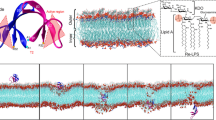
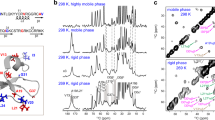
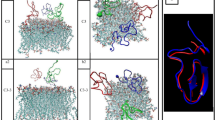
Abstract
Human α-defensin 5 (HD5) is one of the important antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) used against a broad-spectrum of pathogens, especially Gram-negative bacteria. HD5 kills by disrupting and making a pore in the bacterial membrane. The presence of lipopolysaccharide (LPS), located on a membrane surface, is found to have an impact on HD5’s activity, where such binding mechanism in microscopic detail remains unclear. In this work, we therefore employed molecular dynamics (MD) simulations to investigate the binding mechanisms of HD5 on LPS in comparison to a bare DMPC lipid membrane. Two oligomers, dimer and tetramer, are studied here. Apparently, the membrane structure influences the protein binding affinity. HD5 binds tighter to a lipid membrane than LPS. Both dimeric and tetrameric HD5 can penetrate deeply into a phosphate layer in a lipid membrane, whereas only facial contacts are observed for LPS systems. The proteins appear to stay in the polar area instead of diving into a hydrophobic region. Furthermore, it happens in all cases that residues in the active region (A1, T2, R6, R13, R32) contribute to the membrane adsorption. The breakdown of tetramer into two dimers is also found. This implies that the dimer is more favorable for membrane binding. Moreover, both dimeric and tetrameric HD5 can significantly disrupt a LPS layer, whilst no serious distortion of lipid membrane is obtained. This emphasizes the importance of LPS on HD5 activity.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MD:
-
Molecular dynamics
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- HD5:
-
Human α-defensin 5
- DMPC:
-
1,2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
References
Jung SW, Lee J, Cho AE (2017) Elucidating the bacterial membrane disruption mechanism of human alpha-defensin 5: a theoretical study. J Phys Chem B 121(4):741–748. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.6b11806
Nguyen LT, Haney EF, Vogel HJ (2011) The expanding scope of antimicrobial peptide structures and their modes of action. Trends Biotechnol 29(9):464–472
Zhang L (2017) Different dynamics and pathway of disulfide bonds reduction of two human defensins, a molecular dynamics simulation study. Proteins: Struct Funct Bioinf 85(4):665–681
Selsted ME, Ouellette AJ (2005) Mammalian defensins in the antimicrobial immune response. Nat Immunol 6(6):551
Rajabi M, Ericksen B, Wu XJ, de Leeuw E, Zhao L, Pazgier M, Lu WY (2012) Functional determinants of human enteric alpha-defensin HD5 crucial role for hydrophobicity at dimer interface. J Biol Chem 287(26):21615–21627. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.367995
de Leeuw E, Burks SR, Li X, Kao JPY, Lu W (2007) Structure-dependent functional properties of human defensin 5. FEBS Lett 581(3):515–520
de Leeuw E, Rajabi M, Zou G, Pazgier M, Lu W (2009) Selective arginines are important for the antibacterial activity and host cell interaction of human α-defensin 5. FEBS Lett 583(15):2507–2512
Rajabi M, de Leeuw E, Pazgier M, Li J, Lubkowski J, Lu W (2008) The conserved salt bridge in human α-defensin 5 is required for its precursor processing and proteolytic stability. J Biol Chem 283(31):21509–21518
Wei G, de Leeuw E, Pazgier M, Yuan W, Zou G, Wang J, Ericksen B, Lu W-Y, Lehrer RI, Lu W (2009) Through the looking glass, mechanistic insights from enantiomeric human defensins. J Biol Chem 284:29180–29192
Chileveru HR, Lim SA, Chairatana P, Wommack AJ, Chiang IL, Nolan EM (2015) Visualizing attack of Escherichia coli by the antimicrobial peptide human defensin 5. Biochemistry-Us 54(9):1767–1777. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi501483q
Wommack AJ, Robson SA, Wanniarachchi YA, Wan A, Turner CJ, Wagner G, Nolan EM (2012) NMR solution structure and condition-dependent oligomerization of the antimicrobial peptide human defensin 5. Biochemistry-Us 51(48):9624–9637. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi301255u
Lehrer RI, Jung G, Ruchala P, Andre S, Gabius HJ, Lu W (2009) Multivalent binding of carbohydrates by the human alpha-defensin, HD5. J Immunol 183(1):480–490. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0900244
Zhang Y, Cougnon FB, Wanniarachchi YA, Hayden JA, Nolan EM (2013) Reduction of human defensin 5 affords a high-affinity zinc-chelating peptide. ACS Chem Biol 8(9):1907–1911. https://doi.org/10.1021/cb400340k
Wang C, Shen M, Zhang N, Wang S, Xu Y, Chen S, Chen F, Yang K, He T, Wang A, Su Y, Cheng T, Zhao J, Wang J (2016) Reduction impairs the antibacterial activity but benefits the LPS neutralization ability of human enteric defensin 5. Sci Rep 6:22875. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep22875
Scott MG, Vreugdenhil AC, Buurman WA, Hancock RE, Gold MR (2000) Cutting edge: cationic antimicrobial peptides block the binding of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to LPS binding protein. J Immunol 164(2):549–553
Hsu P-C, Jefferies D, Khalid S (2016) Molecular dynamics simulations predict the pathways via which pristine fullerenes penetrate bacterial membranes. J Phys Chem B 120(43):11170–11179. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.6b06615
Wommack AJ, Robson SA, Wanniarachchi YA, Wan A, Turner CJ, Wagner G, Nolan EM (2012) NMR solution structure and condition-dependent oligomerization of the antimicrobial peptide human defensin 5. Biochemistry 51(48):9624–9637
Oostenbrink C, Villa A, Mark AE, Gunsteren WFV (2004) A biomolecular force field based on the free enthalpy of hydration and solvation: the GROMOS force-field parameter sets 53A5 and 53A6. J Comput Chem 25(13):1656–1676. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.20090
Jung SW, Lee J, Cho AE (2017) Elucidating the bacterial membrane disruption mechanism of human α-defensin 5: a theoretical study. J Phys Chem B 121(4):741–748
Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K (1996) VMD: visual molecular dynamics. J Mol Graph 14(1):33–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/0263-7855(96)00018-5
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the financial support received from the Kasetsart University Research and Development Institute (KURDI), Bangkok, Thailand and from a Science Achievement Scholarship of Thailand (SAST). We also thank Prof Syma Khalid for her kind support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 337 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Awang, T., Pongprayoon, P. The adsorption of human defensin 5 on bacterial membranes: simulation studies. J Mol Model 24, 273 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-018-3812-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-018-3812-7