DG, Prockop DJ (2007) Concise review: mesenchymal stem/multipotent stromal cells: the state of transdifferentiation and modes of tissue repair—current views. Stem Cells 25:2896–2902
Motamedian FSTSR, Khosraviani FGK, Khojasteh A (2012) Craniomaxillofacial bone engineering by scaffolds loaded with stem cells: a systematic review. J Dent Sch 116
Huang G-J, Gronthos S, Shi S (2009) Mesenchymal stem cells derived from dental tissues vs. those from other sources: their biology and role in regenerative medicine. J Dent Res 88:792–806
Zhang Z (2011) Bone regeneration by stem cell and tissue engineering in oral and maxillofacial region. Frontiers of medicine 5:401–413
Behnia H, Khojasteh A, Soleimani M, Tehranchi A, Khoshzaban A, Keshel SH et al (2009) Secondary repair of alveolar clefts using human mesenchymal stem cells. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology, and Endodontology 108:e1–e6
Jafarian M, Eslaminejad MB, Khojasteh A, Abbas FM, Dehghan MM, Hassanizadeh R et al (2008) Marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells-directed bone regeneration in the dog mandible: a comparison between biphasic calcium phosphate and natural bone mineral. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology, and Endodontology 105:e14–e24
Khojasteh A, Eslaminejad MB, Nazarian H (2008) Mesenchymal stem cells enhance bone regeneration in rat calvarial critical size defects more than platelete-rich plasma. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology, and Endodontology 106:356–362
Shayesteh YS, Khojasteh A, Soleimani M, Alikhasi M, Khoshzaban A, Ahmadbeigi N (2008) Sinus augmentation using human mesenchymal stem cells loaded into a β-tricalcium phosphate/hydroxyapatite scaffold. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology, and Endodontology 106:203–209
Behnia H, Khojasteh A, Soleimani M, Tehranchi A, Atashi A (2012) Repair of alveolar cleft defect with mesenchymal stem cells and platelet derived growth factors: a preliminary report. J Cranio-Maxillofac Surg 40:2–7
Houshmand B, Behnia H, Khoshzaban A, Morad G, Behrouzi G, Dashti SG et al (2012) Osteoblastic differentiation of human stem cells derived from bone marrow and periodontal ligament under the effect of enamel matrix derivative and transforming growth factor-beta. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 28:e440–e450
Takahashi Y, Yamamoto M, Tabata Y (2005) Osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in biodegradable sponges composed of gelatin and β-tricalcium phosphate. Biomaterials 26:3587–3596
Bowers KT, Keller JC, Randolph BA, Wick DG, Michaels CM (1991) Optimization of surface micromorphology for enhanced osteoblast responses in vitro. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 7:302–310
Eggli P, Moller W, Schenk R (1988) Porous hydroxyapatite and tricalcium phosphate cylinders with two different pore size ranges implanted in the cancellous bone of rabbits: a comparative histomorphometric and histologic study of bony ingrowth and implant substitution. Clin Orthop Relat Res 232:127–138
Matsuda T, Davies J (1987) The in vitro response of osteoblasts to bioactive glass. Biomaterials 8:275–284
Eslaminejad MB, Jafarian M, Khojasteh A, Mashhadi Abbas F, Dehghan MM, Houshmand B (2007) Enhancing ectopic bone formation in canine masseter muscle by loading mesenchymal stem cells onto natural bovine bone minerals. Iranian J Vet Surg 2:25–35
Hao W, Pang L, Jiang M, Lv R, Xiong Z, Hu YY (2010) Skeletal repair in rabbits using a novel biomimetic composite based on adipose-derived stem cells encapsulated in collagen I gel with PLGA-β-TCP scaffold. J Orthop Res 28:252–257
Khojasteh A, Eslaminejad MB, Nazarian H, Morad G, Dashti SG, Behnia H et al (2013) Vertical bone augmentation with simultaneous implant placement using particulate mineralized bone and mesenchymal stem cells: a preliminary study in rabbit. Journal of Oral Implantology 39:3–13
Liu G, Sun J, Li Y, Zhou H, Cui L, Liu W et al (2008) Evaluation of partially demineralized osteoporotic cancellous bone matrix combined with human bone marrow stromal cells for tissue engineering: an in vitro and in vivo study. Calcif Tissue Int 83:176–185
Neamat A, Gawish A, Gamal-Eldeen AM (2009) β-Tricalcium phosphate promotes cell proliferation, osteogenesis and bone regeneration in intrabony defects in dogs. Arch Oral Biol 54:1083–1090
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med 151:264–269
Nather A, David V, Teng JW, Lee CW, Pereira BP (2010) Effect of autologous mesenchymal stem cells on biological healing of allografts in critical-sized tibial defects simulated in adult rabbits. Ann Acad Med Singap 39:599
Lee J-Y, Choi M-H, Shin E-Y, Kang Y-K (2011) Autologous mesenchymal stem cells loaded in Gelfoam® for structural bone allograft healing in rabbits. Cell Tissue Bank 12:299–309
Lucarelli E, Fini M, Beccheroni A, Giavaresi G, Di Bella C, Aldini NN et al (2005) Stromal stem cells and platelet-rich plasma improve bone allograft integration. Clin Orthop Relat Res 435:62–68
Bruder SP, Kraus KH, Goldberg VM, Kadiyala S (1998) The effect of implants loaded with autologous mesenchymal stem cells on the healing of canine segmental bone defects*. The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery 80:985–996
Taira H, Moreno J, Ripalda P, Forriol F (2004) Radiological and histological analysis of cortical allografts: an experimental study in sheep femora. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 124:320–325
Rickert D, Sauerbier S, Nagursky H, Menne D, Vissink A, Raghoebar G (2011) Maxillary sinus floor elevation with bovine bone mineral combined with either autogenous bone or autogenous stem cells: a prospective randomized clinical trial. Clin Oral Implants Res 22:251–258
Raposo-Amaral CE, Bueno DF, Almeida AB, Jorgetti V, Costa CC, Gouveia CH et al (2014) Is bone transplantation the gold standard for repair of alveolar bone defects? Journal of tissue engineering 5:2041731413519352
Yu B-H, Zhou Q, Wang Z-L (2014) Periodontal ligament versus bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in combination with Bio-Oss scaffolds for ectopic and in situ bone formation: a comparative study in the rat. J Biomater Appl 29:243–253
Khorsand A, Eslaminejad MB, Arabsolghar M, Paknejad M, Ghaedi B, Rokn AR et al (2013) Autologous dental pulp stem cells in regeneration of defect created in canine periodontal tissue. Journal of oral implantology 39:433–443
Park J-C, Oh S-Y, Lee J-S, Park S-Y, Choi E-Y, Cho K-S, Kim C-S (2016) In vivo bone formation by humanalveolar-bone-derived mesenchymal stem cells obtained during implant osteotomy using biphasic calcium phosphate ceramics or Bio-Oss as carriers. J Biomed Mater Res Part B 104B:515–524
Yu B-H, Zhou Q, Wang Z-L (2014) Comparison of tissue-engineered bone from different stem cell sources for maxillary sinus floor augmentation: a study in a canine model. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 72:1084–1092
Feng W, Lv S, Cui J, Han X, Du J, Sun J et al (2015) Histochemical examination of adipose derived stem cells combined with β-TCP for bone defects restoration under systemic administration of 1α, 25 (OH) 2 D 3. Mater Sci Eng C 54:133–141
Ueda M, Yamada Y, Ozawa R, Okazaki Y (2005) Clinical case reports of injectable tissue-engineered bone for alveolar augmentation with simultaneous implant placement. J Prosthet Dent 94:560
Thesleff T, Lehtimäki K, Niskakangas T, Mannerström B, Miettinen S, Suuronen R et al (2011) Cranioplasty with adipose-derived stem cells and biomaterial: a novel method for cranial reconstruction. Neurosurgery 68:1535–1540
Zhou J, Lin H, Fang T, Li X, Dai W, Uemura T et al (2010) The repair of large segmental bone defects in the rabbit with vascularized tissue engineered bone. Biomaterials 31:1171–1179
Wang J, Qiao P, Dong L, Li F, Xu T, Xie Q (2013) Microencapsulated rBMMSCs/calcium phosphate cement for bone formation in vivo. Biomed Mater Eng 24:835–843
Damlar I, Erdoğan Ö, Tatli U, Arpağ OF, Görmez U, Üstün Y (2015) Comparison of osteoconductive properties of three different β-tricalcium phosphate graft materials: a pilot histomorphometric study in a pig model. J Cranio-Maxillofac Surg 43:175–180
Li H, Dai K, Tang T, Zhang X, Yan M, Lou J (2007) Bone regeneration by implantation of adipose-derived stromal cells expressing BMP-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 356:836–842
Guan J, Zhang J, Li H, Zhu Z, Guo S, Niu X et al. (2015) Human urine derived stem cells in combination with β-TCP can be applied for bone regeneration
Eftekhari H, Farahpour M, Rabiee S (2014) Histopathological evaluation of potential impact of β-tricalcium phosphate (HA+ β-TCP) granules on healing of segmental femur bone defect. Bratislavske lekarske listy 116:30–34
Sun W, Li Z-R, Yang Y-R, Shi Z-C, Wang B, Liu B et al (2011) Experimental study on phase-contrast imaging with synchrotron hard X-ray for repairing osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Orthopedics 34:699
Liu H-C, Wang D-S, Su F, Wu X, Shi Z-P, Lv Y et al (2011) Reconstruction of alveolar bone defects using bone morphogenetic protein 2 mediated rabbit dental pulp stem cells seeded on nano-hydroxyapatite/collagen/poly (L-lactide). Tissue Eng A 17:2417–2433
Liu X, Li X, Fan Y, Zhang G, Li D, Dong W et al (2010) Repairing goat tibia segmental bone defect using scaffold cultured with mesenchymal stem cells. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 94:44–52
Ling LE, Feng L, Liu HC, Wang DS, Shi ZP, Wang JC et al (2015) The effect of calcium phosphate composite scaffolds on the osteogenic differentiation of rabbit dental pulp stem cells. J Biomed Mater Res A 103:1732–1745
Vahabi S, Amirizadeh N, Shokrgozar M, Mofeed R, Mashhadi A, Aghaloo M et al (2011) A comparison between the efficacy of Bio-Oss, hydroxyapatite tricalcium phosphate and combination of mesenchymal stem cells in inducing bone regeneration. Chang Gung Med J 35:28–37
Kim S-H, Kim K-H, Seo B-M, Koo K-T, Kim T-I, Seol Y-J et al (2009) Alveolar bone regeneration by transplantation of periodontal ligament stem cells and bone marrow stem cells in a canine peri-implant defect model: a pilot study. J Periodontol 80:1815–1823
Arinzeh TL, Peter SJ, Archambault MP, Van Den Bos C, Gordon S, Kraus K et al (2003) Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells regenerate bone in a critical-sized canine segmental defect. The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery 85:1927–1935
He F, Chen Y, Li J, Lin B, Ouyang Y, Yu B et al (2015) Improving bone repair of femoral and radial defects in rabbit by incorporating PRP into PLGA/CPC composite scaffold with unidirectional pore structure. J Biomed Mater Res A 103:1312–1324
Liao H-T, Chen Y-Y, Lai Y-T, Hsieh M-F, Jiang C-P (2014) The osteogenesis of bone marrow stem cells on mPEG-PCL-mPEG/hydroxyapatite composite scaffold via solid freeform fabrication. Biomed Res Int 2014
Pang L, Hao W, Jiang M, Huang J, Yan Y, Hu Y (2013) Bony defect repair in rabbit using hybrid rapid prototyping polylactic-co-glycolic acid/β-tricalciumphosphate collagen I/apatite scaffold and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Indian journal of orthopaedics 47:388
James AW, Levi B, Nelson ER, Peng M, Commons GW, Lee M et al (2010) Deleterious effects of freezing on osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stromal cells in vitro and in vivo. Stem Cells Dev 20:427–439
Rai B, Lin JL, Lim ZX, Guldberg RE, Hutmacher DW, Cool SM (2010) Differences between in vitro viability and differentiation and in vivo bone-forming efficacy of human mesenchymal stem cells cultured on PCL–TCP scaffolds. Biomaterials 31:7960–7970
Konopnicki S, Sharaf B, Resnick C, Patenaude A, Pogal-Sussman T, Hwang K-G et al (2015) Tissue-engineered bone with 3-dimensionally printed β-tricalcium phosphate and polycaprolactone scaffolds and early implantation: an in vivo pilot study in a porcine mandible model. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 73:1016. e1011–1016. e1011
Prosecká E, Rampichová M, Litvinec A, Tonar Z, Králíčková M, Vojtová L et al (2015) Collagen/hydroxyapatite scaffold enriched with polycaprolactone nanofibers, thrombocyte-rich solution and mesenchymal stem cells promotes regeneration in large bone defect in vivo. J Biomed Mater Res A 103:671–682
Kim S-J, Kim M-R, Oh J-S, Han I, Shin S-W (2009) Effects of polycaprolactone-tricalcium phosphate, recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 and dog mesenchymal stem cells on bone formation: pilot study in dogs. Yonsei Med J 50:825–831
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, Slaper-Cortenbach I, Marini F, Krause D et al (2006) Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 8:315–317
Rad MR, Liu D, He H, Brooks H, Xiao M, Wise GE et al (2015) The role of dentin matrix protein 1 (DMP1) in regulation of osteogenic differentiation of rat dental follicle stem cells (DFSCs). Arch Oral Biol 60:546–556
Guo MZ, Xia ZS, Lin LB (1991) The mechanical and biological properties of demineralised cortical bone allografts in animals. Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery, British Volume 73:791–794
Urist MR, Mikulski A, Lietze A (1979) Solubilized and insolubilized bone morphogenetic protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci 76:1828–1832
Enneking WF, Campanacci DA (2001) Retrieved human allografts. The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery 83:971–986
Enneking W, Mindell E (1991) Observations on massive retrieved human allografts. The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery 73:1123–1142
Jensen SS, Broggini N, Hjørting-Hansen E, Schenk R, Buser D (2006) Bone healing and graft resorption of autograft, anorganic bovine bone and β-tricalcium phosphate. A histologic and histomorphometric study in the mandibles of minipigs. Clin Oral Implants Res 17:237–243
Suzuki O, Imaizumi H, Kamakura S, Katagiri T (2008) Bone regeneration by synthetic octacalcium phosphate and its role in biological mineralization. Curr Med Chem 15:305–313
Liao S, Cui F, Zhang W, Feng Q (2004) Hierarchically biomimetic bone scaffold materials: nano-HA/collagen/PLA composite. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 69:158–165
Guarino V, Causa F, Ambrosio L (2007) Bioactive scaffolds for bone and ligament tissue. Expert review of medical devices 4:405–418
Coombes A, Rizzi S, Williamson M, Barralet J, Downes S, Wallace W (2004) Precipitation casting of polycaprolactone for applications in tissue engineering and drug delivery. Biomaterials 25:315–325
Shikinami Y, Okazaki K, Saito M, Okuno M, Hasegawa S, Tamura J et al (2006) Bioactive and bioresorbable cellular cubic-composite scaffolds for use in bone reconstruction. J R Soc Interface 3:805–821
Mondrinos MJ, Dembzynski R, Lu L, Byrapogu VK, Wootton DM, Lelkes PI et al (2006) Porogen-based solid freeform fabrication of polycaprolactone–calcium phosphate scaffolds for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 27:4399–4408
Zhou Y, Hutmacher DW, Varawan SL, Lim TM (2007) In vitro bone engineering based on polycaprolactone and polycaprolactone–tricalcium phosphate composites. Polym Int 56:333–342
Liao HT, Lee MY, Tsai WW, Wang HC, Lu WC (2016) Osteogenesis of adipose-derived stem cells on polycaprolactone–β-tricalcium phosphate scaffold fabricated via selective laser sintering and surface coating with collagen type I. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 10(10):E337–E353
Azevedo M, Reis R, Claase M, Grijpma D, Feijen J (2003) Development and properties of polycaprolactone/hydroxyapatite composite biomaterials. J Mater Sci Mater Med 14:103–107
Farré-Guasch E, Martí-Pagès C, Hernández-Alfaro F, Klein-Nulend J, Casals N (2010) Buccal fat pad, an oral access source of human adipose stem cells with potential for osteochondral tissue engineering: an in vitro study. Tissue Engineering Part C: Methods 16:1083–1094
Huard J, Cao B, Qu-Petersen Z (2003) Muscle-derived stem cells: potential for muscle regeneration. Birth Defects Research Part C: Embryo Today: Reviews 69:230–237
Chaudhry G, Yao D, Smith A, Hussain A (2004) Osteogenic cells derived from embryonic stem cells produced bone nodules in three-dimensional scaffolds. Biomed Res Int 2004:203–210
Lin NH, Gronthos S, Mark Bartold P (2009) Stem cells and future periodontal regeneration. Periodontol 51:239–251
McKay WF, Peckham SM, Badura JM (2007) A comprehensive clinical review of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (INFUSE® Bone Graft). Int Orthop 31:729–734
Weibrich G, Kleis WK, Hafner G, Hitzler WE (2002) Growth factor levels in platelet-rich plasma and correlations with donor age, sex, and platelet count. J Cranio-Maxillofac Surg 30:97–102
Marx RE (2004) Platelet-rich plasma: evidence to support its use. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 62:489–496
Kanno T, Takahashi T, Tsujisawa T, Ariyoshi W, Nishihara T (2005) Platelet-rich plasma enhances human osteoblast-like cell proliferation and differentiation. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 63:362–369
Hollinger JO, Hart CE, Hirsch SN, Lynch S, Friedlaender GE (2008) Recombinant human platelet-derived growth factor: biology and clinical applications. The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery 90:48–54
Tare R, Kanczler J, Aarvold A, Jones A, Dunlop D, Oreffo R (2010) Skeletal stem cells and bone regeneration: translational strategies from bench to clinic. Proc Inst Mech Eng H J Eng Med 224:1455–1470
Schimandle JH, Boden SD (1994) The use of animal models to study spinal fusion. Spine-Hagerstown 19:1988–1991
Liebschner MA (2004) Biomechanical considerations of animal models used in tissue engineering of bone. Biomaterials 25:1697–1714
Hazzard DG, Bronson RT, McClearn GE, Strong R (1992) Selection of an appropriate animal model to study aging processes with special emphasis on the use of rat strains. J Gerontol 47:B63–B64
Egermann M, Goldhahn J, Schneider E (2005) Animal models for fracture treatment in osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int 16:S129–S138
Pearce A, Richards R, Milz S, Schneider E, Pearce S (2007) Animal models for implant biomaterial research in bone: a review. Eur Cell Mater 13:1–10
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hosseinpour, S., Ghazizadeh Ahsaie, M., Rezai Rad, M. et al. Application of selected scaffolds for bone tissue engineering: a systematic review. Oral Maxillofac Surg 21, 109–129 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10006-017-0608-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10006-017-0608-3