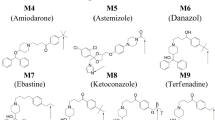
Abstract
An experimentally determined structure for human CYP2J2—a member of the cytochrome P450 family with significant and diverse roles across a number of tissues—does not yet exist. Our understanding of how CYP2J2 accommodates its cognate substrates and how it might be inhibited by other ligands thus relies on our ability to computationally predict such interactions using modelling techniques. In this study we present a computational investigation of the binding of arachidonic acid (AA) to CYP2J2 using homology modelling, induced fit docking (IFD) and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. Our study reveals a catalytically competent binding mode for AA that is distinct from a recently published study that followed a different computational pipeline. Our proposed binding mode for AA is supported by crystal structures of complexes of related enzymes to inhibitors, and evolutionary conservation of a residue whose role appears essential for placing AA in the right site for catalysis.

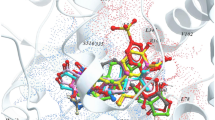
Arachidonic acid docked in the active site of CYP2J2 assumes a catalytically competent binding mode stabilised by hydrogen bonds to Arg117







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CYP:
-
Cytochrome P450
- CYP2J2:
-
Human cytochrome P450 2J2
- AA:
-
Arachidonic acid
- EET:
-
Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid
- MD:
-
Molecular dynamics
- IFD:
-
Induced fit docking
References
Bishop-Bailey D, Thomson S, Askari A et al (2014) Lipid-metabolizing CYPs in the regulation and dysregulation of metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr 34:261–279. doi:10.1146/annurev-nutr-071813-105747
Wu S, Moomaw CR, Tomer KB et al (1996) Molecular cloning and expression of CYP2J2, a human cytochrome P450 arachidonic acid epoxygenase highly expressed in heart. J Biol Chem 271:3460–3468. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.7.3460
Xu M, Ju W, Hao H et al (2013) Cytochrome P450 2J2: distribution, function, regulation, genetic polymorphisms and clinical significance. Drug Metab Rev 45:311–352. doi:10.3109/03602532.2013.806537
Askari AA, Thomson S, Edin ML et al (2014) Basal and inducible anti-inflammatory epoxygenase activity in endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 446:633–637. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.03.020
Bystrom J, Thomson SJ, Johansson J et al (2013) Inducible CYP2J2 and its product 11,12-EET promotes bacterial phagocytosis: a role for CYP2J2 deficiency in the pathogenesis of Crohn’s disease? PLoS ONE 8:e75107. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0075107
El-Serafi I, Fares M, Abedi-Valugerdi M et al (2015) Cytochrome P450 2J2, a new key enzyme in cyclophosphamide bioactivation and a potential biomarker for hematological malignancies. Pharmacogenomics J 15:405–413. doi:10.1038/tpj.2014.82
Zeldin DC (2001) Epoxygenase pathways of arachidonic acid metabolism. J Biol Chem 276:36059–36062. doi:10.1074/jbc.R100030200
Westphal C, Konkel A, Schunck W-H (2011) CYP-eicosanoids—A new link between omega-3 fatty acids and cardiac disease? Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 96:99–108. doi:10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2011.09.001
Lee CA, Neul D, Clouser-Roche A et al (2010) Identification of novel substrates for human cytochrome P450 2J2. Drug Metab Dispos 38:347–356. doi:10.1124/dmd.109.030270
Liu K-H, Kim M-G, Lee D-J et al (2006) Characterization of ebastine, hydroxyebastine, and carebastine metabolism by human liver microsomes and expressed cytochrome P450 enzymes: major roles for CYP2J2 and CYP3A. Drug Metab Dispos 34:1793–1797. doi:10.1124/dmd.106.010488
Askari A, Thomson SJ, Edin ML et al (2013) Roles of the epoxygenase CYP2J2 in the endothelium. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 107:56–63. doi:10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2013.02.003
Lafite P, Dijols S, Zeldin DC et al (2007) Selective, competitive and mechanism-based inhibitors of human cytochrome P450 2J2. Arch Biochem Biophys 464:155–168. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2007.03.028
Lee CA, Jones JP, Katayama J et al (2012) Identifying a selective substrate and inhibitor pair for the evaluation of CYP2J2 activity. Drug Metab Dispos 40:943–951. doi:10.1124/dmd.111.043505
Du H, Brender JR, Zhang J, Zhang Y (2015) Protein structure prediction provides comparable performance to crystallographic structures in docking-based virtual screening. Methods 71:77–84. doi:10.1016/j.ymeth.2014.08.017
Lukk T, Sakai A, Kalyanaraman C et al (2012) Homology models guide discovery of diverse enzyme specificities among dipeptide epimerases in the enolase superfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:4122–4127. doi:10.1073/pnas.1112081109
Ramachandran S, Dokholyan NV (2012) Homology modeling: generating structural models to understand protein function and mechanism. In: Dokholyan NV (ed) Computational modeling of biological systems. Springer, Boston, pp 97–116
Carlsson J, Coleman RG, Setola V et al (2011) Ligand discovery from a dopamine D3 receptor homology model and crystal structure. Nat Chem Biol 7:769–778. doi:10.1038/nchembio.662
Kannan S, Melesina J, Hauser A-T et al (2014) Discovery of inhibitors of Schistosoma mansoni HDAC8 by combining homology modeling, virtual screening, and in vitro validation. J Chem Inf Model 54:3005–3019. doi:10.1021/ci5004653
Lafite P, André F, Zeldin DC et al (2007) Unusual regioselectivity and active site topology of human cytochrome P450 2J2. Biochemistry 46:10237–10247. doi:10.1021/bi700876a
Li W, Tang Y, Liu H et al (2008) Probing ligand binding modes of human cytochrome P450 2J2 by homology modeling, molecular dynamics simulation, and flexible molecular docking. Proteins 71:938–949. doi:10.1002/prot.21778
Williams PA, Cosme J, Ward A et al (2003) Crystal structure of human cytochrome P450 2C9 with bound warfarin. Nature 424:464–468. doi:10.1038/nature01862
Cong S, Ma X-T, Li Y-X, Wang J-F (2013) Structural basis for the mutation-induced dysfunction of human CYP2J2: a computational study. J Chem Inf Model 53:1350–1357. doi:10.1021/ci400003p
Xia X-L, Fa B-T, Cong S et al (2014) Research/review: Insights into the mutation-induced dysfunction of arachidonic acid metabolism from modeling of human CYP2J2. Curr Drug Metab 15:502–513
Berman HM, Westbrook J, Feng Z et al (2000) The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res 28:235–242
Scott EE, White MA, He YA et al (2004) Structure of mammalian cytochrome P450 2B4 complexed with 4-(4-chlorophenyl)imidazole at 1.9-A resolution: insight into the range of P450 conformations and the coordination of redox partner binding. J Biol Chem 279:27294–27301. doi:10.1074/jbc.M403349200
Strushkevich N, Usanov SA, Plotnikov AN et al (2008) Structural analysis of CYP2R1 in complex with vitamin D3. J Mol Biol 380:95–106. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2008.03.065
Schrödinger, LLC Schrödinger Suite 2014–1 Protein Preparation Wizard; Epik version 2.7, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, 2013; Impact version 6.2, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, 2014; Prime version 3.5, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, 2014
Schrödinger, LLC Prime, version 3.5, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, 2014
Lüthy R, Bowie JU, Eisenberg D (1992) Assessment of protein models with three-dimensional profiles. Nature 356:83–85. doi:10.1038/356083a0
Colovos C, Yeates TO (1993) Verification of protein structures: patterns of nonbonded atomic interactions. Protein Sci 2:1511–1519. doi:10.1002/pro.5560020916
Laskowski RA, MacArthur MW, Moss DS et al (1993) PROCHECK: a program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J Appl Crystallogr 26:283–291. doi:10.1107/S0021889892009944
Benkert P, Künzli M, Schwede T (2009) QMEAN server for protein model quality estimation. Nucleic Acids Res 37:gkp322–W514. doi:10.1093/nar/gkp322
Kim S, Thiessen PA, Bolton EE et al (2016) PubChem substance and compound databases. Nucleic Acids Res 44:D1202–D1213. doi:10.1093/nar/gkv951
Schrödinger, LLC Schrödinger Release 2014–1: LigPrep, version 2.9, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, 2014
Schrödinger, LLC Schrödinger Release 2014–1: Epik, version 2.7, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, 2014
Banks JL, Beard HS, Cao Y et al (2005) Integrated Modeling Program, Applied Chemical Theory (IMPACT). J Comput Chem 26:1752–1780. doi:10.1002/jcc.20292
Sherman W, Day T, Jacobson MP et al (2006) Novel procedure for modeling ligand/receptor induced fit effects. J Med Chem 49:534–553. doi:10.1021/jm050540c
Kräutler V, van Gunsteren WF, Hünenberger PH (2001) A fast SHAKE algorithm to solve distance constraint equations for small molecules in molecular dynamics simulations. J Comput Chem 22:501–508. doi:10.1002/1096-987X(20010415)22:5<501::AID-JCC1021>3.0.CO;2-V
Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC et al (2004) UCSF Chimera—a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 25:1605–1612. doi:10.1002/jcc.20084
Pieper U, Webb BM, Dong GQ et al (2014) ModBase, a database of annotated comparative protein structure models and associated resources. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D336–D346. doi:10.1093/nar/gkt1144
Haas J, Roth S, Arnold K et al (2013) The Protein Model Portal—a comprehensive resource for protein structure and model information. Database (Oxford) 2013:bat031. doi:10.1093/database/bat031
Halgren T (2007) New method for fast and accurate binding-site identification and analysis. Chem Biol Drug Des 69:146–148. doi:10.1111/j.1747-0285.2007.00483.x
Le Guilloux V, Schmidtke P, Tuffery P (2009) Fpocket: an open source platform for ligand pocket detection. BMC Bioinforma 10:168. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-10-168
Laskowski RA (2001) PDBsum: summaries and analyses of PDB structures. Nucleic Acids Res 29:221–222
Bhattarai S, Niraula NP, Sohng JK, Oh T-J (2012) In-silico and In-vitro based studies of Streptomyces peucetius CYP107N3 for oleic acid epoxidation. BMB Rep 45:736–741. doi:10.5483/BMBRep.2012.45.12.080
Ren S, Zeng J, Mei Y et al (2013) Discovery and characterization of novel, potent, and selective cytochrome P450 2J2 inhibitors. Drug Metab Dispos 41:60–71. doi:10.1124/dmd.112.048264
Schoch GA, Yano JK, Sansen S et al (2008) Determinants of cytochrome P450 2C8 substrate binding: structures of complexes with montelukast, troglitazone, felodipine, and 9-cis-retinoic acid. J Biol Chem 283:17227–17237. doi:10.1074/jbc.M802180200
DeVore NM, Scott EE (2012) Structures of cytochrome P450 17A1 with prostate cancer drugs abiraterone and TOK-001. Nature 482:116–119. doi:10.1038/nature10743
Zhao Y, White MA, Muralidhara BK et al (2006) Structure of microsomal cytochrome P450 2B4 complexed with the antifungal drug bifonazole: insight into P450 conformational plasticity and membrane interaction. J Biol Chem 281:5973–5981. doi:10.1074/jbc.M511464200
Wu S, Chen W, Murphy E et al (1997) Molecular cloning, expression, and functional significance of a cytochrome P450 highly expressed in rat heart myocytes. J Biol Chem 272:12551–12559. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.19.12551
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
G.P. was funded for this work by an Erasmus Placement Grant (2013/2014) received from the University of Perugia. K.K.A. is funded by a Bloomsbury Colleges PhD studentship.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
G. Proietti and K. K. Abelak contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 34051 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Proietti, G., Abelak, K.K., Bishop-Bailey, D. et al. Computational modelling of the binding of arachidonic acid to the human monooxygenase CYP2J2. J Mol Model 22, 279 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-016-3134-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-016-3134-6