Abstract
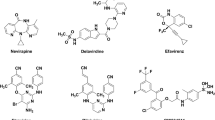
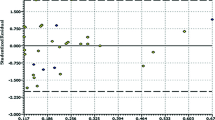
1,3,4,5-tetrasubstituted-pyrazoles (TPs) have been recently identified as a new class of potent non-nucleoside HIV-1 reverse transcriptase (RT) inhibitors. A computational strategy based on molecular docking studies, followed by docking-based comparative molecular fields analysis (CoMFA) and comparative molecular similarity indices analysis (CoMSIA), has been used to elucidate the atomic details of the RT/TP interactions and to identify the most important features impacting the TP antiretroviral activity. The final CoMSIA model resulted to be the more predictive, showing r 2ncv = 0.97, r 2cv = 0.723, SEE = 0.248, F = 240.291, and r2 pred = 0.77. The results allowed us to obtain useful information for the design of new compounds with improved potency toward WT HIV-1 and also against clinically relevant resistant mutants.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jonckheere H, Anne J, De Clercq E (2000) The HIV-1 reverse transcription (RT) process as target for RT inhibitors. Med Res Rev 20:129–154
De Clercq E (2001) New developments in anti-HIV chemotherapy. Farmaco 56:3–12
De Clercq E (2005) Emerging anti-HIV drugs. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs 10:241–273
Clercq E (2005) New approaches toward anti-HIV chemotherapy. Eur J Med Chem 48:1297–1313
Barbaro G, Scozzafava A, Mastrolorenzo A, Supuran CT (2005) Highly active antiretroviral therapy: current state of the art, new agents and their pharmacological interactions useful for improving therapeutic outcome. Curr Pharm Des 11:1805–1843
Balzarini J (2004) Current status of the non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Curr Top Med Chem 4:921–944
De Clercq E (1998) The role of non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) in the therapy of HIV-1 infection. Antiviral Res 38:153–179
Pedersen OS, Pedersen EB (1999) Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, the NNRTI boom. Antiviral Chem Chemother 10:285–314
Pedersen OS, Pedersen EB (2000) The flourishing syntheses of non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Synthesis 4:479–495
Campiani G, Ramunno A, Maga G, Nacci V, Fattorusso C, Catalanotti B, Morelli E, Novellino E (2002) Non-nucleoside HIV-1 reverse transcriptase (RT) inhibitors: past, present, and future perspectives. Curr Pharm Des 8:615–657
De Clercq E (2004) Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs): past, present, and future. Chem Biodiversity 1:44–64
Pauwels R (2004) New non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) in development for the treatment of HIV infections. Curr Opin Pharmacol 4:437–446
Leigh Brown AJ, Frost SD, Mathews WC, Dawson K, Hellmann NS, Daar ES, Richman DD, Little SJ (2003) Transmission fitness of drug-resistant human immunodeficiency virus and the prevalence of resistance in the antiretroviral-treated population. J Infect Dis 187:683–686
Richman DD, Morton SC, Wrin T, Hellmann N, Berry S, Shapiro MF, Bozzette SA (2004) The prevalence of antiretroviral drug resistance in the United States. AIDS 18:1393–1401
De La Rosa M, Kim HW, Gunic E, Jenket C, Boyle U, Koh YH, Korboukh I, Allan M, Zhang W, Chen H, Xu W, Nilar S, Yao N, Hamatake R, Lang SA, Hong Z, Zhang Z, Girardet JL (2006) Tri-substituted triazoles as potent non-nucleoside inhibitors of the HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16:4444–4449
Kirschberg TA, Balakrishnan M, Huang W, Hluhanich R, Kutty N, Liclican AC, McColl DJ, Squires NH, Lansdon EB (2007) Triazole derivatives as non-nucleoside inhibitors of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase–structure-activity relationships and crystallographic analysis. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18:1131–1134
Mowbray CE, Burt C, Corbau R, Perros M, Tran I, Stupple PA, Webster R, Wood A (2009) Pyrazole NNRTIs 1: design and initial optimisation of a novel template. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19:5599–5602
Mowbray CE, Corbau R, Hawes M, Jones LH, Mills JE, Perros M, Selby MD, Stupple PA, Webster R, Wood A (2009) Pyrazole NNRTIs 3: optimisation of physicochemical properties. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19:5603–5606
Mowbray CE, Burt C, Corbau R, Gayton S, Hawes M, Perros M, Tran I, Price DA, Quinton FJ, Selby MD, Stupple PA, Webster R, Wood A (2009) Pyrazole NNRTIs 4: selection of UK-453,061 (lersivirine) as a development candidate. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20:5857–5860
Cichero E, Buffa L, Fossa P (2010) 3,4,5-Trisubstituted-1,2,4-4H-triazoles as WT and Y188L mutant HIV-1 non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors: docking-based CoMFA and CoMSIA analyses. J Mol Model. doi:10.1007/s00894-010-0857-7
MOE: Chemical Computing Group Inc . Montreal. H3A 2R7 Canada. http://www.chemcomp.com
Jain AN (1996) Scoring noncovalent protein-ligand interactions: A continuous differentiable function tuned to compute binding affinities. J Comput Aided Mol Des 10:427–440
Cramer RD III, Patterson DE, Bunce JD (1989) Recent advances in comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA). Prog Clin Biol Res 291:161–165
Klebe G, Abraham U, Mietzner T (1994) Molecular similarity indices in a comparative analysis (CoMSIA) of drug molecules to correlate and predict their biological activity. J Med Chem 37:4130–4146
Sybyl-X 1.0. Tripos Inc 1699 South Hanley Road. St Louis, MO, 63144, USA
Pauwels R (2004) New non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) in development for the treatment of HIV infections. Curr Opin Pharmacol 5:437–446
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the University of Genova.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cichero, E., Fossa, P. Docking-based 3D-QSAR analyses of pyrazole derivatives as HIV-1 non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. J Mol Model 18, 1573–1582 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-011-1190-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-011-1190-5