Abstract
Structural, electronic, and electrical responses of the H-capped (6,0) zigzag single-walled aluminum nitride nanotube was studied under the parallel and transverse electric fields with strengths 0–140 × 10-4 a.u. by using density functional calculations. Geometry optimizations were carried out at the B3LYP/6-31G* level of theory using a locally modified version of the GAMESS electronic structure program. The dipole moments, atomic charge variations, and total energy of the (6,0) zigzag AlNNT show increases with increase in the applied external electric field strengths. The length, tip diameters, electronic spatial extent, and molecular volume of the nanotube do not significantly change with increasing electric field strength. The energy gap of the nanotube decreases with increases of the electric field strength and its reactivity is increased. Increase of the ionization potential, electron affinity, chemical potential, electrophilicity, and HOMO and LUMO in the nanotube with increase of the applied parallel electric field strengths shows that the parallel field has a much stronger interaction with the nanotube with respect to the transverse electric field strengths. Analysis of the parameters indicates that the properties of AlNNTs can be controlled by the proper external electric field.

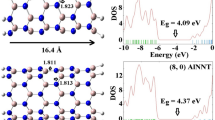
Three-dimensional (3D) views of the (6,0) zigzag AlNNT under electric field effect





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ijima S (1991) Nature 354:56–58
Derycke V, Martel R, Appenzeller J, Avouris Ph (2002) Appl Phys Lett 80:2773–2775
Liu C, Fan YY, Liu M, Cong HT, Cheng HM, Dresselhaus MS (1999) Science 286:1127–1129
Zurek B, Autschbach J (2004) J Am Chem Soc 126:13079–13088
Nojeh A, Lakatos GW, Peng S, Cho K, Pease RFW (2003) Nano Lett 3:1187–1190
Mirzaei M, Shif A, Hadipour NL (2008) Chem Phys Lett 461:246–248
Baei MT (2012) Monatsh Chem 143:545–549
Strite S, Morkoc H (1992) J Vac Sci Technol B 10:1237
Jain C, Willander M, Narayan J, van Overstraeten R (2000) J Appl Phys 87:965
Ruterana P, Albrecht M, Neugebauer J (2003) Nitride semiconductors: handbook on materials and devices. Wiley, New York
Khoo KH, Mazzoni MSC, Louie SG (2004) Phys Rev B 69:201401(R
Guo GY, Ishibashi S, Tamura T, Terakura K (2007) Phys Rev B 75:245403
Attaccalite C, Wirtz L, Marini A, Rubio A (2007) Phys Status Solidi B 244:4288–4292
Machado M, Azevedo S (2011) Eur Phys J B 81:121–125
Chattaraj PK, Sarkar U, Roy DR (2006) Chem Rev 106:2065–2091
Hazarika KK, Baruah NC, Deka RC (2009) Struct Chem 20:1079
Parr RG, Szentpaly L, Liu S (1999) J Am Chem Soc 121:1922–1924
Sabzyan H, Farmanzadeh D (2007) J Comput Chem 28:923
Schmidt M et al (1993) J Comput Chem 14:1347–1363
Politzer P, Lane P, Murray JS, Concha MC (2005) J Mol Model 11(1):1
Peralta-Inga Z, Lane P, Murray JS, Boyd S, Grice ME, O'Connor CJ, Politzer P (2003) Nano Letters 3(1):21–28
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baei, M.T., Peyghan, A.A. & Moghimi, M. Electric field effect on (6,0) zigzag single-walled aluminum nitride nanotube. J Mol Model 18, 4477–4489 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-012-1440-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-012-1440-1